Asymmetric encryption is the type of encryption algorithm that uses 02(two) keys to encrypt and decrypt data.
In the realm of data security, Asymmetric Encryption is a potent safeguarding technique, employing the prowess of dual keys. Contrary to symmetric encryption, which uses a single key for encryption and decryption, asymmetric encryption leverages a couple of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. I will explore asymmetric encryption, its mechanisms, applications, and its pivotal role in ensuring data confidentiality and thwarting cyber threats.
Understanding Asymmetric Encryption
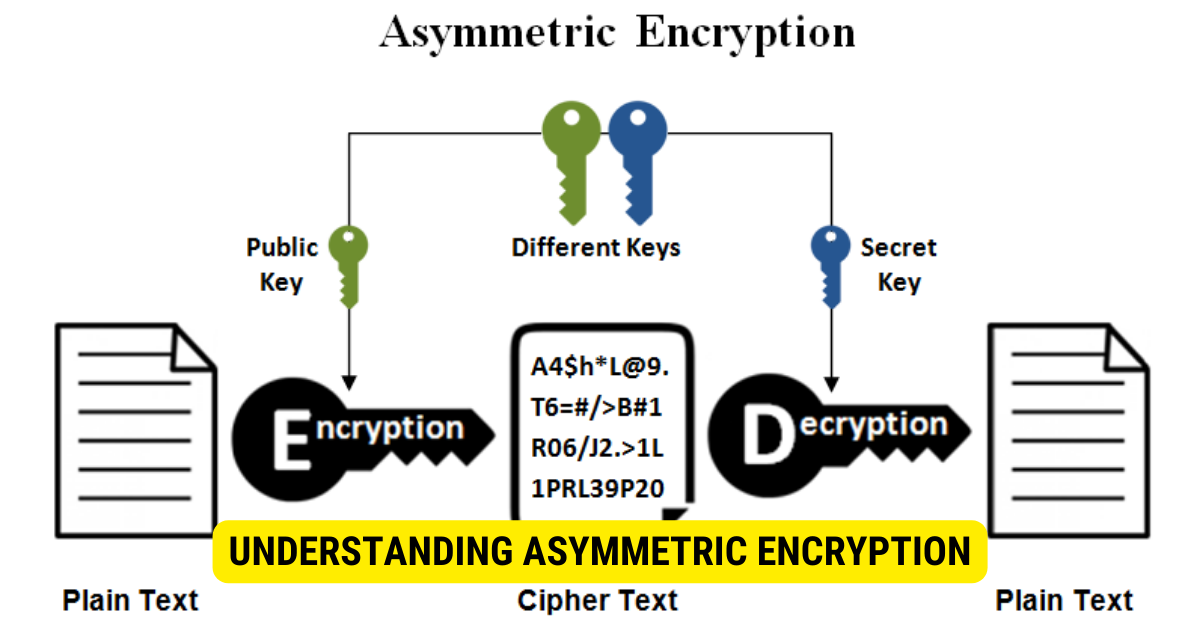
Asymmetric encryption, well known as public-key cryptography, is a cryptographic system that employs two distinct yet mathematically related keys for data protection:
- Public Key:
- The public key is openly shared and used for encryption.
- Anyone can use the public key to cryptograph(encrypt) messages or data intended for the owner of the corresponding private key.
- Private Key(Non-Public Key)
- The private key, also known as a non-public key, is kept secret by the owner and used for decryption.
- Only the owner possesses the private key and can decrypt messages encrypted with their public key.
How Asymmetric Encryption Works?
The process of asymmetric encryption involves the following steps:
- Key Generation: The user generates a couple of keys – a public key and a private key.
- Encryption: When a sender wants to send an encrypted(Cryptographic) message to a recipient, they use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the data.
- Decryption: The recipient, who holds the corresponding private key, decrypts the received message using their private key.
Advantages of Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption offers several key advantages over symmetric encryption:
-
- Enhanced Security: Asymmetric encryption offers higher security by utilizing a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This eliminates the need to share a single secret key, reducing the risk of key compromise.
- Secure Communication: Asymmetric encryption enables secure communication between parties who have never shared secrets before. Users can exchange messages securely without the need for prior communication or shared keys.
