Definition of Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting plain text or data into a coded message or cipher, to prevent unauthorized access or interception during transmission or storage. This is achieved by using an algorithm or mathematical formula to scramble the original data, making it unreadable without the proper decryption key. Encryption is commonly used to protect sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal or confidential data.
What are Encryption Algorithms?
Encryption algorithms are the mathematical formulas or procedures used to encrypt and decrypt data. There are various encryption algorithms available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some of the commonly used encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), and Blowfish. These algorithms use different techniques such as substitution, permutation, and transposition to scramble the original data and make it unreadable.
Popular Encryption Algorithms
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- DES (Data Encryption Standard)
How Encryption Works
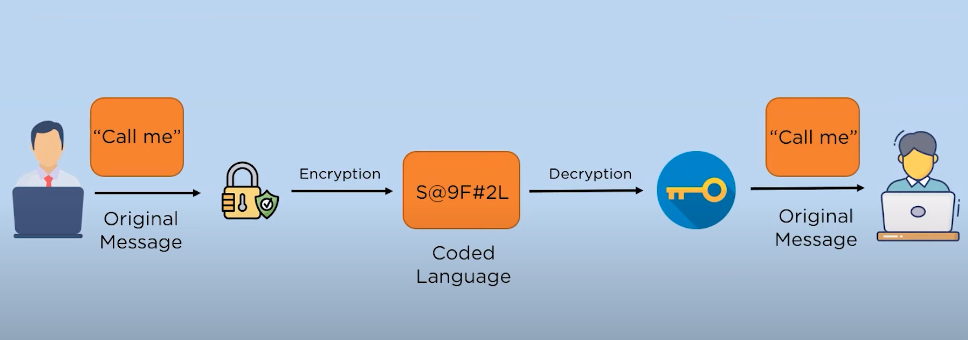
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into cypher text, which is unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. The encryption process involves using a specific algorithm to scramble the data, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access and read the information. The encryption process typically involves three main components: the plaintext, the encryption algorithm, and the encryption key. (https://mundonow.com/) The plaintext is the original data that needs to be encrypted, while the encryption algorithm determines how the plaintext is transformed into cypher text.
Encryption Process
The encryption process is a method of encoding data to protect it from unauthorized access. It involves using an encryption algorithm to transform the original data, known as plaintext, into a coded form, known as ciphertext. The encryption algorithm uses a specific key to scramble the plaintext, making it unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the key to decrypt it.
Decryption Process
The decryption process is the reverse of the encryption process. It involves using a decryption algorithm and the correct key to transform the ciphertext back into plaintext. This allows authorized users to access and read the original data. The decryption algorithm essentially reverses the encryption algorithm, unscrambling the ciphertext and restoring it to its original form. It is important to keep the key secure and only share it with authorized users to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data.
Benefits of Encryption
Encryption provides several benefits, including:
1. Confidentiality: Encryption helps to keep sensitive information confidential by making it unreadable to unauthorized users. This is especially important for data such as personal information, financial records, and medical records.
2. Integrity: Encryption helps to maintain the integrity of data by ensuring that it has not been tampered with or altered in any way. This is important for data such as legal documents, contracts, and financial transactions.
3. Protection against hacking: Encryption can help protect against hacking by making it more difficult for hackers to access and understand the data they are trying to steal. This is particularly important for businesses and organizations that handle sensitive information, as a data breach can be devastating.
4. Compliance: Encryption can help businesses and organizations comply with regulatory requirements for data protection and privacy. Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict regulations that require the use of encryption to protect sensitive data.
Limitations of Encryption
While encryption offers many benefits, there are also some limitations to consider:
1. Key management: Encryption requires the use of keys to encrypt and decrypt data. Managing these keys can be challenging, especially for large organizations that have many users and devices accessing encrypted data.
2. Performance impact: Encryption can have a performance impact on devices and systems, particularly older or less powerful ones. This can slow down operations and affect user experience.
3. Cost: Implementing encryption can be costly, particularly for small businesses.
Complex Key Management
Encryption is a vital tool for securing data, but it can also be challenging to manage, particularly when it comes to key management. When using encryption, keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data. These keys must be kept secure and accessible only to authorized users. For large organizations with many users and devices accessing encrypted data, managing these keys can be a significant challenge.
Performance and Speed Issues
Another potential challenge with encryption is performance and speed issues. Encryption can slow down the processing and transmission of data, particularly for large files or when using complex encryption algorithms. This can impact the user experience and productivity, particularly in high-demand environments such as financial transactions or healthcare records. It is important to balance the need for security with the need for efficient data processing and transmission.
Real-Life Applications of Encryption
- Banking and Finance
- Healthcare
- E-commerce
Future of Encryption
- Quantum Computing
- Post-Quantum Encryption
- Blockchain Encryption
Encryption Tools and Software
- VeraCrypt: A free open-source disk encryption software that can create a virtual encrypted disk within a file and mount it as a real disk.
- GnuPG: A free encryption software that provides encryption and digital signature capabilities for data communication and storage.
- OpenSSL: A widely-used encryption library that provides support for SSL and TLS protocols used in secure communications.
Choosing the Right Encryption Method
When it comes to choosing the right encryption method, it’s important to consider the level of security needed, the type of data being encrypted, and the intended use of the encryption. For example, if you’re looking to encrypt sensitive financial data, you may want to consider using a more advanced encryption method such as quantum encryption. On the other hand, if you’re simply looking to secure personal files on your computer, software like VeraCrypt may be sufficient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, encryption is a valuable tool for protecting sensitive data and ensuring privacy in the digital age. While it is generally legal, it is important to be aware of any restrictions or requirements in your specific location. As a writing assistant, I can help you research and present information on encryption and related topics clearly and concisely.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Encryption differ from Hashing?
Encryption and hashing are both methods of protecting data, but they serve different purposes. Encryption is a process of converting plain text into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with a key or password. It is used to secure data during transmission or storage. On the other hand, hashing is a one-way process of converting data into a fixed-length string of characters that represents the original data.
Can encrypted data be decrypted?
Yes, encrypted data can be decrypted with the correct key or password. The purpose of encryption is to make the data unreadable to anyone who does not have the key or password, but it can be decrypted by those who do have access to it.
How do I know if my encryption is secure?
The security of encryption depends on the strength of the encryption algorithm and the length and complexity of the encryption key or password. Generally, encryption algorithms that are widely used and have been extensively tested by security experts are considered more secure. It is also important to use a long and complex encryption key or password that is not easily guessable. Additionally, regularly updating encryption methods and keys can help maintain the security of encrypted data.
Is Encryption legal?
Encryption is legal in most countries, but there may be some restrictions on the use of encryption for certain purposes or by certain individuals or organizations. It is important to check the laws and regulations in your specific location to ensure that you are using encryption legally. In some cases, governments may require individuals or organizations to provide access to encrypted data for law enforcement or national security purposes.
