Introduction
The importance of data security cannot be overstated. With the increasing amount of sensitive information being stored on digital devices and in the cloud, the risk of cyber attacks is greater than ever before. Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, damage to a company’s reputation, and legal consequences. Therefore, it is critical for organizations to implement a comprehensive data security plan that addresses all phases of the data security lifecycle.
The six phases of the data security lifecycle include Data Discovery and Classification, Data Protection and Monitoring, Data Retention and Storage, Data Backup and Recovery, Incident Response and Management, and compliance. Each phase plays an important role in ensuring that sensitive information remains secure. For example, during the planning stage, organizations need to identify potential threats to their systems and develop strategies for mitigating those risks. In contrast, during the response phase, companies must have protocols in place for responding quickly to an attack or breach.
Ultimately, effective data security requires ongoing vigilance – it is not something that can be achieved with a single solution or implementation. Organizations should regularly assess their systems for vulnerabilities; train employees on best practices for protecting sensitive information; monitor networks for suspicious activity; and stay up-to-date with new technologies that can help prevent cyber attacks. By taking these steps throughout each phase of the data security lifecycle, companies can greatly reduce their risk of a devastating breach.
Phase 1: Data Discovery and Classification
Importance Of Data Discovery And Classification
Data discovery and classification is an essential part of the data security lifecycle. It involves identifying all the sources of data that exist within an organization and categorizing them based on their sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and business value. This process helps organizations understand what types of data they have, where it resides, how it is used, and who has access to it.
By performing this vital step in the data security lifecycle, organizations can take a proactive approach to protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access or misuse. By classifying data by its level of sensitivity or regulatory requirements, organizations can implement appropriate controls such as encryption or access restrictions to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to that information.
Moreover, understanding the different types of data an organization possesses allows for better decision-making when it comes to assigning security protocols. Without proper discovery and classification methods in place, companies risk failing audits on compliance with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA because they don’t know what data they are holding.
Tools And Techniques For Identifying Sensitive Data
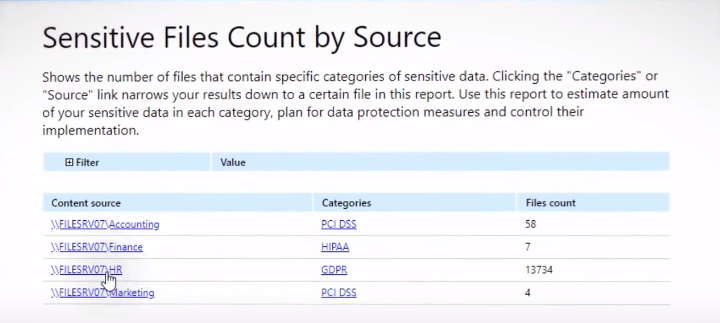
There are many tools and techniques available to identify sensitive data, such as automated discovery scans, manual audits, and interviews with stakeholders. Automated discovery scans use software to scan an organization’s network and identify sensitive data based on predefined criteria. Manual audits involve reviewing an organization’s databases, file systems, and applications to find sensitive information manually.
Interviews with stakeholders can also be helpful in identifying sensitive data. Stakeholders may include business owners or end-users who have knowledge of where critical information resides within the organization. It is important to consider all types of data when identifying sensitive information, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property (IP), trade secrets, and confidential documents, among others.
How To Classify Data Based On Its Level Of Sensitivity?
In general, data can be classified into four categories: public, internal use, confidential, and highly confidential.
The first category includes information that is available to the public without any restrictions or limitations. The second category refers to information that is intended for internal use only but does not contain sensitive or proprietary information. The third category includes sensitive information such as financial records, customer data, and trade secrets that could cause harm if accessed by unauthorized parties. Finally, the fourth category includes highly confidential information such as government secrets or intellectual property that requires the highest level of protection.
Phase 2: Data Protection and Monitoring
Strategies For Protecting Data From Unauthorized Access Or Theft
After identifying and classifying data, the next step is to protect it. This involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access or theft. One effective strategy is to use encryption technology to scramble data so that only authorized users with the decryption key can access it. Another approach is to implement access controls such as passwords, two-factor authentication, and role-based permissions.
In addition, physical security measures should also be considered. This includes securing servers, hard drives, and other storage devices in locked rooms or cabinets with limited access. Data backups should also be securely stored offsite in case of a disaster or breach.
