Introduction
Cellular data refers to the communication services provided by mobile network operators, such as voice and data transmission. Essentially, cellular data is a way for your smartphone or tablet to connect to the internet when Wi-Fi isn’t available. It allows you to access websites, send messages, make calls and use apps on the go using a cellular network.
Unlike WiFi connections that rely on fixed hotspots or routers, cellular networks are made up of towers that transmit signals over long distances. These signals are then picked up by your device’s antenna and converted into digital information.
With the widespread use of smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices, cellular networks have become a common means of transmitting sensitive data such as personal information, banking details, and confidential business information. However, this increased reliance on cellular networks has also led to various security concerns.
Hackers can intercept wireless signals transmitted between devices and cell towers, potentially accessing sensitive information without any warning to either party. Another concern is that smartphones are highly vulnerable to malware attacks due to their open-source nature; attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in operating systems or through third-party apps.
Understanding Cellular Data Security
Types Of Cellular Data Security Threats

The three major types of cellular data threats include physical security threats, network-based security threats, and application-level security threats.
Physical Security Threats
Physical security threats to cellular data involve the physical access of mobile devices, which can occur through theft or loss. When such an event occurs, any unauthorized person who has access to the device can gain entry into sensitive information and use it for malicious purposes.
Network-based Security Threats
Network-based security threats in cellular data refer to attacks that target network components like routers, switches or firewalls. These attacks are designed to exploit vulnerabilities within these components and gain unauthorized access to cell phone networks.
Application-level Security Threats)
Application-level security threats are another type of cellular data threat that targets applications installed on mobile devices. Such attacks can exploit application vulnerabilities and steal data, intercept communications between processes or inject malicious code into running processes.
Understanding Encryption
Encryption is converting plain text into code to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption uses complex algorithms to transform data into an unreadable format, which can only be deciphered by the intended recipient with a decryption key.
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption involves using the same key to encrypt and decrypt data, making it faster but less secure since anyone who gets hold of the key could access the encrypted data. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption uses two different keys – private and public keys – to encrypt and decrypt data, respectively. This makes it more secure than symmetric encryption but slower in comparison.
Importance Of Encryption In Cellular Data Security
Encryption technology has improved significantly, with major advancements such as 4G and 5G networks providing enhanced security features. With 4G, all data transmitted between devices and cell towers are encrypted using advanced encryption standards (AES). Similarly, with 5G networks, end-to-end encryption ensures that no one except the intended recipient can access the transmitted data.
Cellular Data Security Measures
Security measures implemented by cellular service providers are as follows:
Authentication
One of the most common methods is two-factor authentication (2FA), which requires users to provide both a password and a unique code sent to their device for access. This method adds an extra layer of security and makes it harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
Another popular authentication method is biometric authentication, which uses your unique physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition as a secure login credential. This method has proven more secure than traditional passwords because they cannot be guessed or replicated easily.
Authorization
Authorization involves verifying and validating user credentials before granting access to sensitive information. In cellular data, authorization is critical in safeguarding against unauthorized access, particularly for confidential business or personal data.
The authorization ensures that only authorized users can access specific mobile applications or services. This process typically involves authentication mechanisms like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication protocols. Administrators can define authorization policies to specify which users can access which resources under what conditions.
Encryption
Cellular service providers use various encryption methods to protect client information while it’s being transmitted over their networks. This ensures that even if an unauthorized individual or entity intercepts the data, they cannot decipher it.
Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation refers to the ability of a system to prove that a particular user carried out an action or transaction and cannot deny it later on. In other words, non-repudiation ensures no dispute over the authenticity of data and transactions.
Non-repudiation can be implemented in several ways, such as digital signatures, timestamps, and audit trails. These measures ensure that every transaction or communication made by users is recorded and kept secure so that it cannot be altered or deleted. This process helps to prevent fraud and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Security Measures Implemented By Device Manufacturers
Biometric Authentication

Biometric authentication provides an extra layer of security for cellular data access. Many smartphones now have built-in biometric sensors allowing easy and fast login without sacrificing security. Some financial institutions also use biometric authentication to verify transactions made through mobile banking apps.
