Using flash drives securely involves encrypting your drive with a strong password, regularly updating your antivirus software, and employing a write-protect switch when necessary. After using the drive on a shared computer, scan it for malware, and always avoid public computers if possible. Backing up your data, using strong and unique passwords, and staying informed about security threats are essential best practices.
What Is a USB Flash Drive?
A USB flash drive, often simply called a “flash drive,” is a small, portable data storage device that utilizes flash memory technology to store and transfer data between computers, laptops, and other compatible devices. These compact and versatile gadgets have become ubiquitous in the digital age, offering a convenient and reliable means of carrying and sharing data.
Uses of USB Flash Drives:

1. Data Storage and Backup
Users often store important files, documents, photos, and videos on flash drives as a portable backup or for easy access on different devices.
Flash drives are ideal for transferring files between computers that may not be connected through a network, such as in business meetings, classrooms, or when sharing files with friends and colleagues.
3. Bootable Drives
Flash drives can be made bootable, allowing users to run operating systems or diagnostic tools directly from the drive. This is useful for troubleshooting and system maintenance.
4. Portable Applications
Some users install portable applications on flash drives, enabling them to run software from any computer without installation. This is particularly handy for productivity tools and utilities.
5. Presentation and Media
Professionals often use flash drives to store and carry presentations, videos, and multimedia content for meetings, conferences, and entertainment purposes.
Understanding the Risks:
1. Data Theft
Data theft is one of the most significant concerns when using flash drives. If you lose your drive or it falls into the wrong hands, sensitive data can be easily accessed and misused.
2. Malware and Viruses
When connected to infected computers, flash drives can become carriers of malware and viruses. This can lead to compromised data and system damage.
3. Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access can occur if someone gains physical access to your flash drive. They may view, copy, or manipulate your files without adequate protection.
Using Flash Drives Securely:
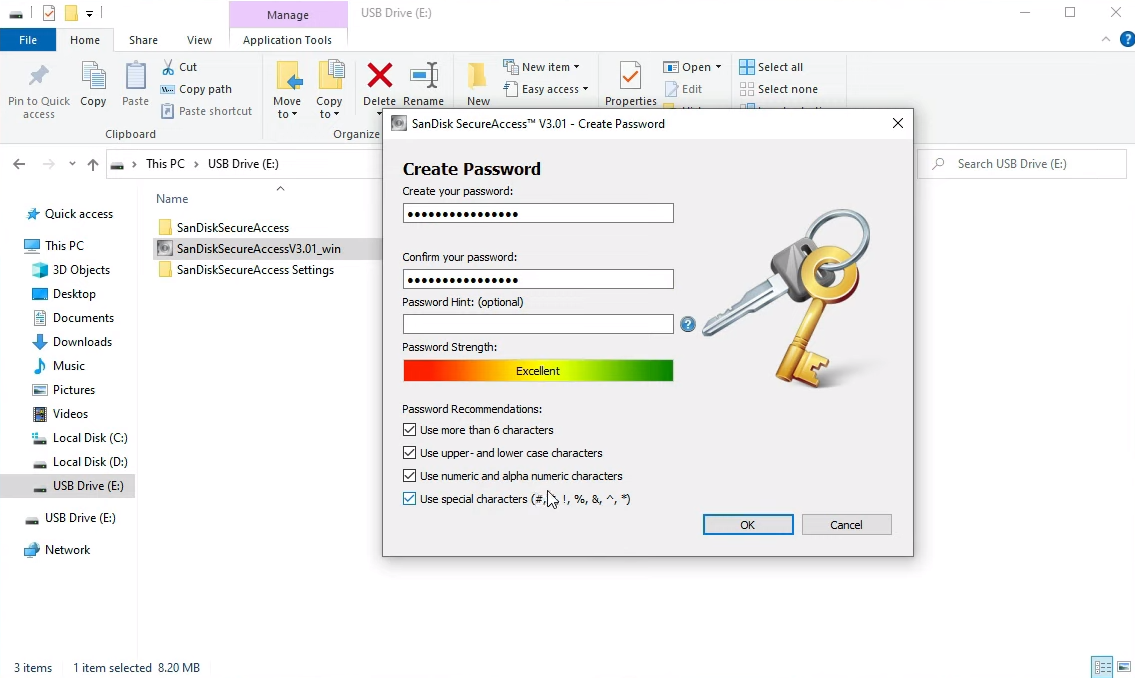
1. Encrypt Your Flash Drive: Your First Line of Defense
Most flash drives have built-in encryption tools, while others can be easily encrypted using third-party software. The fundamental idea behind encryption is to transform your data into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key or password. Here’s how to go about it:
- Password Protection: Always set a strong, unique password for your flash drive. This password is your initial defense, as it prevents unauthorized access. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or those tied to personal information.
- Built-in Encryption Tools: Many flash drives come with their encryption software. These tools often guide you through setting up encryption and password protection. Ensure you activate and configure them according to your security needs.
- Third-Party Encryption Software: If your flash drive doesn’t have built-in encryption features, you can turn to third-party encryption software like VeraCrypt or BitLocker (for Windows). These programs allow you to create secure, encrypted partitions on your flash drive.
2. Regularly Update Antivirus Software: Keeping Threats at Bay
Before plugging your flash drive into any computer, it’s imperative to ensure that your antivirus software is installed and up-to-date. If you insert them into an infected computer, malware and viruses can easily find their way onto your flash drive. Regularly updating your antivirus software helps in the following ways:
- Threat Detection: Updated antivirus programs are better equipped to identify and neutralize potential threats lurking on your flash drive. They can promptly quarantine or delete malicious files, preventing them from causing harm.
