Dive into the essence of resetting end-to-end encrypted data for enhanced security. Learn about its importance, processes, and future in the digital realm.
In today’s digital age, where data breaches and privacy concerns have become all too common, it is crucial to understand the concept of end-to-end encryption and the implications of resetting encrypted data. I will probe into the intricacies of end-to-end encryption, the process of resetting encrypted data, its implications, best practices to follow, and the future of this technology.
Understanding End-to-End Encryption
Before researching the idea of resetting encrypted data, it is important to grasp the fundamentals of end-to-end encryption. At its core, end-to-end encryption is a security measure that safeguards only the sender and intended recipient can access the contents of a message or file. End-to-end encryption is achieved by encrypting the sender’s device and decrypting the data on the recipient’s device, eliminating any intermediaries or potential eavesdroppers.
The Basics of Encryption

Encryption is the process of altering data into a format that is unreadable to anyone except those with the appropriate decryption key. It utilizes sophisticated algorithms to scramble the data, making it nearly impossible for unlicensed individuals to decipher. Without encryption, sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal messages would be susceptible to interception and misuse.
Let’s dive deeper into the workings of encryption. When data is encrypted, it undergoes a transformation using a cryptographic algorithm. This algorithm takes the original data, known as plaintext, and applies a series of measured operations to convert it into ciphertext. The resulting ciphertext looks like a random string of characters, making it unintelligible to anyone without the decryption key.
One commonly used encryption algorithm is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES employs a symmetric key encryption method, using the same key for both encryption and decryption. This means the sender and recipient must share the same secret key to communicate securely. Other encryption algorithms, such as RSA, use asymmetric key encryption, where unlike keys are used for encryption and decryption.
Encryption is not limited to text-based data. It can also be applied to various files, including images, videos, and documents. By encrypting these files, they become unreadable to unauthorized individuals, providing an additional layer of protection.
The Importance of End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding our privacy and data security. Ensuring that the intended recipient can access the decrypted information protects our digital communications and files. This is especially crucial in an era where cyberattacks and data breaches have become prevalent, emphasizing the need for robust security measures.
Imagine a scenario where you are sending a confidential document to a colleague. Without end-to-end encryption, unauthorized individuals could potentially intercept and access the document during transmission. However, with end-to-end encryption, the document is encrypted on your device. It can only be decrypted by your colleague’s device, ensuring no one else can access its contents.
End-to-end encryption also protects against potential vulnerabilities in communication channels. Even if a hacker accomplishes to gain access to the network or the servers through which the data is being transmitted, they would still be unable to decipher the encrypted information. End-to-end encryption provides peace of mind that our complex data remains secure despite sophisticated cyber threats.
Furthermore, end-to-end encryption helps preserve the confidentiality of our conversations and messages. Whether it’s personal conversations, business negotiations, or sensitive information shared among colleagues, end-to-end encryption ensures that only the intended recipients can read the communications. This fosters trust and encourages open communication in various aspects of our lives.
In conclusion, end-to-end encryption is a powerful security measure that protects our privacy and data integrity. Encrypting data on the sender’s device and decrypting it on the recipient’s device ensures that only the intended parties can access the information. This is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where privacy breaches and unauthorized access are prevalent. Embracing end-to-end encryption is a step towards a more secure and private digital world.
The Process of Resetting Encrypted Data
Now that we have established the significance of end-to-end encryption let us delve into the process of resetting encrypted data, an action that should not be taken lightly.
Resetting encrypted data is typically done to protect sensitive information during a security breach, device loss, or when sharing data with new recipients. By resetting encrypted data, users can revoke access to the existing encryption keys and generate new ones, rendering the previous data inaccessible.
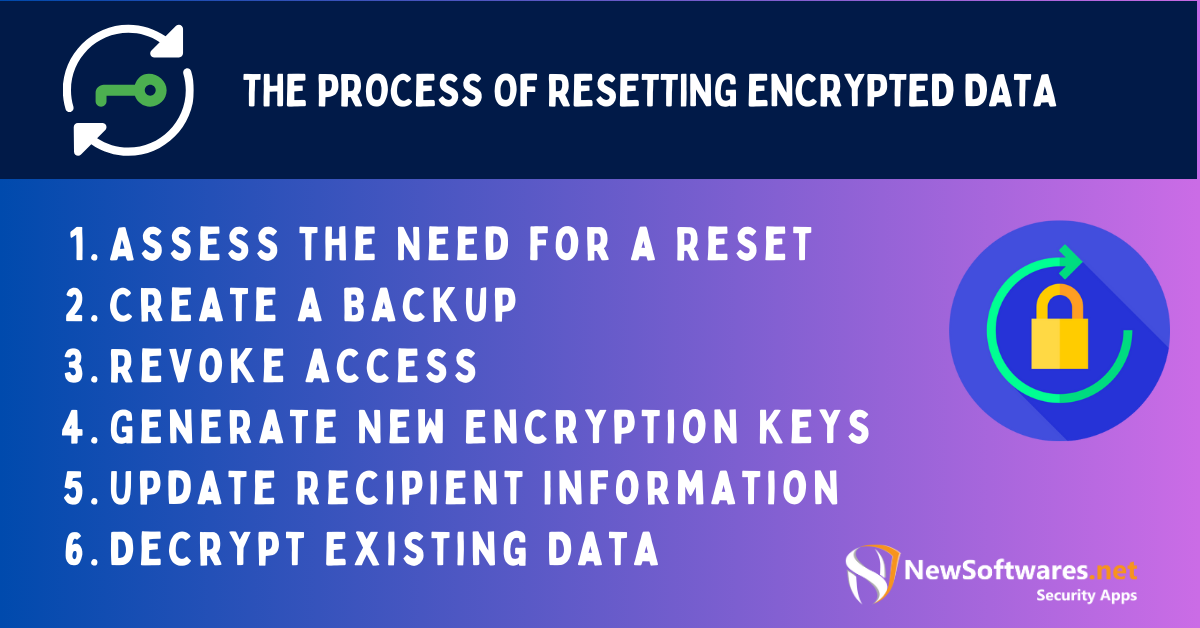
When resetting encrypted data, there are several important steps to follow. These steps ensure that the process is carried out effectively and securely. Let’s take a closer look at each step:
-
Assess the Need for a Reset
The first step in resetting encrypted data is to assess the need for a reset. This involves evaluating the situation and determining whether resetting the encrypted data is necessary. Factors such as a security breach, device loss, or the need to share data with new recipients may warrant a reset.