Device Lock Screens

Device lock screens provide an added layer of protection to your cellular data. They act as a barrier between unauthorized access and the sensitive information stored on your phone. Lock screens can be set up with various options such as pattern, pin, or biometric authentication (fingerprint/face recognition). The type of lock screen that you choose depends on your device’s capabilities and personal preferences.
It is crucial to note that while device lock screens are essential in protecting your data, they are not foolproof. Hackers have bypassed these security measures by using specialized software or hardware tools.
Encryption
Most modern smartphones have encryption software, but it’s important to ensure you’re using strong passwords and keeping them safe.
Risks of Cellular Data Security
Examples Of Security Breaches In Cellular Networks
The SS7 Protocol Vulnerability:
The Signaling System 7 (SS7) protocol is used to exchange information between different telecommunication networks, but it has a significant flaw that allows hackers to intercept and redirect calls and text messages. This means someone can eavesdrop on your conversations or steal private information by exploiting this weakness.
Sim Swapping:
This occurs when a hacker convinces a cell phone carrier to transfer someone’s phone number to their SIM card. Once they can access the victim’s phone number, they can reset passwords for various accounts, such as banking or social media accounts, since many companies use two-factor authentication via text message.
IMSI Catchers
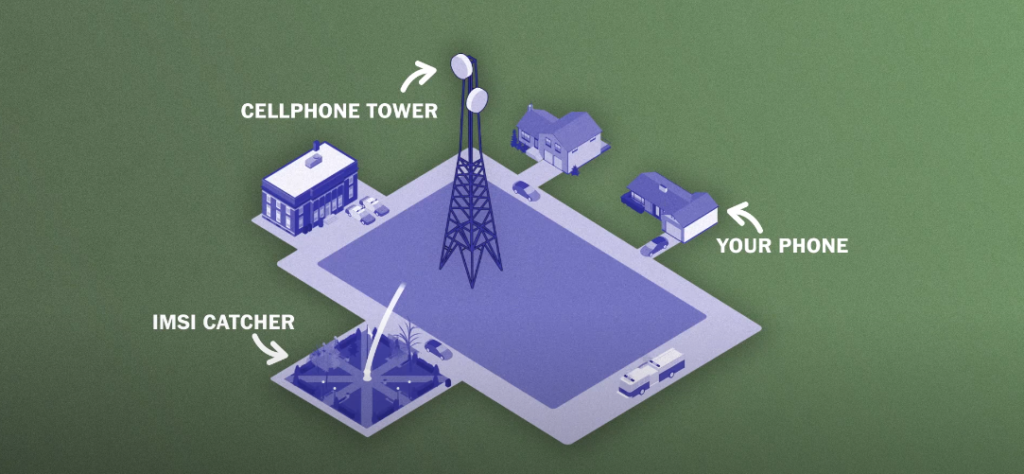
There have been incidents where fake cell towers called IMSI catchers are set up by hackers who pose as legitimate carriers. These devices collect data about nearby phones and can even intercept calls and texts from specific targets. Anyone connecting to one of these fake towers risks having their sensitive information compromised until it is too late.
The Consequences Of Security Breaches In Cellular Networks
The consequences of these breaches can be devastating for both individuals and businesses. Personal information such as credit card details, passwords, and sensitive business data can be compromised. Malicious software installed on infected devices can also cause significant damage to the network infrastructure itself.
The Financial Implications Of Data Breaches
The direct costs associated with a data breach can be astronomical. Businesses may face fines and legal fees for non-compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Additionally, companies may need to spend money on credit monitoring services for affected individuals, forensic investigations, public relations efforts to rebuild trust, and cybersecurity improvements to prevent future breaches.
Risks Of Not Securing Cellular Data
One of the most common risks is data theft, where hackers can access personal and sensitive information stored on mobile devices. This breach can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or even blackmail.
Another risk is network vulnerability, which occurs when a device connects to an unsecured public Wi-Fi network or other types of unencrypted networks. Hackers can easily intercept communication between the device and the network, allowing them to eavesdrop on conversations or steal confidential information.
