Introduction
It is possible to perform a secure erase of data without losing the operating system. Secure data erasure is important for protecting sensitive information from being accessed or recovered by unauthorized parties. It is often necessary when disposing of old computers or hard drives, or when transferring ownership of a device.
Methods Of Secure Data Erasure

Software-Based Methods
One common method of secure data erasure is through the use of software-based methods. These programs overwrite the existing data on the hard drive with random data, making it virtually impossible for anyone to recover the original information. This process can be done without affecting the operating system, as the software is designed to only erase specific data files or folders.
Hardware-Based Methods
Another method of secure data erasure is through hardware-based methods, such as degaussing or physical destruction of the hard drive. Degaussing involves using a strong magnetic field to erase the data on the drive, while physical destruction involves physically damaging the drive beyond repair. These methods can also be done without affecting the operating system, as they do not require any software to be installed.
Understanding Secure Data Erasure
Secure data erasure is the process of completely and permanently removing all data from a device or storage medium, ensuring that it cannot be recovered or accessed by unauthorized individuals. This is important for protecting sensitive information and preventing data breaches. There are several methods of secure data erasure, including overwriting, degaussing, and encryption. Overwriting involves writing new data over the existing data multiple times, effectively erasing it. Degaussing involves using a strong magnetic field to erase the data on a magnetic storage medium. Encryption involves scrambling the data using a key, making it unreadable without the key.
It is important to choose the appropriate method of secure data erasure based on the type of device and storage medium being used. It is also important to ensure that the method used is effective in completely erasing the data and cannot be easily circumvented.
Challenges In Secure Data Erasure
There are several challenges in securely erasing data, especially in today’s digital age. Some of these challenges include:
- Increasing storage capacities: With the increase in storage capacities, it’s becoming harder to securely erase data. For example, a hard drive with a capacity of 1TB may take several hours to securely erase, and this time will increase with larger storage capacities.
- Cloud storage: With the rise of cloud storage, it’s becoming harder to know where your data is stored and who has access to it. This makes it harder to securely erase data, especially if you don’t have control over the storage infrastructure.
- Wear-leveling technology: SSDs use wear-leveling technology to distribute data evenly across the drive. This makes it harder to securely erase data, as data may still be present on the drive even after a wipe.
- Hidden areas on the drive: Some drives have hidden areas that are not accessible to the user, and these areas may contain data that can’t be erased. This makes it harder to securely erase data, as you may not be able to access all areas of the drive.
- Data recovery tools: There are many data recovery tools available that can recover data from wiped drives. This can make it difficult to securely erase data, as even if you think you have wiped the data, it may still be recoverable by someone with the right tools and knowledge.
To ensure that your data is securely erased, it is important to use a reliable data-wiping tool that meets industry standards for secure data erasure. It is also important to follow the instructions carefully and ensure that all areas of the drive are wiped, including any hidden areas.
Methods For Secure Data Erasure Without Losing The OS
There are several methods for securely erasing data without losing the operating system (OS):
- Use a data wiping tool specifically designed for selective file deletion. This type of tool allows you to choose which files and folders to erase while leaving the OS and other important system files intact.
- Use a partitioning tool to create a separate partition on your hard drive for your data. This way, you can erase the data partition without affecting the OS partition.
- Use a virtual machine to run your OS and applications, and store your data in a separate virtual disk. This way, you can easily erase the virtual disk without affecting the OS and applications.
- Use encryption to protect your data. If you encrypt your data using a strong encryption algorithm, you can simply delete the encryption key to render the data unreadable.
It is important to note that these methods may not be as secure as physically destroying the drive or using a professional data destruction service. However, they can provide a good level of security for most users.
How To Securely Wipe Data On SSD?
