Introduction
In today’s world, big data is everywhere. Every time we use our phones, computers, or any other digital device, we generate data that is collected and analyzed by companies and organizations. While this data can be used to improve products and services, it also raises privacy concerns. With so much personal information being collected, how can we ensure that our data is safe? This article will explore five practical ways to safeguard privacy in big data and keep your information safe.
What are the five practical ways to protect privacy in big data?
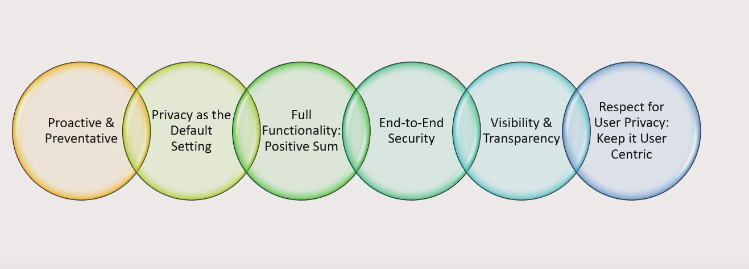
Here are five practical ways to safeguard privacy in big data:
1. Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication: Strong passwords and two-factor authentication can help prevent unauthorized access to your data. Make sure to use unique passwords for different accounts and avoid using easily guessable information like your name or birthdate.
2. Read privacy policies carefully: Before providing personal information to a company or organization, make sure to read their privacy policy carefully. Look for details on collecting, using, and sharing your data.
3. Limit the amount of personal information you share: Be cautious about sharing personal information on social media or other public platforms. Consider limiting the amount of personal information you share online and avoid sharing sensitive information like your address or social security number.
4. Use a virtual private network (VPN): A VPN can help encrypt your internet traffic and protect your online privacy. It can also help you bypass geo-restrictions and access content that may be blocked in your region.
5. Stay up-to-date with software updates and security patches: Make sure to regularly update your software and security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities and exploits. This includes updating your operating system, web browser, and other software regularly.
Practical Ways To Protect Privacy In Big Data
Implement Strong Access Control Measures
Role-Based Access Control
One practical way to protect privacy in big data is to implement strong access control measures. This can be done through role-based access control, where users are assigned specific roles and permissions based on their job responsibilities and the level of access needed. This helps to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Another practical way to protect privacy in big data is to encrypt sensitive data. This can be done through various encryption techniques, such as symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Encryption helps to ensure that even if unauthorized users gain access to the data, they will not be able to read or use it without the decryption key.
Implement Data Masking
Data masking is another effective technique to protect privacy in big data. This involves replacing sensitive data with fictitious data that looks real but does not reveal any actual information. For example, masking a social security number by replacing the first five digits with Xs.
Monitor Access And Activity
Regular access and activity monitoring is crucial to ensure that only authorized users are accessing and using the data. This can be done through various tools and technologies that track user activity, such as audit logs and access controls. By monitoring access and activity, any unauthorized or suspicious behavior can be detected and investigated promptly.
Implement User Authentication And Authorization
User authentication and authorization are essential measures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This involves verifying the identity of users and granting them access only to the data they are authorized to view or modify. This can be done through various authentication mechanisms.
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to provide two forms of identification to access data or systems. This can include a password or PIN, as well as a unique code sent to the user’s phone or email. By requiring two forms of identification, 2FA adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
Role-Based Access Control
Role-based access control (RBAC) is another method of controlling access to sensitive data. RBAC involves assigning users to specific roles based on their job responsibilities and granting them access only to the data and systems necessary to perform their job functions. This helps to ensure that users only have access to the information they need to do their jobs and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data. RBAC can also simplify the process of managing access permissions, as changes can be made at the role level rather than for each user.
