Data storage options have diversified to meet various needs. Traditional hard drives offer affordability but are vulnerable to physical damage. Solid State Drives (SSDs) provide speed and durability but come at a higher cost. Network Attached Storage (NAS) systems are ideal for data sharing and redundancy, while cloud storage offers accessibility and scalability. Emerging technologies such as DNA data storage, quantum storage, holographic storage, and 5D optical storage promise to revolutionize data storage possibilities.
Top Options For Data Storage:
Traditional Hard Drives:
Pros and Cons
Traditional hard drives have been the go-to option for data storage for decades. These drives store data on spinning disks and come in both internal and external forms.
Pros:
- Cost-effective: Traditional hard drives are generally more affordable per gigabyte of storage compared to other options.
- High capacity: They offer ample storage space for large files, making them suitable for storing media files and backups.
Cons:
- Vulnerable to physical damage: Because of their mechanical parts, traditional hard drives are susceptible to damage from drops or shocks.
- Slower data access: Retrieving data from a traditional hard drive can be slower than newer technologies like SSDs.
Solid State Drives (SSDs):
Pros and Cons
Solid State Drives, or SSDs, represent a significant advancement in data storage technology. They use flash memory to store data and have become increasingly popular for personal and professional use.
Pros:
- Speed: SSDs are significantly faster than traditional hard drives, resulting in quicker data access and faster system performance.
- Durability: SSDs have no moving parts, making them more resistant to physical damage.
- Energy efficiency: SSDs consume less power, which can lead to longer battery life in laptops and lower energy bills for businesses.
Cons:
- Cost: SSDs are typically more expensive per gigabyte than traditional hard drives.
- Limited lifespan: While SSDs have a longer lifespan than they used to, they can wear out over time due to the finite number of write cycles.
Network Attached Storage (NAS):
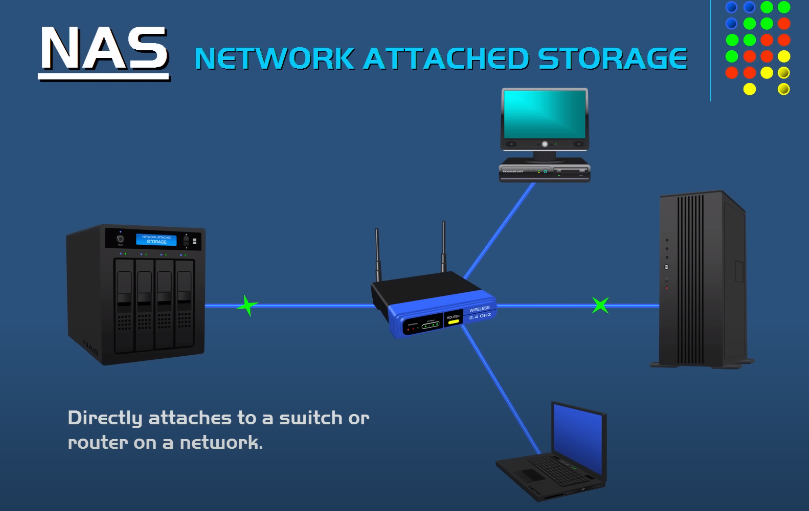
Pros and Cons
Network Attached Storage, or NAS, is an excellent option for those who require centralized storage that multiple devices can access on a network.
Pros:
- Data sharing: NAS devices allow multiple users to access and share data, making them ideal for businesses and families.
- Redundancy: Many NAS systems offer built-in redundancy through RAID configurations, protecting against data loss.
- Remote access: NAS devices often come with remote access capabilities, allowing you to access your data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cons:
- Initial cost: Setting up a NAS system can be more expensive than buying a single external hard drive.
- Complex setup: Configuring a NAS system may require technical expertise.
- Limited portability: NAS devices are stationary and not designed for on-the-go use.
Cloud Storage:
Pros and Cons
Cloud storage has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its convenience and accessibility. It involves storing your data on remote servers maintained by a third party.
Pros:
- Accessibility: Cloud storage allows you to access your data from anywhere with an internet connection, making it perfect for remote work and collaboration.