Best Practices For Data Encryption, Access Control, And Monitoring
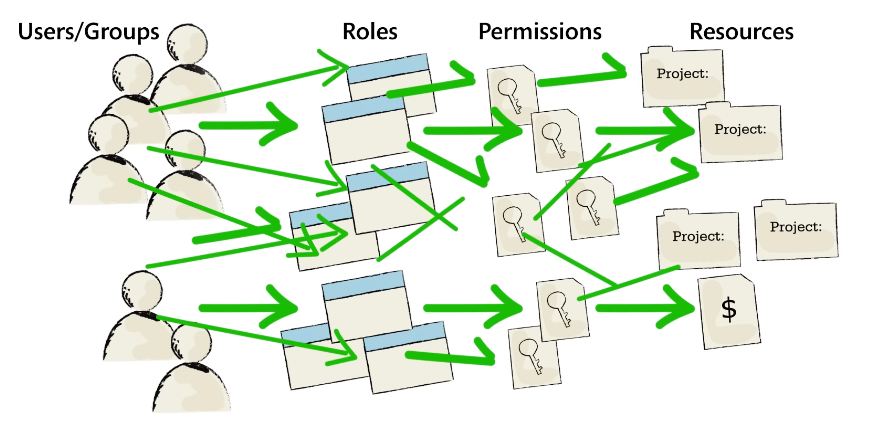
Encryption involves converting sensitive information into an unreadable format to prevent unauthorized access. It is important to ensure that encryption keys are properly managed and kept secure. Access control involves setting up restrictions on who can view or modify sensitive data based on their permissions level. This can be achieved through user authentication methods such as username and password or multi-factor authentication.
Monitoring is crucial for detecting any unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activities within the system. Regular monitoring should be conducted to identify any anomalies in data transfer activities or unusual network traffic patterns which may signal a breach attempt. Monitoring also helps in identifying potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Best practices for data encryption, access control, and monitoring include proper key management for encryption, setting up restricted access controls based on user permissions levels, implementing strong authentication methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular monitoring of all systems including networks and endpoints to detect suspicious activities and identifying potential vulnerabilities that could lead to a security breach.
The Role Of Security Software And Hardware In Data Protection
Security software such as firewalls, antivirus programs, and intrusion detection systems are designed to protect against common cyber threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. These programs work by monitoring network traffic and identifying any suspicious activity that could potentially harm the system.
On the other hand, security hardware like encryption devices and biometric authentication tools provide an additional layer of protection for sensitive information. Encryption devices scramble data into a code that only authorized parties can access using a decryption key. Biometric authentication tools use unique physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition to verify user identities before granting them access to confidential information.
Phase 3: Data Retention and Storage
Guidelines For Data Retention And Storage
Companies need to implement robust guidelines that cover the entire data lifecycle. These guidelines must detail procedures for capturing, classifying, storing, retaining, archiving and deleting data.
One important strategy is to classify data according to its type and sensitivity level so that appropriate storage measures can be put in place. For example, critical data such as financial records or personally identifiable information (PII) should be encrypted while being stored in secure servers. Non-critical data can be stored on less secure devices such as external hard drives or cloud-based platforms.
Another key guideline is an effective backup system that ensures all essential files are regularly saved in multiple locations. Regular backups help organizations restore lost or corrupted files quickly so they can continue operations without any significant disruptions.
The Impact Of Storage Media On Data Security
Different types of storage media offer different levels of security, and choosing the right one for your organization is essential. For instance, hard drives offer a high level of convenience and speed but are susceptible to physical damage, making them more vulnerable to data breaches.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are another popular option as they are faster than traditional hard drives and less prone to physical damage. However, they are still vulnerable to cyber-attacks such as hacking or malware attacks that can compromise sensitive information stored on them.
Cloud-based storage is becoming increasingly popular due to its convenience and flexibility. However, it comes with its own set of risks such as unauthorized access by third parties or data loss in case of server failures. Therefore, it’s crucial for organizations to conduct thorough risk assessments before deciding on which type of storage media best suits their data security needs.
The Importance Of Secure Data Destruction And Disposal
Companies and organizations have access to mountains of information about their customers, employees, and business operations. However, with great power comes great responsibility. It is crucial for businesses to securely dispose of any data that is no longer needed or relevant. Failing to do so can result in significant consequences such as data breaches and legal penalties.