Limiting Data Access
One way to limit data access is through the use of access controls. Access controls can be implemented at various levels, such as at the network, system, or application level. These controls can restrict access to certain data based on factors such as user identity, location, and device used to access the data. Another way to limit data access is through the use of encryption. Encryption can be used to protect sensitive data by rendering it unreadable to unauthorized users. This can be particularly useful in cases where data needs to be stored or transmitted over public networks where it may be vulnerable to interception. Additionally, implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication can also help to limit data access. By requiring users to use complex, unique passwords and verifying their identity through multiple methods, it becomes more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to sensitive data.
Regularly monitoring and auditing access to data can also help to identify any potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. This can allow for prompt action to be taken to prevent further unauthorized access and to mitigate any damage that may have already occurred. In addition to these measures, it is important to regularly update software and systems to ensure that any known vulnerabilities are patched and that security features are up-to-date. Keeping up with the latest security best practices and staying informed about emerging threats can also help to prevent security breaches.
Finally, it is important to have a plan in place for responding to security incidents. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a breach and should include procedures for containing the breach, assessing the damage, notifying affected parties, and restoring normal operations. In summary, to prevent security breaches, it is important to implement strong security measures, regularly update software and systems, stay informed about emerging threats, and have a plan in place for responding to security incidents. By taking these steps, organizations can greatly reduce the risk of security breaches and protect sensitive data and assets.
Use Anonymization Techniques
Anonymization techniques are an effective way to protect sensitive data from being exposed in the event of a security breach. Removing or obfuscating identifying information from data makes it much more difficult for attackers to use that data for malicious purposes. Some common anonymization techniques include data masking, where sensitive information is replaced with random or fictional data, and data aggregation, where data is combined with other data to make it less identifiable. It is important to note, however, that these techniques are not foolproof and may not provide complete protection against determined attackers. It is always best to use a combination of anonymization techniques and other security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to ensure the protection of sensitive data. Additionally, it is important to regularly review and update your anonymization methods to stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure the ongoing security of your data.
Secure Transmission Of Personal Health Data Over The Internet Usually Relies On Which Two Methods?
The two methods that are commonly used for the secure transmission of personal health data over the internet are encryption and secure sockets layer (SSL) technology. Encryption involves encoding the data in a way that only authorized parties can access it, while SSL technology provides a secure channel for transmitting the data over the internet by encrypting the data in transit and verifying the identity of the parties involved in the communication. Together, these methods help to ensure that personal health data is transmitted securely and protected from unauthorized access or interception.
Create Robust Privacy Policies And Procedures
To create robust privacy policies and procedures, organizations should consider the following steps:
1. Conduct a privacy impact assessment: This will help identify potential privacy risks and determine the appropriate controls to mitigate those risks.
2. Develop a privacy policy: The policy should clearly outline the organization’s commitment to protecting personal health data and the procedures for handling that data.
3. Train employees: All employees who handle personal health data should receive training on the organization’s privacy policies and procedures.
4. Implement technical controls: This includes measures such as access controls, encryption, and monitoring to ensure that personal health data is protected.
5. Establish a breach notification process: In the event of a data breach, the organization should have a clear process for notifying affected individuals and authorities.
6. Regularly review and update policies and procedures: Privacy risks and regulations are constantly evolving, so it’s important to regularly review and update policies and procedures to ensure they remain effective.
By following these steps, organizations can develop and maintain robust privacy policies and procedures that help to protect personal health data and maintain the trust of their patients and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Organizations can protect privacy in big data by implementing five practical ways: conducting privacy impact assessments, implementing data minimization strategies, implementing strong security measures, providing privacy training for employees, and regularly reviewing and updating policies and procedures. These steps can help organizations protect personal health data, maintain the trust of their patients and stakeholders, and comply with privacy regulations.
Consider implementing these practical ways to protect privacy in big data in your organization. Conduct privacy impact assessments, implement data minimization strategies, implement strong security measures, provide privacy training for employees, and regularly review and update policies and procedures. By doing so, you can protect personal health data, maintain the trust of your patients and stakeholders, and comply with privacy regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is Big Data?