-
Create a Backup
Before resetting the encrypted data, creating a secure backup of the existing encrypted data is crucial. This backup ensures that no data is permanently lost during the reset process. A backup also provides an additional layer of protection in case any issues arise during the reset.
-
Revoke access
Once a backup is created, the next step is restricting access to the current encryption keys. This prevents unlawful access to the encrypted data while the reset is being performed. By revoking access, any attempts to decrypt the data using the old encryption keys will be futile.
-
Generate New Encryption Keys
With access revoked, it is time to generate new encryption keys. This step is crucial for ensuring enhanced security. The new encryption keys will replace the old ones, making the previously encrypted data inaccessible without the new keys. Generating strong and unique encryption keys is essential to protect the data from threats.
-
Update Recipient Information
It is important to inform relevant recipients about the change in encryption keys if necessary. This step ensures that communication can continue seamlessly. By updating recipient information, you ensure that they know the new encryption keys and can decrypt any future data sent to them.
-
Decrypt Existing Data
Once the new encryption keys are generated, and recipient information is updated, it is time to decrypt the existing data. The previously encrypted data can be decrypted and accessed using the new encryption keys. It is important to ensure that the decryption process is carried out securely to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
Following these steps, users can effectively reset encrypted data and guard sensitive information from unauthorized access. It is essential to approach the process with caution and adhere to best practices to ensure data security.
Implications of Resetting Encrypted Data
While resetting encrypted data can provide enhanced security, it is essential to consider its implications on data security and overall system performance.
Impact on Data Security
Resetting encrypted data can mitigate the risks associated with compromised encryption keys. By generating new keys, the chances of unauthorized access to sensitive information are significantly reduced. However, it is vital to implement robust security measures to protect the newly reset data and encryption keys from potential threats.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Resetting encrypted data may pose certain challenges and risks. When resetting keys, data loss or unintentional denial of access to authorized users is always possible. Additionally, ensuring a seamless transition to the new encryption keys can be complex, especially when dealing with large volumes of data or multiple recipients.
Best Practices for Resetting Encrypted Data
It is important to follow industry best practices to minimize potential risks and ensure a smooth reset process,
Precautions to Take
- Thoroughly assess the need for resetting encrypted data.
- Implement a robust backup strategy to avoid data loss.
- Ensure all necessary stakeholders are informed about the reset process.
- Implement multi-factor authentication and strong access controls to safeguard the new encryption keys.
Ensuring Data Integrity Post-Reset
After resetting encrypted data, it is crucial to verify the integrity of the newly reset data. Regular audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration difficulties can help identify and address potential weaknesses.
The Future of End-to-End Encryption
As technology progresses, we can expect advancements in end-to-end encryption and its role in ensuring data privacy.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence, will undoubtedly influence the future of encryption. Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms and AI-powered threat detection systems are expected to play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of end-to-end encrypted data.
The Role of Encryption in Data Privacy
As individuals and organizations become more aware of the importance of data privacy, encryption will continue to play a crucial role. Stricter regulations and standards will likely be introduced to protect sensitive information, making end-to-end encryption an integral part of everyday digital communication.
Key Takeaways:
- End-to-end encryption is a vital security measure that encrypts data on the sender’s side and decrypts it only on the recipient’s side.
- To avoid potential risks, resetting encrypted data while enhancing security should be approached with caution.
- Creating backups before initiating the reset process is crucial to prevent any data loss.
- Informing all relevant stakeholders about the reset ensures smooth communication and access using the new encryption keys.
- With technological advancements, the future holds potential for even more robust encryption methods, ensuring greater data privacy.
FAQs:
What is end-to-end encryption?
End-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and intended recipient can access the contents of a message or file, eliminating potential eavesdroppers.
Why might one need to reset encrypted data?
Resetting might be necessary to maintain data privacy in case of a security breach, device loss, or sharing data with new recipients.
What are the steps involved in resetting encrypted data?
Steps include assessing the need for a reset, creating a backup, revoking access to existing keys, generating new encryption keys, updating recipient information, and decrypting existing data using the new keys.
What risks are associated with resetting encrypted data?
Potential risks include data loss, denial of access to authorized users, and challenges in ensuring a seamless transition to the new encryption keys.
How will future technological advancements impact end-to-end encryption?
Technologies like quantum computing and AI may influence the development of advanced encryption techniques, further enhancing data privacy.
Conclusion:
Resetting end-to-end encrypted data is a complex process with significant implications for data security. By understanding the basics of encryption, the importance of end-to-end encryption, and following best practices, users can ensure their sensitive information’s confidentiality, integrity, and privacy. As technological advancements continue, the future of end-to-end encryption holds promise for even stronger data protection.
