Encryption is a powerful tool for data security with numerous merits. It safeguards stored data, allows centralized key management, secures portable storage and email attachments, and enhances smartphone and email security. However, public key encryption comes with its own set of demerits, including potential vulnerabilities in file names, speed issues, certification concerns, and the risk of direct compromise. It’s important to recognize that encryption isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution and must be chosen and implemented wisely.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is a process that transforms your files and folders into an unreadable form. It scrambles your data using complex mathematical procedures, rendering it incomprehensible to anyone without the decryption key. This means that even if a nefarious hacker gains access to your files, all they’ll find is a jumble of bits and bytes – utterly useless.
The crux of encryption lies in a secret known only to you – the key. This key acts as a digital lock, allowing you to enter and exit the realm of encryption, where your precious password-protected files and folders reside.
Different Types of Encryption:
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption, also known as private-key encryption, is one of the oldest and simplest encryption techniques. The same key is used for encryption and decryption processes in symmetric encryption. This means the sender and the recipient must share the same secret key.
How Symmetric Encryption Works?
- Key Generation: A secret key is generated by the sender or a designated authority.
- Encryption: The data is encrypted using the secret key, transforming it into ciphertext.
- Transmission: The ciphertext is sent to the recipient through a secure channel.
- Decryption: The recipient uses the same secret key to decrypt the ciphertext, reverting it to its original plaintext form.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys: public and private. These keys are mathematically related but have distinct functions.
How Asymmetric Encryption Works?
- Key Pair Generation: The recipient generates a key pair consisting of a public key (shared with anyone) and a private key (kept secret).
- Encryption: When the sender wants to send a secure message to the recipient, they use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the data, creating ciphertext.
- Transmission: The ciphertext is sent to the recipient.
- Decryption: The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the ciphertext and retrieve the original plaintext.
Hybrid Encryption
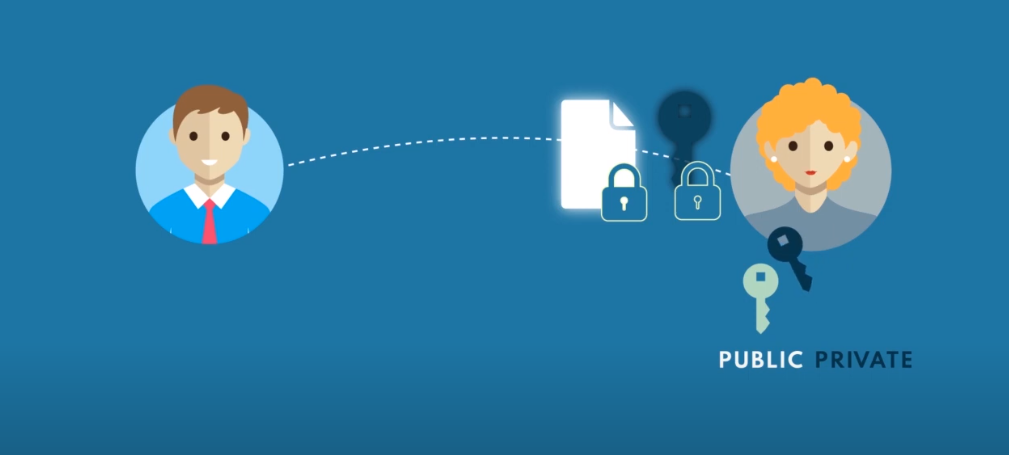
Hybrid encryption combines the strengths of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption to address their respective weaknesses. It is a commonly used method in secure communication systems.
How Hybrid Encryption Works?
- Key Pair Generation: The recipient generates a key pair with a public key and a private key.
- Symmetric Key Creation: A random symmetric key is generated for each session or message.
- Symmetric Encryption: The sender encrypts the data using the randomly generated symmetric key (fast and efficient).
- Public Key Encryption: The sender encrypts the symmetric key with the recipient’s public key and attaches it to the message.
- Transmission: The encrypted data and symmetric key are sent to the recipient.
- Decryption: The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the symmetric key, which is then used to decrypt the data.
Merits of Encryption:

1. Data Protection on Your Mac or PC
Encryption empowers you to safeguard your files and folders stored on your computers effectively. Using robust encryption methods like AES 256-bit encryption, unauthorized access is virtually impossible. For Windows users with business editions (e.g., Windows 7 Professional or 8.1 Enterprise), BitLocker provides full disk encryption, while Mac users can activate FileVault encryption. Remember to create a strong, unguessable password for an added layer of security.