- Digital Signatures: Asymmetric encryption creates digital signatures, providing authentication and ensuring the origin and integrity of digital documents or transactions. Digital signatures offer non-repudiation, proving that a specific user has approved or sent the document.
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Asymmetric encryption is crucial in securing web browsing by enabling SSL/TLS encryption protocols. It safeguards online transactions and protects sensitive information like credit card details and login credentials.
- Key Exchange Not Required: Unlike symmetric encryption, which requires a secure key exchange method, asymmetric encryption does not necessitate key exchange for communication. This simplifies the encryption process and enhances data security.
Applications of Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption finds applications in various domains due to its robust security capabilities:
- Secure Data Transmission: Asymmetric encryption is widely used in secure communication channels, such as encrypted emails and messaging services. It ensures that only the intended recipient, with the corresponding private key, can access and decrypt the transmitted data.
- Digital Signatures: Asymmetric encryption is crucial in creating digital signatures for documents and transactions. Digital signatures authenticate and verify digital content’s origin and integrity, offering non-repudiation and ensuring the sender’s authenticity.
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Asymmetric encryption is a fundamental component of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. It secures web browsing and online transactions by encrypting sensitive data, such as credit card information and login credentials, preventing unauthorized access during data transmission.
- Key Management Systems: Asymmetric encryption is employed in key management systems to secure encryption keys. It allows users to securely store, distribute, and revoke keys, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of cryptographic operations.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Asymmetric encryption is utilized in VPNs to establish secure connections between devices and networks. It creates a secure tunnel for data transmission, ensuring privacy and confidentiality over public networks.
- Secure File Encryption: Asymmetric encryption is applied to secure files and folders, protecting unauthorized access. It is commonly used in data encryption software to safeguard sensitive information stored on devices and in the cloud.
- Secure Online Transactions: Asymmetric encryption safeguards online financial transactions, including online banking and e-commerce. Encrypting transactional data prevents unauthorized parties from accessing sensitive financial information.
- Secure Digital Identity: Asymmetric encryption is used in digital identity management to protect personal information and ensure secure access to online services and accounts.
- IoT Security: Asymmetric encryption is crucial in securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices and communications. It ensures that data transmitted between connected devices remains confidential and authenticates the identity of IoT devices.
- Data Integrity in Blockchain: Asymmetric encryption is integral to blockchain technology, providing secure digital signatures and ensuring the immutability and integrity of data stored in distributed ledgers.
Comparison: Asymmetric vs. Symmetric Encryption
To better understand the differences, let’s compare asymmetric encryption with symmetric encryption:
| Aspect | Asymmetric Encryption | Symmetric Encryption |
| Key Usage | Dual keys: Public & Private | Single key for both encryption & decryption |
| Key Exchange | Not required for communication | Requires secure key exchange method |
| Security Strength | Higher security due to dual keys | Lesser security due to single key |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Use Case | Secure communication & digital signatures | Data encryption for storage & faster communication |
Key Takeaways
- Asymmetric encryption uses two keys – a public key for encryption and a non-public key for decryption. The public key is openly shared and used to encrypt data, while the non-public or private key is kept secret and used for decryption.
- Asymmetric encryption offers enhanced security by eliminating the need to share a single secret key.
- It enables secure communication between parties without requiring prior communication or shared keys.
- Applications of asymmetric encryption include secure data transmission, digital signatures, and SSL/TLS encryption for web browsing.
- Compared to symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption provides higher security but is slower.
- Asymmetric encryption plays a pivotal role in securing sensitive information and ensuring the integrity of online interactions.
FAQs
Where is asymmetric encryption applied?
Asymmetric encryption finds applications in secure data transmission, digital signatures, and SSL/TLS encryption for secure web browsing.
What is the role of the public key in Asymmetric encryption?
The public key is used for encryption, allowing anyone to encrypt messages intended for the recipient with the corresponding private key.
How does Asymmetric encryption ensure data confidentiality?
Asymmetric encryption ensures data confidentiality by using the recipient’s private key to decrypt the data encrypted with their public key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, asymmetric encryption is a formidable data security solution that utilizes dual keys for encryption and decryption. Its enhanced security and ability to facilitate secure communication make it an indispensable tool in the digital age. Asymmetric encryption’s applications in secure data transmission, digital signatures, and SSL/TLS encryption underscore its significance in protecting sensitive information and ensuring the integrity of online interactions.