Phase 4: Data Backup and Recovery
The Significance Of Data Backup And Recovery
It is essential for businesses to have a reliable backup and recovery system in place to ensure business continuity. Data backup involves creating copies of essential files and storing them in secure locations. This process helps businesses to recover lost or corrupted data quickly. On the other hand, data recovery involves retrieving lost or damaged data from backup storage systems. It allows businesses to restore their operations after an unexpected event such as a cyber-attack or natural disaster.
Different Types Of Backup And Recovery Techniques
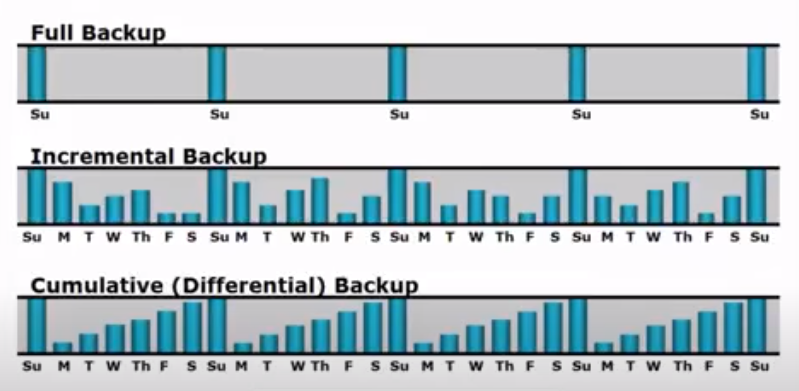
There are different types of backup and recovery techniques, each with its own unique advantages. The most common types include full backups, incremental backups, differential backups, and snapshot backups.
Full backups involve backing up all data files at once onto a storage device or cloud service. This technique is time-consuming but guarantees that all data is backed up entirely. Incremental backups only back up the changes made since the last backup was taken; this method saves storage space but takes longer to recover data. Differential backups are similar to incremental ones but save changes made since the last full backup was taken instead of the last differential one. Snapshot backups capture a point-in-time view of an entire system’s state; this technique enables fast disaster recovery by reverting to a previous “snapshot” if needed.
The Role Of Backup And Recovery In Business Continuity Planning
Business data is susceptible to various threats, including system crashes, hardware failures, cyberattacks, and natural disasters. The loss of data can be disastrous for any organization as it can lead to financial losses, reputation damage, and legal implications. Effective backup and recovery processes ensure that an organization has a reliable copy of its essential data in case of any disruption.
Backup involves creating a duplicate copy of important data stored in primary systems. This process can be performed manually or automatically by using specialized software tools that perform backups at regular intervals. Recovery refers to the process of retrieving copies of lost or damaged files from backups. An efficient recovery plan ensures that an organization quickly restores its operations after a disruption and minimizes downtime.
Phase 5: Incident Response And Management
The Importance Of Having An Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan provides a clear and structured approach to handling cybersecurity incidents, ensuring that the right people are notified, the appropriate actions are taken, and the incident is contained as quickly as possible. Without an incident response plan, organizations risk financial and reputational damage.
Having an effective incident response plan in place can also help organizations comply with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA by demonstrating due diligence in protecting sensitive data.
Steps For Developing An Incident Response Plan
Here are some steps to follow in order to create an effective incident response plan:
- Define what constitutes an incident: The first step in creating an incident response plan is defining what events or actions would qualify as incidents.
- Identify key stakeholders: Determine who should be involved in the development and implementation of the incident response plan, including internal teams and external partners.
- Assess risks and potential impacts: Analyze potential risks and their corresponding impact on business operations to determine which incidents require immediate attention.
- Establish communication protocols: Develop clear communication channels for reporting incidents, notifying stakeholders, and providing updates throughout the resolution process.
- Create escalation procedures: Define when and how incidents should escalate if initial attempts at mitigation fail.
- Outline a remediation strategy: Develop a detailed action plan for addressing each type of incident identified in Step 1, including measures for containment, recovery, investigation, reporting, and prevention.
How To Effectively Manage A Data Breach Or Security Incident
Assess the situation and contain the damage. This involves identifying the scope of the breach, determining which systems and data have been compromised, and isolating affected areas to prevent further spreading of the attack.
Identify how the breach occurred and what information was accessed. This may involve working with forensic investigators or law enforcement agencies. Once you understand what happened, you can begin remediation by removing any malware or other malicious code from your systems.
After remediation comes recovery, where you restore impacted systems and data back to their pre-breach state. Finally, it’s important to conduct a thorough post-incident review in order to identify any gaps in your security measures that allowed for the breach to occur in the first place.