- Database Updates: Antivirus software relies on databases of known threats. Frequent updates ensure that your software has information on the latest malware and viruses, enhancing its ability to protect your flash drive and computer.
3. Use a Write-Protect Switch: Preserving Data Integrity
Certain flash drives are equipped with a valuable feature: the write-protect switch. This switch locks your flash drive, preventing any data from being written or modified. It’s a simple yet effective method to safeguard your data, especially when using the drive for read-only purposes like sharing documents.
- Activation: Locate the write-protect switch on your flash drive. Typically, it’s a small physical switch or slider. Move it to the “locked” or “write-protect” position to enable this feature.
- Read-Only Use: When the write-protect switch is activated, you can confidently use your flash drive to share documents or any data you don’t want to be altered accidentally.
4. Scan for Malware After Use: A Post-Use Safety Measure
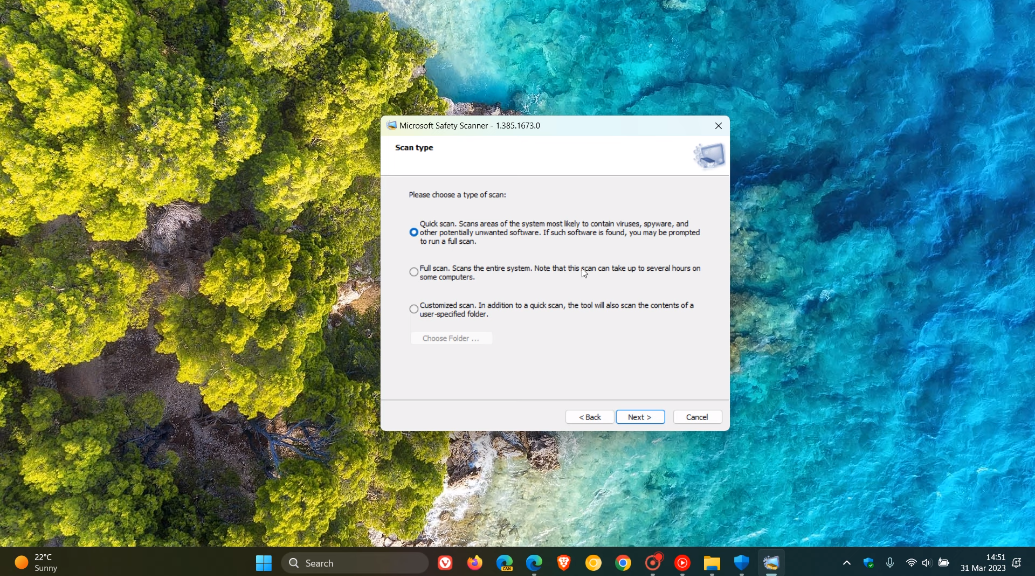
After using your flash drive on a public or shared computer, it’s prudent to run a malware scan both on the drive itself and your computer. This step can help detect and remove any potential threats that may have been picked up during use.
- On the Public Computer: Run a thorough malware scan using the computer’s antivirus software. This action ensures that no malware from the computer has infected your flash drive.
- On Your Computer: Run another malware scan once you’ve plugged your flash drive into your trusted computer. This double-check ensures that your system remains clean and no lingering threats from the flash drive are left behind.
5. Avoid Public Computers: Minimizing Risk
Whenever possible, avoid using public or untrusted computers with your flash drive. These computers may lack adequate security measures, increasing the data compromise risk. Instead, opt for your personal or trusted devices. If you must use a public computer, consider the following precautions:
- Limited Use: Only use public computers for tasks that don’t involve sensitive data or use a dedicated, disposable flash drive.
- Use a Guest Account: If available, use a guest or temporary account on the public computer to minimize the risk of exposing your data.
- Log Out and Disconnect: After using your flash drive, log out of any accounts and safely eject the drive to prevent any data from being left behind.
Best Practices To Secure Your USB Flash Drive
Regularly backing up your data is a fundamental practice in data security. You’ll have a copy of your essential information if your flash drive is compromised or lost.
- Cloud Storage: Use secure cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or iCloud for seamless and automated backups.
- Physical Backup: Maintain a physical backup of your data on another flash drive or an external hard drive kept in a secure location.
In addition to password-protecting your flash drive, apply strong, complex, and unique passwords to all your accounts and devices. A strong password should include upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters.
3. Educate Yourself:
Staying informed about the latest security threats and best practices is crucial. Regularly update your understanding of cybersecurity and privacy measures. Follow technology news and consider attending online courses or seminars to enhance your knowledge.
Conclusion:
Using flash drives without the risk of data leaks requires a combination of smart practices and security measures. By encrypting your drive, regularly updating antivirus software, and following best practices for data security, you can enjoy the convenience of flash drives without compromising your sensitive information.
FAQs
1. Can I use any flash drive for secure data storage?
While many flash drives offer security features, it’s crucial to choose one from a reputable manufacturer and ensure it supports encryption and password protection.
2. What should I do if I lose my encrypted flash drive?
If you lose an encrypted flash drive, immediately change the password for the encrypted data and monitor your accounts and personal information for any unusual activity.
3. Are there any free antivirus programs for flash drives?
Yes, some antivirus programs offer free versions with basic features that can help protect your flash drive from malware. However, for comprehensive protection, consider investing in a premium antivirus solution.
4. Can I recover data from a write-protected flash drive?
Data recovery from a write-protected flash drive is challenging. It’s best to create backups of your data to avoid data loss.
5. Are there any alternative methods for secure data storage?
You can use secure cloud storage, external hard drives, and encrypted email services besides flash drives for secure data storage and sharing. Each method has advantages and disadvantages, so choose the one that best fits your needs and security requirements.