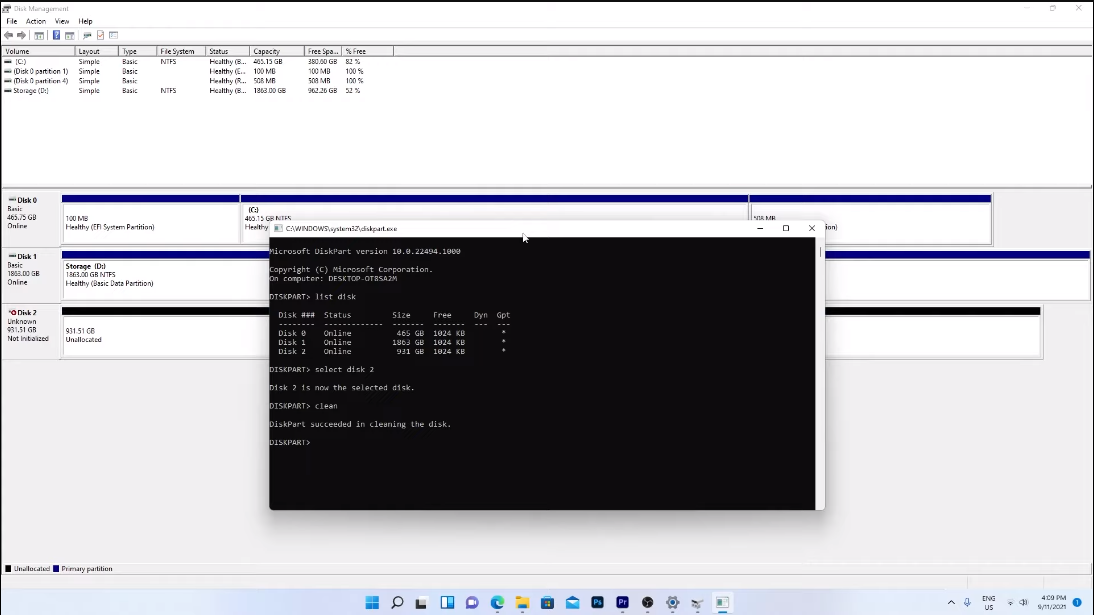
Securely wiping data from an SSD (solid-state drive) involves a different process than wiping data from a traditional hard drive. Here are the steps to securely wipe data from an SSD:
- Back up any important data: Before wiping the SSD, make sure to back up any important data that you want to keep.
- Use a secure erase utility: Most SSD manufacturers provide a secure erase utility that you can use to wipe the drive. This utility will erase all the data on the drive and reset it to its factory settings.
- Use a third-party tool: If your SSD manufacturer doesn’t provide a secure erase utility, you can use a third-party tool like Parted Magic or DBAN to wipe the drive. These tools overwrite the entire drive with random data, making it impossible to recover any of the original data.
- Verify the wipe: After wiping the drive, you should verify that all the data has been erased. You can do this by using a data recovery tool to try and recover any of the original data. If the tool can’t recover any data, then the wipe was successful.
It’s important to note that securely wiping an SSD can reduce its lifespan, so it should only be done when necessary.
Best Practices For Secure Data Erasure
When it comes to securely erasing data, several best practices should be followed:
- Use a reputable data erasure method: As mentioned earlier, there are several methods for securely erasing data on Linux. It is important to choose a reputable method that has been tested and proven to be effective.
- Verify that data has been securely erased: After data has been erased, it is important to verify that it has been securely erased. This can be done by using data recovery software to attempt to recover the erased data. If the data cannot be recovered, then it has been securely erased.
- Erase all copies of the data: It is important to ensure that all copies of the data have been securely erased. This includes backups, temporary files, and any other copies of the data that may exist.
- Follow company policies and regulations: Many companies have policies and regulations in place for securely erasing data. It is important to follow these policies and regulations to ensure that sensitive information is protected.
- Use encryption: In addition to securely erasing data, it is also important to use encryption to protect sensitive information. This can help prevent unauthorized access to the data in the first place.
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect sensitive information. As a writing assistant, I can help you create clear and concise policies and guidelines for data security, as well as assist in drafting training materials to educate employees on best practices for data protection. Additionally, I can guide you in selecting and implementing encryption tools to safeguard sensitive data.
