Changing the Windows administrator password is essential for enhancing system security. This practice safeguards your computer or network from unauthorized access, averts potential compromises, and complies with security standards. However, it’s not without risks, including the possibility of locking yourself out or disrupting services. You can use the Control Panel or Command Prompt to change the password, depending on your access level. Always remember to communicate changes in shared environments, update applications, and services, and maintain robust backup and recovery mechanisms.
Reasons to Change the Windows Admin Password:
1. Security Enhancement
Enhancing security is perhaps the most compelling reason to regularly change the Windows admin password. Passwords serve as the first line of defense against unauthorized access. By changing your admin password periodically, you reduce the risk of someone gaining unauthorized access to your system.
2. Password Compromise
If you suspect that your admin password has been compromised or if you’ve shared it with someone you no longer trust, changing it immediately is essential to prevent unauthorized access to your system. Password compromise can occur through various means, such as phishing attacks or unintentional disclosure.
3. Employee Departure
When an employee with administrative privileges leaves the company, it’s crucial to change the admin password in a business or organizational setting. This ensures that former employees can no longer access sensitive data or system settings, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized actions.
4. Compliance and Best Practices
Many security policies and compliance standards mandate regular password changes as part of good security practices. This includes regulations such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR. Compliance with these standards is essential for organizations to protect sensitive data and maintain trust.
5. Password Aging Policies
Some organizations or network administrators implement password-aging policies that require users, including administrators, to change their passwords periodically. These policies help ensure that passwords remain secure over time and are less susceptible to brute force or dictionary attacks.
6. Password Strength Improvement
If you’ve been using a weak or easily guessable admin password, changing it to a stronger, more complex one can significantly improve your system’s security. A strong password typically includes letters, numbers, and special characters.
7. Forgotten Password
In some cases, users may forget their admin password and find themselves locked out of their computer. When this happens, changing the password using recovery options or tools becomes necessary to regain access.
Risks in Changing Windows Admin Password
