Introduction
Data safeguards protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or destruction. They are essential to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, especially in the face of security threats such as hacking, malware, phishing, and insider attacks. This article will discuss some examples of data safeguards against security threats and their effectiveness.
Data security threats can come from various sources and take different forms. Some of the most common features of security threats to data include:
- Hacking: This involves unauthorized access to a computer system or network to steal or manipulate data.
- Malware is malicious software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unsanctioned computer systems or network access.
- Phishing: This social engineering attack involves tricking users into revealing sensitive data like passwords, credit card numbers, or additional personal information.
- Insider attacks: These are attacks carried out by someone who has authorized access to a computer system or network, such as an employee, contractor, or vendor.
Example Of A Data Safeguard Against Security Threats
One example of a data safeguard against security threats is access controls. Access controls limit who can access sensitive data and ensure that only approved individuals have access. This can include passwords, biometric authentication, and two-factor authentication. By implementing access controls, organizations can help prevent unauthorized access to data and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Types of Data Security Threats
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing is a fraudulent technique that tricks individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card details, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity.
- Malware Infections: Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to infiltrate systems and cause harm. It includes viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware, among others.
- Social Engineering: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals through psychological tactics to gain unauthorized access to information or systems.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats arise from individuals within an organization who abuse their authorized access to data for personal gain or malicious purposes.
Recognizing and Defending Against Data Security Threats
Data security threats have become increasingly sophisticated in today’s digital landscape. With the growing reliance on technology and the massive amounts of data being generated, it is crucial for individuals and organizations to understand these threats and take proactive measures to defend against them. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into recognizing and defending against data security threats, empowering you to safeguard your sensitive information effectively.
Data Safeguard Against Security Threats
Access controls are a data safeguard against security threats. They limit access to sensitive data and ensure that only authorized individuals have access. This helps prevent unsanctioned access and reduces the risk of security breaches.
Access Controls
Access controls are an essential component of information security. They are used to restrict access to sensitive information or systems to only authorized individuals. Access controls can be physical, such as locks and security cameras, or digital, such as passwords and encryption. Effective access controls should ensure that only those who need access to sensitive data or systems are granted access. This can be achieved through role-based access controls, where access is granted based on an individual’s job function or level of responsibility.
Access controls should also be regularly reviewed and updated to remain effective. This can involve conducting regular audits to identify unauthorized access attempts or potential vulnerabilities in the access control system.
Access controls are an important component of a comprehensive information security program and should be carefully considered in any organization’s security strategy.
Passwords

Passwords are also a data safeguard against security threats. They provide a layer of security to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. However, it is important to use strong passwords that are not easily guessable and to change them regularly to maintain their effectiveness as a safeguard. Additionally, organizations should consider implementing multi-factor authentication further to enhance the security of their systems and data.
Encryption
Encryption is another important tool in protecting sensitive data. It involves converting plain text into a code or cipher that someone with the decryption key can only read. This ensures that even if hackers can access the data, they cannot read it without the key. Encryption can be applied to data at rest, such as stored on a hard drive, or in transit, such as when transmitted over the internet. It is significant to use strong encryption algorithms and to keep the decryption keys secure to ensure the effectiveness of this safeguard.
Firewalls
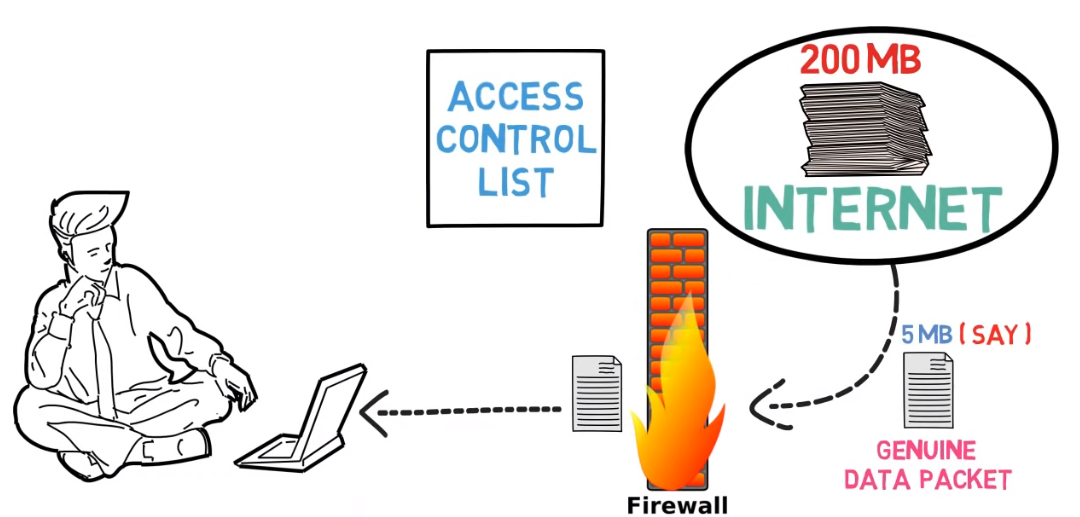
Firewalls are a network security system that looks after and handles incoming and outgoing network traffic. It is a barrier between a reliable internal network and unreliable external networks like the internet. Firewalls can be hardware, software, or an amalgamation of both. They use a set of rules to determine which traffic is permitted to pass through and which traffic should be blocked. This helps prevent unauthorized access to the network and the spread of malware or other malicious activity. Firewalls can also be configured to log and alert on suspicious activity, providing an additional layer of security.
Antivirus Software