Phase 6: Audit and Compliance
The Significance Of Compliance With Regulatory And Industry Standards
Compliance with regulatory and industry standards is a critical aspect of data security, which involves protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. Regulatory bodies such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) have established guidelines that organizations must follow to ensure data privacy and security. Compliance with these regulations not only protects customer information but also helps to avoid legal issues that may arise due to non-compliance.
Industry standards like Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) are also important for businesses that deal with credit card transactions. PCI DSS offers guidelines on how businesses should handle sensitive payment card information to prevent data breaches. By complying with these standards, businesses can build trust among customers by assuring them of their commitment to protecting their personal data. Additionally, compliance helps companies improve their reputation in the market by demonstrating their adherence to industry best practices for data security.
How To Conduct A Security Audit
- Preparation: The first phase of a security audit involves preparing the necessary documentation and tools to conduct the audit. This includes documenting all existing security policies, procedures, and controls in place, as well as identifying any potential risk factors that may exist within an organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Scoping: The second phase of a security audit involves scoping out the areas that will be audited. This includes identifying all assets within an organization’s IT infrastructure that are relevant to the audit, such as servers, applications, databases, and network devices.
- Assessment: During this phase of a security audit, assessors will conduct various tests and analyses to identify vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure. These assessments may include vulnerability scans or penetration testing to identify weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Reporting: Once the assessment phase is complete, findings must be documented in a report format. The report should provide details on identified vulnerabilities along with recommendations for remediation.
- Remediation: After reviewing the report findings, organizations must take necessary steps to remediate vulnerabilities identified during the assessment process.
- Verification: Once remediation efforts have been completed an additional round of testing should be conducted to ensure previously identified issues have been resolved effectively.
Best Practices For Achieving And Maintaining Compliance
The first step in achieving compliance is understanding the relevant regulations that apply to your organization and industry. This may include laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Once you have identified the applicable regulations, it’s important to develop policies and procedures that align with those requirements.
Regular training and awareness programs for employees are also essential for maintaining compliance. All staff members should be aware of their responsibilities when handling sensitive data, including how to identify potential security threats and what steps to take in the event of a breach. Regular evaluations and audits can help ensure that your organization remains compliant over time.
Partnering with an experienced IT security provider can offer assistance in achieving compliance by providing expert guidance on regulatory requirements and best practices for data protection. By keeping up-to-date with evolving regulations, regularly reviewing policies and procedures, investing in employee training programs, and working with trusted technology partners; organizations can maintain compliance throughout all phases of the data security lifecycle while protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.
Conclusion
Implementing an effective data security lifecycle is crucial in today’s digital age. It not only helps businesses keep their sensitive information secure but also provides peace of mind to their customers.
Each phase plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and integrity of data. Discovery involves identifying all the sensitive information within an organization’s environment; classification is about categorizing the data based on its level of sensitivity; protection includes implementing appropriate controls to safeguard the data from unauthorized access or breaches; detection refers to monitoring the network for any suspicious activity that may indicate a security threat; response is about taking immediate action in case of an attack or incident, while recovery involves restoring normal operations after an incident has been resolved.
FAQs
What Are Some Common Data Security Threats?
Some of the most common data security threats include phishing attacks, malware infections, password breaches, and insider threats.
Phishing attacks involve sending fraudulent emails or messages that trick users into revealing personal information or clicking on malicious links. Malware infections can occur when users unknowingly download infected files or software onto their devices, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Password breaches happen when passwords are stolen through various means such as brute-force attacks or social engineering tactics. Insider threats refer to employees who have access to confidential data but misuse it intentionally or unintentionally.
How Often Should Data Backups Be Performed?
The frequency of performing data backups depends on the type and volume of data, as well as the business needs. For instance, a small business with fewer than ten employees may not require daily backups. Instead, weekly or monthly backups could suffice. In contrast, a large corporation handling sensitive customer information may need to perform hourly backups to minimize risks.
What Is The Difference Between A Data Backup And A Data Archive?
A data backup is a copy of your data that is intended to be used in the event of data loss or corruption. It is meant to be a temporary solution to restore information that has been lost or corrupted due to various reasons such as hardware failure, human error, or cyberattacks.
On the other hand, a data archive is a long-term storage solution for information that may no longer be needed for day-to-day operations but still needs to be retained for legal compliance or historical purposes. Data archives store inactive files and documents in an organized manner, making it easy to retrieve them when necessary.