Operating System Structures And Data Storage
Operating system structures and data storage are fundamental components of any computer system. The operating system manages the resources of the computer and provides a platform for applications to run on. It also provides a file system for organizing and storing data on the computer’s storage media. The file system is responsible for managing the organization of data on a storage medium, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive. It provides a hierarchical structure of directories and files that allows users to easily access and manage their data. The file system also provides mechanisms for protecting data from unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
In addition to the file system, the operating system also provides mechanisms for managing memory, processes, and input/output operations. Memory management involves allocating and deallocating memory to applications as needed. Process management involves managing the execution of multiple applications or processes on the system. Input/output operations involve managing the flow of data between the computer and its peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, and printers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, secure data erasure is crucial for organizations to protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. Failure to properly erase data can lead to serious consequences, including data breaches, legal penalties, and damage to an organization’s reputation. By implementing a secure data erasure policy and following best practices, organizations can ensure that their data is properly erased and disposed of, reducing the risk of data breaches and protecting their reputation. Organizations need to prioritize data security and take proactive measures to protect their sensitive information.
There are several methods available for secure data erasure without loss of operating system (OS). One such method is using data erasure software, which overwrites the data on the hard drive multiple times with random patterns to ensure that it cannot be recovered. This software can be installed on the existing OS and can erase data from individual files, folders, or entire hard drives. Another method is using a hardware-based solution, such as a data erasure device, which can erase data from hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and other storage devices without the need for an OS. These devices use various methods, such as magnetic fields or electrical pulses, to erase the data and ensure that it cannot be recovered. Organizations can also choose to physically destroy the storage devices, such as shredding or melting them, to ensure that the data cannot be recovered. However, this method is not environmentally friendly and can be expensive. It is important for organizations to choose a method that suits their needs and ensures that their data is securely erased without loss of OS. It is also important to follow best practices and guidelines for data erasure to ensure that the process is carried out effectively and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Data Be Securely Erased Without Losing The Operating System?
Yes, data can be securely erased without losing the operating system. There are various software tools available that can securely erase specific files or entire hard drives while leaving the operating system intact. It is important to note that securely erasing data can be a complex process and should be done carefully to avoid any unintended consequences. It is recommended to seek professional assistance or guidance before attempting to securely erase any data.
Is Physical Destruction The Only Foolproof Method For Data Erasure?
No, physical destruction is not the only foolproof method for data erasure. There are other methods such as degaussing, which uses a strong magnetic field to erase data from a hard drive or other magnetic media. Additionally, there are specialized software tools and services that use advanced algorithms to securely erase data beyond recovery. However, it is important to note that no method is 100% foolproof and it is always recommended to seek professional assistance or guidance before attempting to erase sensitive data.
How Does Overwriting Data Ensure Its Complete Removal?
Overwriting data ensures its complete removal by replacing the existing data with new data. When data is overwritten, it is no longer accessible in its original form and cannot be recovered using standard data recovery tools. The more times data is overwritten, the more difficult it becomes to recover the original data. This is because each overwrite makes it more likely that the original data will be corrupted or destroyed. Therefore, overwriting data multiple times using random patterns or algorithms is considered a secure method of data destruction. However, it is important to note that overwriting may not be effective for certain types of storage media, such as solid-state drives, and professional assistance should be sought to ensure complete data destruction.
Can Data Remnants Still Exist After A Secure Erase?
It is unlikely that data remnants will exist after a secure erase, as the process is designed to completely overwrite and destroy all data on the storage media. However, there is always a small possibility that some data remnants may remain, especially if the storage media is damaged or malfunctioning. It is important to use a reputable and secure data destruction method, and to seek professional assistance if necessary, to ensure that all data remnants are destroyed.
What Are The Risks Of Using Unreliable Data Erasure Tools?
Using unreliable data erasure tools can pose a significant risk to the security of your sensitive data. These tools may not completely overwrite and destroy all data on the storage media, leaving data remnants that can be recovered by unauthorized individuals using specialized software. This can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime. Additionally, unreliable data erasure tools may cause damage to the storage media, rendering it unreadable and potentially causing data loss. To avoid these risks, it is important to use reputable and secure data destruction methods and to seek professional assistance if necessary.
Can Data Be Securely Erased From Solid-State Drives (SSDs)?
Yes, data can be securely erased from solid-state drives (SSDs) using specialized software that overwrites the entire drive with random data or zeroes. This process is called “secure erase” and it ensures that all data on the drive is irretrievably erased. However, it is important to note that not all SSDs support secure erase, and some may require specific tools or firmware updates to operate. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek professional assistance to ensure that the secure erase process is performed correctly.