Antivirus software is a program designed to detect, prevent, and eliminate malicious software, also known as malware. Malware can include viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, and other categories of harmful software that can cause damage to a computer system or steal sensitive information. Antivirus software typically scans files and programs on a computer system for known malicious code patterns. If a file or program is found to contain malware, the antivirus software will either quarantine or delete the file or attempt to remove the malicious code.
In addition to real-time scanning, many antivirus programs offer features such as email scanning, web protection, and automatic updates to ensure the software is up-to-date with the latest malware definitions.
Antivirus software is an important part of maintaining the security of a computer system, as it can help prevent malware infections and protect sensitive information from being stolen or compromised.
Backups
Backing up your important data is crucial to confirm you don’t lose it in case of a system failure or a malware attack. Several ways to back up your data include using an external hard drive, cloud storage services, or a network-attached storage device. It’s recommended to schedule backups regularly, ideally daily or weekly, to ensure that your data is always up-to-date. You can also use backup software to automate the process and make it easier.
When selecting a backup method, consider the amount of data you require to back up, the frequency of backups, and the level of security you require. It’s also significant to test your backups regularly to confirm that they are working properly and that you can restore your data if needed.
Remember, having a backup of your important data is essential to avoid losing it permanently, so ensure you have a reliable backup system.
Employee Training

Employee training is an important aspect of any organization. It helps employees to develop new skills and knowledge and to stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends and best practices. Effective training can also improve employee morale, job satisfaction, and productivity. To ensure that your employee training program is successful, you should first identify the specific skills and knowledge your employees need to acquire. This can be done through a needs assessment, which involves analyzing your workforce’s current skills and knowledge and identifying gaps.
Once you have identified the training needs of your employees, you can develop a training plan that includes clear objectives, a timeline, and specific training methods and resources. You should also consider the most effective delivery methods for your training, such as classroom training, online courses, or on-the-job training.
It’s important to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the training program and make adjustments as required. This can involve gathering employee feedback, analyzing training outcomes, and changing the training content or delivery methods.
Investing in employee training can positively impact your organization’s success and competitiveness. By providing your employees with the skills and knowledge they need to excel in their roles, you can improve productivity, reduce turnover, and enhance your organization’s overall performance.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is a crucial aspect of a comprehensive security strategy. It involves separating a network into smaller subnetworks, known as segments, to limit the spread of potential security threats. By separating sensitive data and resources from other parts of the network, network segmentation can help to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the impact of a security breach. Implementing network segmentation requires careful planning and consideration of the organization’s specific needs and risks. It typically involves using firewalls, virtual LANs (VLANs), and other network devices to create separate segments for different departments, applications, or user groups. Access controls and monitoring tools can also ensure that only legal users and devices can access each segment.
Overall, network segmentation can help to improve the security and resilience of an organization’s network infrastructure. It can reduce the risk of data breaches, minimize the impact of any occurring, and make it easier to identify and contain threats.
Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is a recognized set of procedures that outlines how an organization will respond to and manage a cybersecurity incident. Organizations need to have a well-defined incident response plan to reduce the impact of a cyber attack and ensure a timely and effective response. The incident response plan should involve the following components:
1. Preparation: This includes identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, defining roles and responsibilities for incident response team members, and establishing communication protocols.
2. Detection and analysis: Identifying and classifying incidents, assessing the impact, and determining the appropriate response.
3. Containment, eradication, and recovery: This includes containing the incident to prevent further damage, eradicating the threat, and restoring systems and data to their pre-incident state.
4. Post-incident activities involve analyzing the incident, identifying lessons learned, and implementing changes to prevent similar incidents.
An incident response plan can help organizations minimize the effect of a cyber attack and ensure a timely and effective response. It is important to regularly evaluate and update the plan to ensure it remains effective in the face of evolving threats.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security measures are an important aspect of overall security for any organization. These measures include physical access controls, such as locks and keycards, surveillance cameras, and security personnel. Access controls limit physical access to sensitive areas of a facility, such as data centers or server rooms. Keycards or biometric authentication can ensure that only authorized personnel can enter these areas.
Surveillance cameras can be used to monitor activity in and around a facility, providing a record of any incidents that occur. Security personnel can also be stationed at entrances and other critical areas to deter unauthorized access and respond to incidents.
Other physical security measures may include alarm systems, fencing, and secure storage for sensitive equipment and data. Regular maintenance and testing of these measures are important to ensure their effectiveness in protecting the organization’s assets and data.
Common Security Threats

Common security threats include malware, phishing attacks, social engineering, ransomware, and denial-of-service attacks. It’s important to have measures to protect against these threats, such as firewalls, antivirus software, employee training, and regular backups. Additionally, staying current on security threats and trends can help organizations avoid potential attacks.
Conclusion
A denial-of-service attack is a cyber attack in which the attacker floods a network or website with traffic or requests, overwhelming the system and causing it to become unavailable to valid users. This can result in important disruption to business operations or online services.
A denial-of-service attack is a cyber-attack where an attacker attempts to make a website or network unavailable to users by flooding it with traffic or requests. This can cause noteworthy disruption to business operations or online services. Implementing data safeguards to protect against security threats such as denial-of-service attacks is important. This can include measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. By implementing these safeguards, businesses can help to mitigate the risk of cyber-attacks and protect their sensitive data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are Some Common Data-Safeguarding Measures?
Common data safeguarding measures include firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, employee training, regular backups, and access controls.
What Is Malware?
Malware is a type of software that is designed to damage or exploit computer systems. Examples of malware involve viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware.
What Is Phishing?
Phishing is a social engineering attack in which attackers attempt to trick individuals into providing sensitive information by posing as a reliable entity, such as login credentials or financial information.
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is malware that encrypts a victim’s files or system and demands payment for the decryption key.
