Introduction
iCloud is a cloud storage and cloud computing service that was introduced by Apple Inc. in 2011. The service allows users to store their data such as documents, music, photos and videos on remote servers owned by Apple, and access them from any of their devices that are connected to the internet. iCloud also enables users to synchronize their calendars, contacts, bookmarks and notes across all of their Apple devices.
iCloud also has a feature called “Find My iPhone” which allows users to track the location of lost or stolen iOS devices remotely. This feature uses end-to-end encryption to ensure that the location data is kept private between the device owner and Apple’s servers. Overall, iCloud provides several security measures for protecting user data from unauthorized access or breaches while still offering convenient syncing capabilities across multiple devices.
Understanding Icloud Security Features
Encryption Overview
Data security is one of the most important features of iCloud, and encryption plays a critical role in protecting user data on this platform. All data that is stored on iCloud is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Encryption Types For iCloud
One type of encryption used by iCloud is AES-128-bit encryption for data in transit. This encryption protocol ensures that any information being transferred between devices or servers is encrypted with a 128-bit key. Additionally, all communications over the internet are secured using SSL/TLS technology.
Another type of encryption used by iCloud is end-to-end encryption for certain types of content like iMessage conversations and FaceTime calls. When this feature is enabled on both ends of the communication, only the sender and receiver have access to the content exchanged during a conversation.
Apple also uses two-factor authentication (2FA) as an additional layer of security for users’ accounts. This security feature requires users to enter their password and an additional code sent via SMS or generated through an authenticator app before accessing their account.
Secure Key Management
Secure key management is a crucial aspect of iCloud security. That’s why Apple has implemented a highly secure system for managing encryption keys. In this system, each file stored in iCloud is encrypted with its own unique key, which is then encrypted again using a master key that only Apple knows. This means that even if someone were to gain access to one of your files, they would not be able to access any other files in your account since each file has its own unique key.
Furthermore, Apple uses hardware security modules (HSMs) to store and manage encryption keys securely. HSMs are tamper-resistant devices designed specifically for secure key management and storage. They ensure that no one can access or modify an encryption key without proper authorization from Apple’s servers.
iCloud Data Storage Security
Physical Security Measures For Icloud
To ensure the safety of user data stored in iCloud, Apple has implemented various physical security measures. One of the physical security measures that iCloud employs is strict access controls. All iCloud servers are located in secure data centres with limited entry points that allow only authorized personnel to enter. Additionally, these data centres have state-of-the-art surveillance systems in place to monitor any unauthorized access attempts.
Network Security Measures For Icloud
All data transferred between an Apple device and iCloud servers is encrypted using industry-standard protocols. This means that even if a hacker intercepts the data during transmission, they will not be able to read or access it without proper decryption keys.
In addition to encryption, iCloud also offers two-factor authentication as an extra layer of security for user accounts. This means that in addition to entering their password, users will also need to verify their identity through another device or method before gaining access to their account.
iCloud Data Transmission Security
SSL Encryption For iCloud Data Transmission
SSL encryption ensures that any communication between a user’s device and iCloud servers is protected from eavesdropping or tampering by unauthorized parties. When a user accesses iCloud services through their device or computer, their data is encrypted with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) technology before it is transmitted over the internet. The encrypted data can only be decrypted by authorized parties with proper authentication keys.
TLS Encryption For iCloud Data Transmission
TLS provides secure communication between two devices by encrypting all data transmitted between them. It ensures that no unauthorized third party can intercept or access any information exchanged between devices. Every time a user accesses iCloud services or sends information over iCloud, TLS encryption is used to protect it.
iCloud Security For End-User Data
iCloud Two-Factor Authentication
Enabling 2FA for iCloud is simple and can be done through the settings on your iOS or macOS device. Once enabled, any attempt to log into your iCloud account will require both your password and a verification code that is sent to one of your trusted devices. This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information such as photos, documents, and messages stored in iCloud.
iCloud Security Code Verification
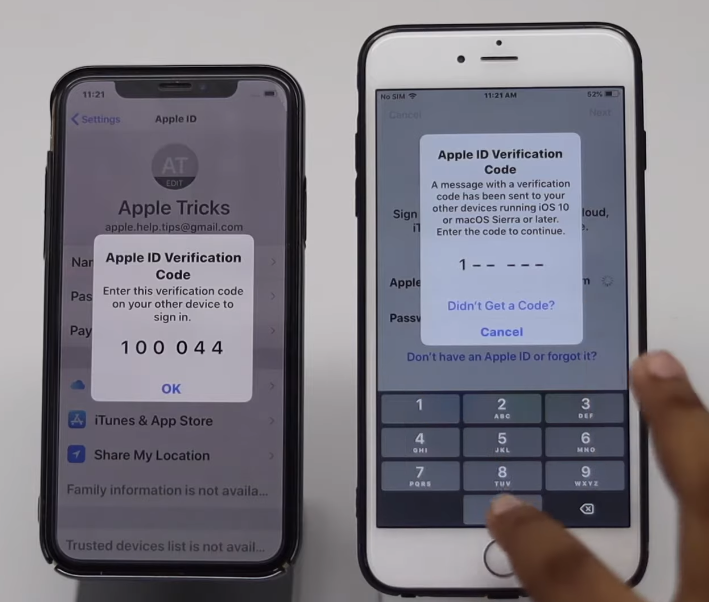
iCloud Security Code Verification ensures that only you can access your data stored in iCloud, even if someone else has access to your device or your Apple ID credentials. When enabled, security code verification is required each time you sign in to iCloud on a new device or web browser.
