Encrypted data refers to information that has been transformed using encryption algorithms to make it unreadable and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Encryption involves the process of converting plain, understandable data into an encoded format, often referred to as ciphertext, which can only be deciphered by those who possess the corresponding decryption key.
This technique provides a secure method of protecting sensitive or confidential information, such as personal data, financial transactions, or trade secrets, from unauthorized access or interception. Encrypted data ensures that even if intercepted or accessed by an unauthorized party, the information remains unintelligible, maintaining its confidentiality and integrity.
In this comprehensive guide, I will take you on an exciting journey, shedding light on the definition, inner workings of data encryption, the different types of encryption, best practices, and the undeniable benefits it brings to the table. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the understanding of Encrypted Data, safeguarding your valuable information and protect it from prying eyes.
How Data Encryption Works?
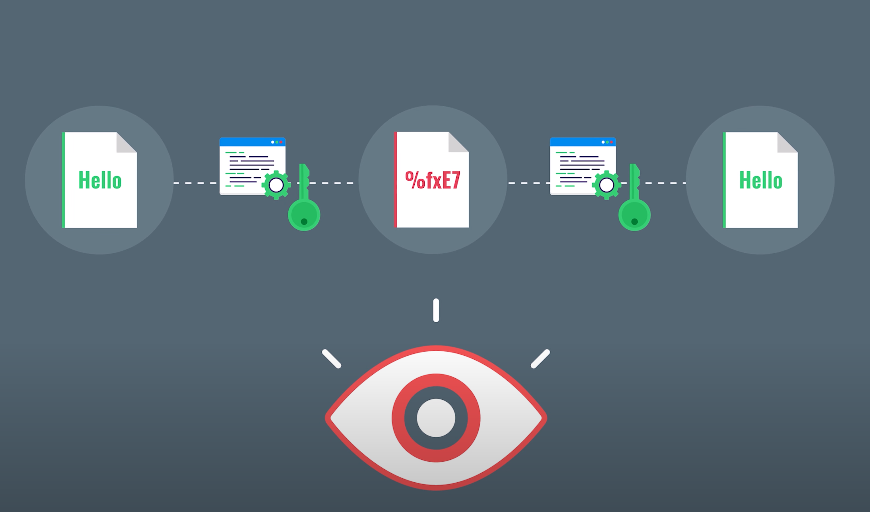
Understanding the Encryption Process
- Encryption algorithms and keys
- Encryption methods
- Encryption process
Types of Data Encryption
Symmetric Encryption
- Symmetric encryption overview
- Popular symmetric encryption algorithms
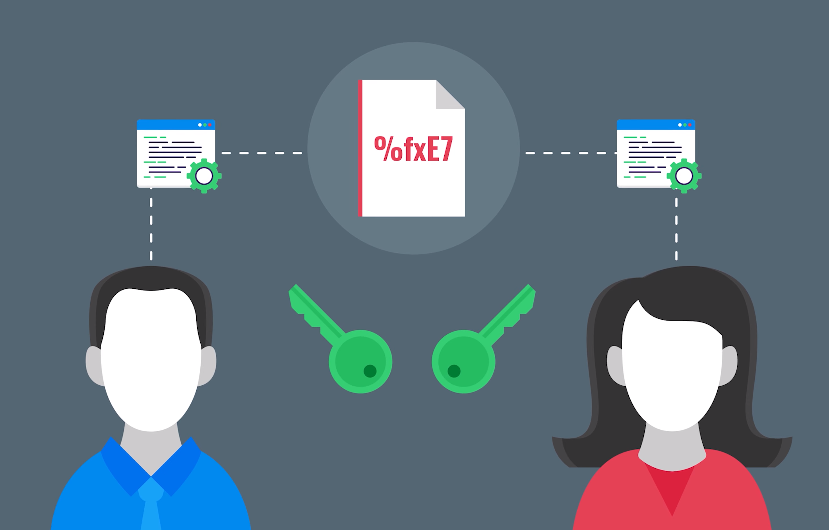
Asymmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric encryption fundamentals
- RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Hashing: A Powerful Data Integrity Tool
- The purpose of hashing
- Common hashing algorithms
Data Encryption Best Practices
Choosing the Right Encryption Algorithm
- Understanding algorithm characteristics
- Keeping up with advancements
Effective Key Management
- Generating strong encryption keys
- Key storage and protection
- Key rotation and revocation
Strengthening Encryption Implementations
- Secure coding practices
- Regular software updates
- Monitoring and auditing encryption processes
Can Encrypted Data be Hacked?