Securing Cellular Data
This technology allows you to create a secure and encrypted connection over an unsecured network such as the internet. VPNs protect your online activities from prying eyes and keep your data secure. When you connect to a VPN, all your online traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel, making it impossible for anyone to intercept or steal your data.
Use Of VPNs
One of the most significant benefits of using a VPN is that it provides anonymity when browsing the internet. By hiding your IP address, no one can track what you’re doing online. This makes it an excellent tool for people who want to access websites or content that may be restricted in their region due to geo-blocking or censorship laws.
Avoiding Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks
Hackers can easily access unsecured networks and intercept data transmitted between devices and the internet. This puts sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and other personal data at risk of theft.
Updating Software Regularly
Regular updates include important patches that fix vulnerabilities and bugs and improve your device’s overall performance. Developers introduce enhanced security features to protect against cyber threats with each new update.
Hackers are constantly looking for ways to exploit weaknesses in software and gain access to sensitive information. By delaying software updates, you’re leaving your device vulnerable to attacks from hackers who exploit these loopholes. Outdated software can also make it easier for malware and viruses to infiltrate your system, putting your cellular data at risk.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an extra layer of security that requires users to provide two types of identification before accessing their accounts. It is a must-have security feature for online transactions, especially on mobile devices. The first factor is usually a password or PIN; the second factor could be a fingerprint scan or one-time code sent to the user’s phone via SMS or an authenticator app.
Being Mindful Of The Apps Downloaded
Ensure that the apps you download are secure by only downloading from trusted sources such as Apple’s App Store or Google Play Store. Apps often ask for access to features such as your camera, microphone, location services, and more. It’s important to understand why an app needs access to these features and whether or not granting permission could potentially compromise your cellular data security.
Using Strong Passwords And Passcodes
A strong password or passcode is difficult to guess and contains a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. You should avoid using common words or phrases and personal information such as names, birthdays, or phone numbers.
Legal and Ethical Issues
Laws And Regulations On Cellular Data Security
In response to this growing concern, governments worldwide have enacted laws and regulations to protect consumers’ privacy and secure their data.
One such law is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. This regulation requires companies to obtain explicit user consent before collecting or processing their data and implement measures to protect that data from unauthorized access or theft. Failure to comply with GDPR can result in hefty fines for companies.
In the United States, various federal and state laws govern cellular data security, including the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), which prohibits unauthorized access to computer systems, including mobile devices. Additionally, states like California have enacted privacy laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which gives consumers more control over how their personal information is collected and used by businesses operating within the state.
The Role Of Governments And Businesses In Ensuring Cellular Data Security
Governments are responsible for establishing regulations and laws protecting citizens’ personal information. They also work to ensure that companies are held accountable for any security breaches or violations of privacy rights. On the other hand, businesses must proactively safeguard their customers’ data by implementing robust security measures.
Governments can help by creating standards for secure data transmission protocols. For example, they could mandate end-to-end encryption for all cellular communications. Additionally, governments could require companies to provide regular updates about their cybersecurity practices and undergo independent audits to ensure compliance with these standards.
Businesses can adopt best practices such as using multi-factor authentication, encrypting sensitive data, monitoring network activity in real time and having a response plan ready in case of a breach. Moreover, they should educate their employees about the importance of mobile device safety and encourage them to follow strong password policies.
Challenges To Cellular Data Security
Emerging trends and technologies that pose a risk to cellular data security 5G networks. While 5G technology offers faster speeds and lower latency, it also introduces new vulnerabilities. For instance, the use of virtualized and cloud-based network functions means that there are more attack surfaces for cybercriminals to exploit. Also, with more devices connected to the network, there is a higher risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Artificial intelligence (AI). AI-powered attacks can be incredibly sophisticated and difficult to detect. Hackers can use machine learning algorithms to identify vulnerabilities in cellular networks or create convincing phishing attacks that trick users into revealing sensitive information. Additionally, AI can automate attacks on mobile devices by exploiting weaknesses in software or hardware.