iCloud Recovery Key
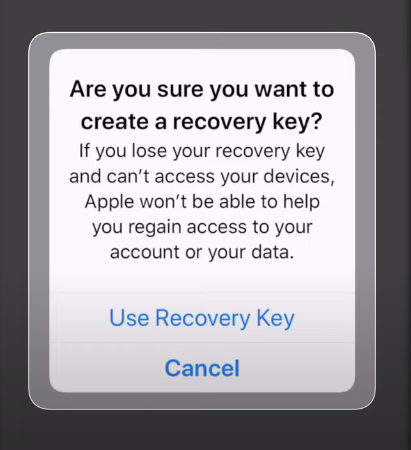
The iCloud Recovery Key is a 14-character key generated by Apple to encrypt and secure your iCloud account. In case you forget your password or lose access to your trusted devices, the recovery key can be used to regain access to your account. The recovery key provides another layer of protection by ensuring that only authorized users can gain access to their accounts.

iCloud is a cloud storage and computing service developed by Apple Inc. that allows users to store their data on remote servers. To ensure the privacy and security of its users’ data, iCloud implements various encryption methods.
Apple’s Policy On Accessing User Data
Apple is deeply committed to protecting user privacy, and this commitment extends to the company’s policies on accessing user data. In general, Apple will only hand over user data to law enforcement officials when compelled by a valid legal request such as a warrant or court order. The company also provides clear guidelines for how it handles requests for user data from government agencies around the world.
Apple’s strict policies on accessing user data have been put to the test in high-profile cases such as the standoff between Apple and the FBI over unlocking an iPhone belonging to one of the San Bernardino shooters. In this case, Apple refused to create a backdoor into its encryption software that could compromise user privacy and security. Ultimately, the FBI was able to unlock the phone with help from a third-party vendor rather than from Apple itself.
User Control Over iCloud Data
The company believes that users should have complete control over their data, and this is reflected in the various options available under the iCloud settings menu. Users can choose what types of data they want to store on iCloud, including contacts, calendars, photos, documents and more.
Apple’s commitment to privacy means that even they cannot access a user’s information without their explicit consent. This includes everything from messages to photos and videos stored on iCloud. With end-to-end encryption enabled by default for iMessage and FaceTime communications between two Apple devices running iOS 13 or later or macOS 10.15 or later, users can be confident that their conversations are secure and private when stored in iCloud backups as well.
iCloud Security For Third-Party Applications
Security Measures For Third-Party Apps Accessing iCloud Data
When it comes to third-party apps accessing iCloud data, security is of utmost importance. Apple takes several measures to ensure that the user’s personal information stays safe and secure. When granting access to third-party apps, users are required to give permission for specific types of data access such as contacts or photos. Users can also revoke this access at any time if they feel that their privacy is being compromised. Additionally, Apple regularly reviews and audits third-party apps to make sure they comply with strict security requirements.
User Control Over Third-Party Access To iCloud Data
Apple has also implemented user control over third-party access to iCloud data. This means that users have the ability to choose which third-party apps they allow to access their iCloud data, such as contacts or calendar events. Users can manage this through their Apple ID account settings.
iCloud VS. Other Cloud Storage Platforms
iCloud provides several security features that set it apart from other cloud storage platforms. Unlike many other cloud services, iCloud uses end-to-end encryption to protect user data both in transit and at rest.
In comparison with Google Drive or Dropbox, which also offer great value for cloud storage solutions but are known to have had some security issues in the past. Google Drive stores its users’ data on servers located around the world, which may be subject to different legal requirements regarding data privacy than those of a user’s home country. Meanwhile, Dropbox has faced criticism for storing plaintext passwords and for sharing some users’ files unintentionally.
FAQs
What Is End-To-End Encryption?
End-to-end encryption works by encrypting data at both ends of a conversation, meaning that any third party trying to intercept or access the information will be unable to do so. Apple’s iCloud storage service offers end-to-end encryption for certain features such as iMessage, FaceTime, and HomeKit. This means that all conversations and data exchanged through these services are encrypted from one device to another, providing an added layer of security against unauthorized access or interception. However, it is important to note that not all iCloud data is encrypted with end-to-end encryption.
Is My Icloud Data Safe?
iCloud data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. This means that all information transferred to and from iCloud servers is protected with advanced encryption algorithms. iCloud uses several security features to ensure the safety of its users’ data. For instance, all data stored on iCloud servers are encrypted using AES 128-bit encryption technology. This ensures that your files are unreadable without your unique encryption key. Additionally, Apple uses two-factor authentication as an added layer of protection for user accounts.
How Do I Protect My iCloud Account?
To protect your iCloud account, enable two-factor authentication (2FA). This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second factor (such as a code sent via SMS) in addition to your password when logging into your account from a new device. Use strong, unique passwords for all of your online accounts (including iCloud) and avoid using public Wi-Fi networks whenever possible.
Is It Safe To Use Third-Party Apps With iCloud?
Yes, but with some caveats. Apple has strict security measures in place to ensure the safety and privacy of user data. Third-party apps must adhere to Apple’s guidelines for data sharing and protection. These guidelines include using encryption when transferring data between the app and iCloud servers, storing the minimum amount of information necessary, and obtaining user consent before accessing or storing any personal information.
Conclusion
IiCloud data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. This means that all information stored on Apple’s servers is protected from prying eyes, including hackers and government agencies. Apple uses a combination of encryption methods to ensure that user data remains private and secure.
One of the most important security features of iCloud is two-factor authentication. This requires users to input a code sent to their trusted device in addition to their password when logging into iCloud or making purchases from Apple’s online store. This extra layer of security helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