2. Centralized Key Management
For enterprise networks, centralizing encryption keys is a valuable advantage. It streamlines data recovery processes in case of a forgotten or lost password. For PCs not centrally managed, keeping a recovery key in a secure location is crucial to prevent data loss incidents.
3. Secure Portable Storage
USB drives are easy to lose and even easier for someone to access if found. Encrypting these portable storage devices adds a critical layer of security. Windows 7 or 8.1 Pro users can activate BitLocker by right-clicking on the drive icon in Windows Explorer. Mac users can do the same through Finder.
4. Email Attachments
Sending confidential files as email attachments is risky. Encrypting the files and using a secure cloud service for transfer, followed by link removal post-transfer, enhances data security.
5. Smartphone Data Encryption
In the age of smartphones, protecting personal and sensitive information is paramount. Encrypting your smartphone with a PIN, pattern, or password is essential. To enable encryption on Android, navigate to ‘Security’ in ‘Settings. For iOS, hardware encryption is active by default, with the option to activate the Erase Data feature.
6. Email Encryption
Encrypting email messages on your server ensures secure communication. However, it may require specialized software and digital certificates, making it more suitable for confidential projects.
Demerits of Public Key Encryption

1. Encrypting File Names
Public key encryption involves two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. While the public key can be freely shared, the private key must remain secure. However, if the private key falls into the wrong hands, it can be used to decrypt sensitive data.
2. Speed
Public key encryption relies on complex mathematics, making it computationally intensive. This can slow down systems when handling large quantities of encrypted data.
3. Certification Issues
Most public key systems rely on third-party certification authorities to verify public keys. False certificates can be issued if these authorities are compromised, leading to data breaches.
4. Direct Compromise
Cracking encrypted data using public key systems can involve finding mathematical vulnerabilities or making random password guesses. As technology advances, so do the capabilities of hackers, making such attacks increasingly common.
5. False Sense of Security
Encryption only protects data in transit or storage, not when it’s actively used. This means that even with encryption, certain security threats can persist.
Recommendations:
- Folder Lock: Folder Lock is a robust encryption software known for its AES-256-bit encryption capabilities. What sets it apart are additional features such as file shredding and secure backups. The shredder ensures that unnecessary files are securely eliminated, preventing potential data leaks. Plus, creating secure backups on a cloud service offers peace of mind regarding data recovery.
- AxCrypt: AxCrypt is a user-friendly encryption tool designed for individual users. It simplifies the process of encrypting files and folders, making it accessible even for those with limited technical expertise. It also offers strong encryption methods to keep your data safe.
- VeraCrypt: VeraCrypt is an open-source encryption software that provides high-level security for your data. It’s a successor to TrueCrypt and is well-regarded for its ability to create encrypted volumes or containers. VeraCrypt is a versatile option for users who require a secure and free encryption solution.
- BitLocker (Windows): For Windows users, BitLocker is an integrated encryption solution available in the professional and enterprise editions. It offers full disk encryption, ensuring that all data on the drive is protected. BitLocker is a solid choice if you already use a Windows operating system.
- FileVault (Mac): Mac users can rely on FileVault, an integrated encryption tool provided by Apple. It offers full-disk encryption, securing your entire Mac’s storage. FileVault is user-friendly and can be activated through your Mac’s settings.
Conclusion:
Encryption offers invaluable protection for our digital lives, safeguarding sensitive information from prying eyes and cyber threats. It empowers us to secure our devices, emails, and portable storage with an assurance of confidentiality. However, the world of encryption is not without its complexities and limitations. Public key encryption, in particular, presents challenges such as potential speed issues, certification vulnerabilities, and the ever-looming threat of quantum computing. Moreover, encryption is just part of a comprehensive security strategy and cannot shield us from all possible threats. Understanding both the merits and demerits of encryption is essential for making informed decisions about how best to protect our digital assets in an increasingly interconnected world.
FAQs:
Is encryption the same as password protection?
No, encryption and password protection serve different purposes. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable form, requiring a decryption key for access. On the other hand, password protection adds a password barrier to access files but doesn’t alter their content.
Can advanced hackers break encryption?
While encryption provides robust security, determined and resourceful hackers can break it through various means, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in the encryption algorithms or using powerful computing resources.
How do I choose a strong encryption key?
A strong encryption key should be long, complex, and unique. Combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters is advisable. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words.
Can I encrypt my smartphone after setting it up?
Yes, you can encrypt your smartphone after the initial setup. Look for encryption options in your device’s settings, typically under the “Security” or “Privacy” section.
Are there any free encryption tools available?
Yes, free encryption tools are available, such as VeraCrypt and BitLocker (for Windows Pro editions). These tools offer robust encryption capabilities without the need for additional costs.