- Automatic backups: Many cloud services offer automated backup solutions, reducing the risk of data loss.
- Scalability: Cloud storage is highly scalable, allowing you to increase or decrease your storage space as needed.
Cons:
- Security concerns: Some individuals and businesses worry about the security of their data in the cloud, although reputable providers use robust security measures.
- Monthly costs: While some cloud services offer free plans, larger storage needs may require a monthly subscription.
- Internet dependency: Access to cloud-stored data relies on a stable internet connection.
The Future of Data Storage:
Quantum Data Storage:
One of the most promising advancements in data storage is quantum data storage. Quantum mechanics, with its intriguing principles of superposition and entanglement, offers the potential to revolutionize the way we store and process information.
Pros:
- Unprecedented Speed: Quantum data storage promises data access at speeds that are orders of magnitude faster than current technologies, making real-time data processing a reality.
- Security: Quantum encryption methods could provide unbreakable security for sensitive data, thwarting even the most advanced cyberattacks.
- Dramatic Capacity Increase: Quantum bits, or qubits, can store vast amounts of data in a fraction of the space required by traditional storage devices.
Challenges:
- Technical Complexity: Quantum data storage is still in its infancy and presents significant technical challenges, including the need for extremely low temperatures to maintain qubit stability.
- Cost: The development and implementation of quantum data storage solutions can be prohibitively expensive.
DNA Data Storage:
DNA data storage represents a fascinating merger of biology and technology. DNA molecules, with their inherent capacity to store genetic information, are being explored as a means of storing digital data.
Pros:
- Incredible Density: DNA has an astonishing data storage density, with the potential to store exabytes (millions of terabytes) of data in a single gram of material.
- Longevity: DNA can remain stable for thousands of years, offering a promising solution for long-term data preservation.
- Environmental Friendliness: DNA data storage doesn’t rely on energy-consuming hardware and could be a greener alternative to traditional storage solutions.
Challenges:
- Read and Write Speed: Current DNA data storage methods are slow in terms of data retrieval and writing, making them less practical for certain applications.
- Complex Encoding and Decoding: Encoding and decoding data into DNA sequences require specialized equipment and expertise.
Holographic Data Storage:
Holographic data storage is a concept that has been explored for years but is now gaining traction as a potential future solution. It involves recording data in three dimensions using lasers.
Pros:
- Vast Storage Capacities: Holographic storage has the potential to store immense amounts of data on a single medium.
- High Data Transfer Rates: Retrieving data from a holographic storage system can be exceptionally fast, thanks to parallel data access.
- Data Security: Holographic storage can provide robust security features to protect sensitive information.
Challenges:
- Cost: Implementing holographic storage systems can be expensive and may require specialized hardware.
- Read and Write Complexity: The technology for reading and writing data holographically is still evolving and may not be readily accessible to the average consumer.
Conclusion:
The world of data storage is a dynamic and diverse landscape, offering a range of options to suit individual and business needs. From the tried-and-true traditional hard drives to the lightning-fast SSDs, the collaborative capabilities of NAS, and the accessibility of cloud storage, there’s a solution for everyone. As technology continues to advance, we can also look forward to a future where data storage becomes even more efficient, secure, and innovative through emerging technologies like DNA data storage, quantum storage, holographic storage, and 5D optical storage.
FAQs:
What is the primary difference between traditional hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs)?
The primary difference lies in the technology they use. Traditional hard drives store data on spinning disks, while SSDs use flash memory. SSDs are faster, more durable, and energy-efficient compared to traditional hard drives.
How do I choose the right data storage solution for my needs?
Your choice should depend on your specific requirements, budget, and future growth expectations. Consider factors like affordability, speed, durability, shared access, and convenience when selecting a data storage option.
What should I consider when implementing a NAS system in my home or office?
When setting up a NAS system, consider factors like the initial cost, the technical expertise required for setup, and whether it meets your data sharing and redundancy needs. Ensure you choose the right NAS device for your specific requirements.
How can I stay updated on the latest developments in data storage technology?
To stay informed about the latest developments, follow technology news sources, blogs, and industry publications. Additionally, consider attending conferences or webinars related to data storage and information technology.