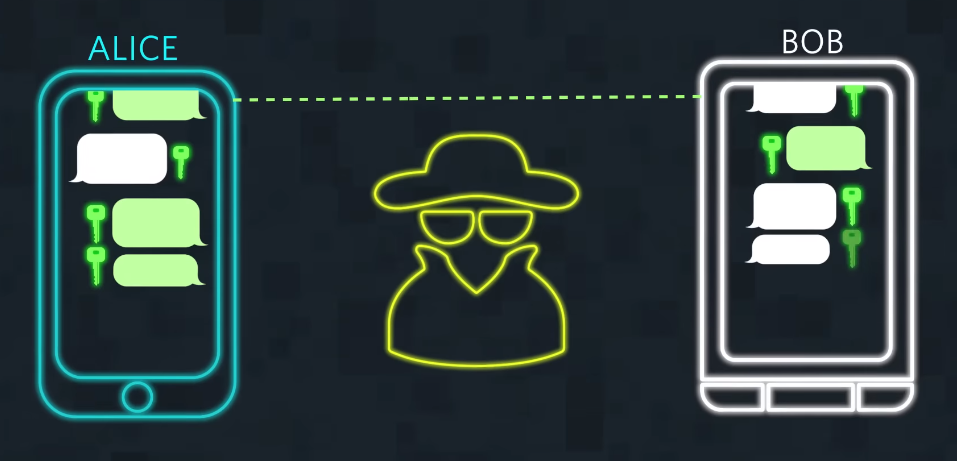
The Impossibility of Cracking Strong Encryption
- Computational complexity
- Encryption algorithm vulnerabilities
Protecting Against Brute Force Attacks
- Key length and complexity
- Implementation of lockout mechanisms
Ensuring Robust Encryption for Enhanced Security
- Constantly evolving encryption standards
- Multi-layered security approach
Benefits of Encrypted Data
- Ensuring Confidentiality of Sensitive Information
- Protection against unauthorized access
- Privacy compliance
- Safeguarding Data Integrity and Authenticity
- Detecting tampering and unauthorized modifications
- Digital signatures
- Compliance and Trust: Meeting Regulatory Standards
- Data protection regulations
- Building trust with customers and partners
Data Encryption Solutions
Encrypting Data at Rest
- Full-disk encryption
- File-level encryption
Securing Data in Transit
- Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS)
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Implementing End-to-End Encryption
- Secure messaging applications
- Secure video conferencing
How to Implement Data Encryption?
Understanding Your Encryption Requirements
- Assessing data sensitivity
- Compliance considerations
Choosing the Right Encryption Tools and Technologies
- Evaluating encryption solutions
- Compatibility and ease of integration
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
- Define encryption policies and procedures
- Encrypting existing data
- Training and awareness
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully navigated through the captivating world of encrypted data. Armed with the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide, you now possess the keys to protect your sensitive information, preserve its integrity, and comply with regulatory standards. Remember, data security is an ongoing endeavor, and by implementing best practices and staying vigilant, you can confidently safeguard your digital assets from the ever-evolving threats in today’s digital landscape. So go forth, embrace encryption, and let your data rest in the secure embrace of impenetrable protection.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What is data encryption? Data encryption is the process of converting plain text into encoded, unreadable data using complex algorithms and keys, ensuring that it remains secure and confidential.
Q: How does data encryption work? Data encryption involves transforming information into ciphertext through encryption algorithms and encryption keys. This process makes the data unreadable to unauthorized individuals, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Q: What are the types of data encryption? There are primarily two types of data encryption: symmetric encryption, which uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption, which employs a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Q: What is hashing? Hashing is a technique used to ensure data integrity and authenticity. It involves applying a hashing algorithm to data to generate a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash value or hash code.
Q: Can encrypted data be hacked? Strong encryption makes hacking encrypted data virtually impossible. The computational complexity involved and vulnerabilities in encryption algorithms make it extremely challenging for attackers to crack encrypted data.
Q: What are the benefits of encrypted data? Encrypted data provides several benefits, including confidentiality of sensitive information, protection against unauthorized access, compliance with privacy regulations, safeguarding data integrity and authenticity, and building trust with customers and partners.
Q: How can data encryption be implemented? To implement data encryption, it is essential to understand your encryption requirements, choose the right encryption tools and technologies, and follow a step-by-step implementation guide. This involves defining encryption policies and procedures, encrypting existing data, and providing training and awareness to users.
Key Points
- Encryption secures data through complex algorithms and keys.
- Symmetric and asymmetric encryption offer different approaches to data protection.
- Hashing ensures data integrity and authenticity.
- Best practices include algorithm selection, key management, and secure implementations.
- Strong encryption makes hacking encrypted data virtually impossible.
- Encrypted data benefits include confidentiality, integrity, compliance, and trust.
- Encryption solutions cover data at rest, in transit, and end-to-end encryption.
- Implementing encryption requires understanding requirements, selecting tools, and step-by-step implementation.