The Future Of Cellular Data Security
The Outlook For Cellular Data Security
The outlook for cellular data security is uncertain. The proliferation of mobile devices and the increasing dependence on them for personal and professional use exposes users to a growing range of threats. While cell phone manufacturers have made strides in enhancing device security through features like biometric authentication and encryption, these measures alone may not be enough to safeguard against evolving cyber-attacks.
In addition to traditional methods such as phishing scams and malware, hackers target mobile devices through new tactics like rogue Wi-Fi networks and fake apps. These sophisticated techniques can trick users into divulging sensitive information or downloading malicious software that gives attackers access to their devices.
The Role Of Cellular Data Security In The Evolution Of The Digital Economy
Our personal information must remain private and secure as we rely on our mobile devices for everything from banking to social media. Cell phone carriers are responsible for protecting their customers’ data, but hackers and cybercriminals constantly look for ways to exploit vulnerabilities in cellular networks.
In recent years, several high-profile cases of data breaches and thefts have exposed sensitive information like credit card numbers and social security numbers. This has raised concerns about the security of mobile devices and the need for stronger protections. With technologies like 5G on the horizon, cellular networks must be equipped with advanced encryption tools and strong authentication protocols to protect user privacy.
As businesses increasingly rely on mobile technology to connect with their customers, they must also safeguard the data and customer information they collect through mobile apps or other digital channels. Companies must prioritize cybersecurity measures such as regular vulnerability testing, employee training programs on best practices for handling sensitive data, and investing in advanced threat detection tools that can identify potential threats before an attack occurs.
FAQs
Is Cellular Data Encrypted?
In general, cellular data is encrypted at some level as it travels from your device to the nearest cell tower and through various other points in the network before reaching its final destination.
However, the level of encryption may vary depending on your carrier and location. For example, carriers in countries with stricter regulations on privacy and security may have stronger encryption methods than those with more flexible policies.
What Are The Legal And Ethical Issues Surrounding Cellular Data Security?
One of the primary concerns is the potential for unauthorized access to personal information, such as financial and medical data, through mobile devices. Using biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition, has raised questions about privacy and consent.
Another issue is the responsibility of companies that collect and store user data. Companies must comply with various regulations to protect consumer privacy, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in legal consequences for companies mishandling user data.
What Are The Challenges To Cellular Data Security?
One of the biggest challenges to cellular data security is the prevalence of public Wi-Fi networks. When using public Wi-Fi, it’s easy for hackers to intercept cellular data transmissions, making it possible to steal sensitive information such as credit card numbers and login credentials. Another challenge is the increased use of personal devices for work purposes. Many employees can access corporate data on their smartphones or tablets, which can be vulnerable to hacking if not properly secured.
Another challenge facing cellular data security is the increasing number of mobile apps that collect and transmit user data without proper authorization or protection. Many users are unaware of the risks of sharing their personal information with third-party apps, leaving them vulnerable to attacks. In addition, many mobile devices are not updated regularly with security patches and software updates, leaving them open to known vulnerabilities.
How Can I Ensure My Cellular Data Is Secure?
When using a public Wi-Fi network, such as in a coffee shop or airport, a VPN can be particularly beneficial in protecting sensitive information. Another method for securing cellular data is through the use of two-factor authentication. This involves providing two forms of identification when logging into an account or accessing certain information. For example, you may need to enter a password and provide a fingerprint scan or answer security questions. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
What Are The Consequences Of Not Securing Cellular Data?
Hackers can intercept and access sensitive information such as passwords, banking details, and personal data. This can lead to identity theft or financial fraud, which can have long-lasting repercussions for individuals.
Moreover, not securing cellular data leaves users vulnerable to malware attacks. Malware is software designed to cause damage or disrupt operations on a device. It can be downloaded onto a device through phishing emails, malicious websites or apps, and insecure networks. Once on a device, malware can potentially steal sensitive information or render the device unusable.
Conclusion
Cellular data security is a crucial aspect that cannot be ignored. While several risks are associated with using cellular networks, it is possible to protect your data by following the best practices outlined in this guide. Using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication on all your accounts is essential.
Also, third-party applications can help secure your data and protect you from potential threats. It’s important to keep up-to-date with the latest security updates and patches for your device’s operating system and any apps you use.