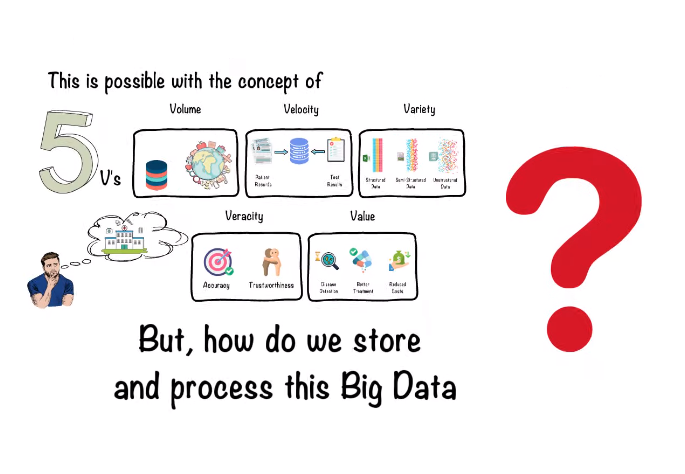
Big data refers to large and complex sets of data that cannot be easily processed or analyzed using traditional data processing tools. It is characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety, and is often used to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform business decisions and strategies.
What Is Privacy Protection In Big Data?
Privacy protection in big data refers to the measures taken to ensure that personal information is kept confidential and secure when it is collected, processed, and analyzed. This includes implementing technical and organizational measures to safeguard data, obtaining consent from individuals before collecting their data, and complying with privacy laws and regulations. It is important to maintain the trust of individuals and stakeholders by respecting their privacy and ensuring that their personal information is not misused or mishandled.
Why Is Privacy Protection Important In Big Data?
Privacy protection is important in big data because it helps to maintain the trust of individuals and stakeholders. Big data often involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal information, which can be sensitive and private. Without proper privacy protection measures in place, this information can be misused or mishandled, leading to negative consequences for both individuals and organizations. Additionally, compliance with privacy laws and regulations is essential to avoid legal and financial penalties.
What Is Access Control In Big Data?
Access Control in Big Data refers to the practice of controlling who has access to specific data within a big data system. This involves setting up permissions and restrictions on who can view, modify, or delete certain data sets or files. Access control is important in big data because it helps to ensure that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals, reducing the risk of data breaches or misuse. Access control can be implemented through various methods such as role-based access control, attribute-based access control, and discretionary access control.
What Are Anonymization Techniques?
Anonymization techniques are methods used to remove or obscure identifying information from data sets, while still preserving their usefulness for analysis or research purposes. These techniques can include methods such as data masking, where certain data values are replaced with generic or random values, or data perturbation, where data values are intentionally modified to prevent identification. Other techniques include data aggregation, where data is grouped to prevent individual identification, and data swapping, where data values are exchanged between different individuals or entities to prevent identification.
What Is Secure Data Storage And Transmission?
Secure Data Storage and Transmission refers to the methods and techniques used to protect data while it is being stored or transmitted. This can include encryption, access control, and other security measures to prevent unauthorized access, theft, or loss of data. Secure data storage and transmission is essential for protecting sensitive information such as personal or financial data and is often used in industries such as healthcare, finance, and government.
Why Is Monitoring And Auditing Data Access And Usage Important?
Monitoring and auditing data access and usage are important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to ensure that data is being used by company policies and regulations. This can help to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents. Additionally, monitoring and auditing can help to identify potential security threats or vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take proactive measures to address these issues before they become serious problems. Finally, monitoring and auditing data access and usage can help to provide accountability and transparency, ensuring that employees and other users are adhering to company policies and procedures. To effectively monitor and audit data access and usage, organizations should implement a robust system for tracking and analyzing data activity. This can include tools such as activity logs, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and user behavior analytics (UBA) software. These tools can help to identify patterns and anomalies in data access and usage, allowing organizations to quickly detect and respond to potential security threats.