1. Lockout
Choosing a complex password is essential, but selecting one you can remember is equally important. If you forget the new password immediately after changing it, you could lock yourself out of your computer. Make use of password management tools if needed to store complex passwords securely.
2. Access to Encrypted Files
If you use features like BitLocker to encrypt files or the Encrypting File System (EFS) in Windows, changing the admin password could result in losing access to encrypted files if you don’t have the necessary recovery keys. Ensure you have proper backup and recovery mechanisms in place.
3. Service Interruption
Changing the admin password may disrupt services and scheduled tasks that rely on the old password for authentication. To prevent service interruptions, updating any services, scheduled tasks, or scripts that use the admin credentials with the new password is crucial.
4. Shared Resources
Changing the password might affect access to those resources if the admin account is used to access shared resources on a network. You may need to update the stored credentials on other devices or systems that rely on the old password.
5. Applications and Services
Some applications or services may store the admin password internally for various purposes. Changing the password may require reconfiguring these applications or services to use the new credentials. Ensure you identify and update these configurations as needed.
6. Backup and Recovery
Before changing the admin password, ensure you have appropriate backup and recovery mechanisms, especially if you’re responsible for critical systems. This can help you recover access if something goes wrong during the password change process.
How to Change Windows Admin Password?
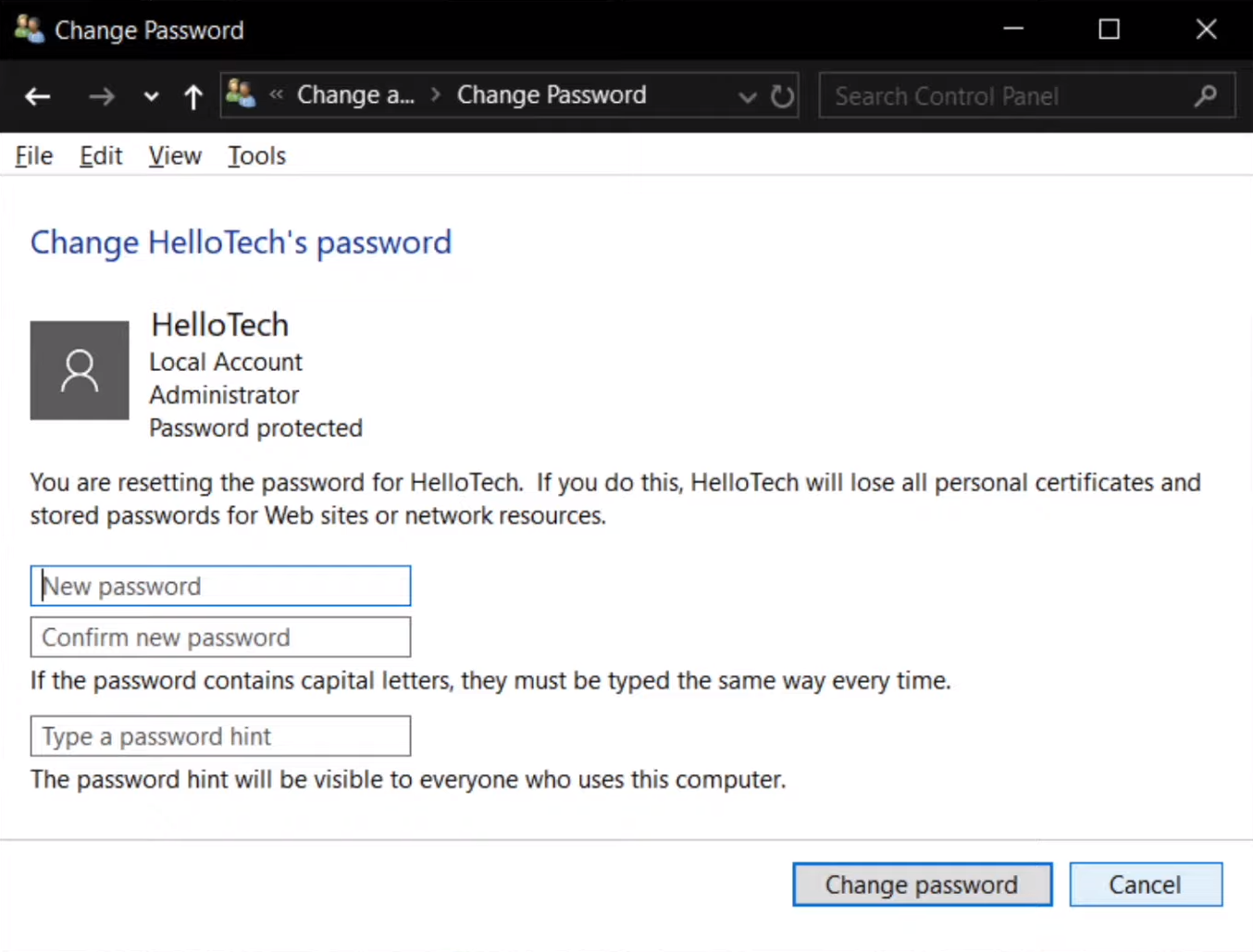
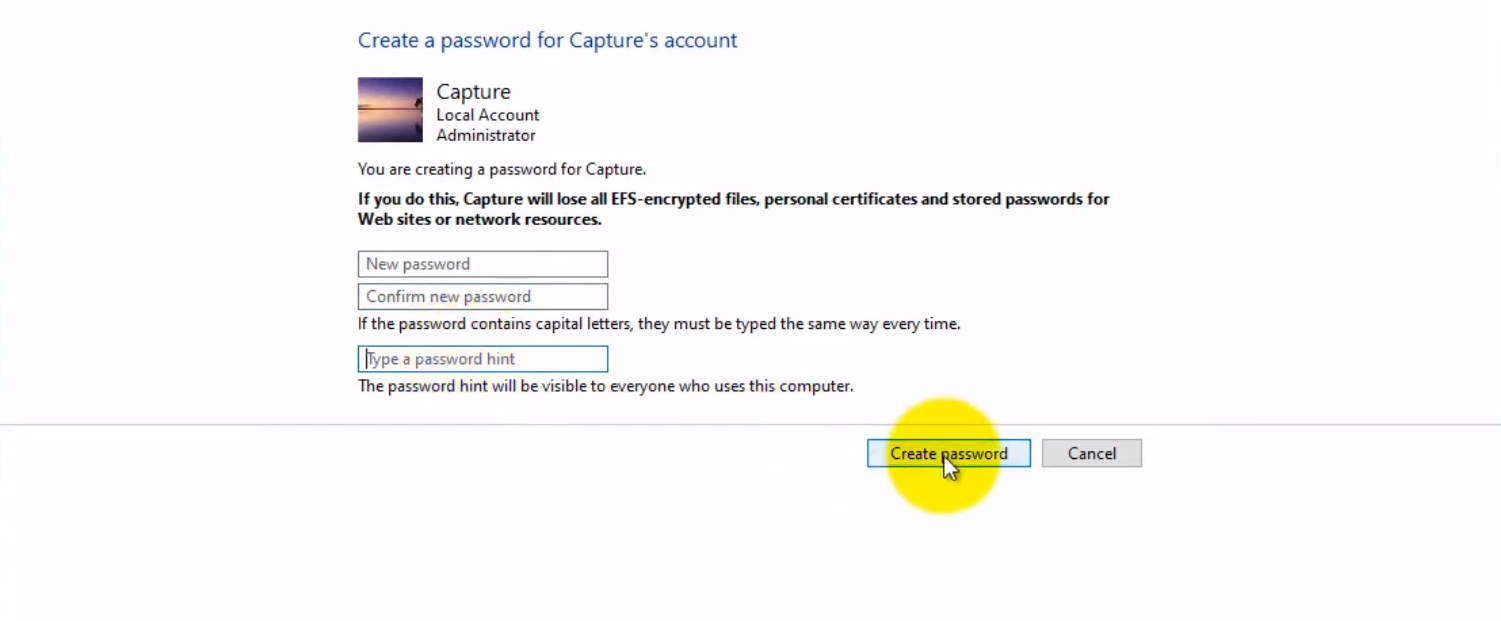
Method 1: Change Password via Control Panel (Windows 10/8/7)
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete: Press these keys together on the Windows login screen.
- Select “Change a password”: On Windows 10 and 8, you’ll see this option directly. On Windows 7, you might need to choose “Lock this computer,” and then you’ll see the option.
- Enter your current password: You need to provide your current administrator password.
- Type the new password: Create a new password. Make sure it’s a strong and secure password with a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Reenter the new password: Confirm the new password by entering it again.
- Add a password hint (optional): This step can be helpful if you forget your password. A hint can give you a clue to remember it.
- Click “Change password.”: Save your new password.
- Log in with the new password: Log in using the new credentials after successfully changing the password.
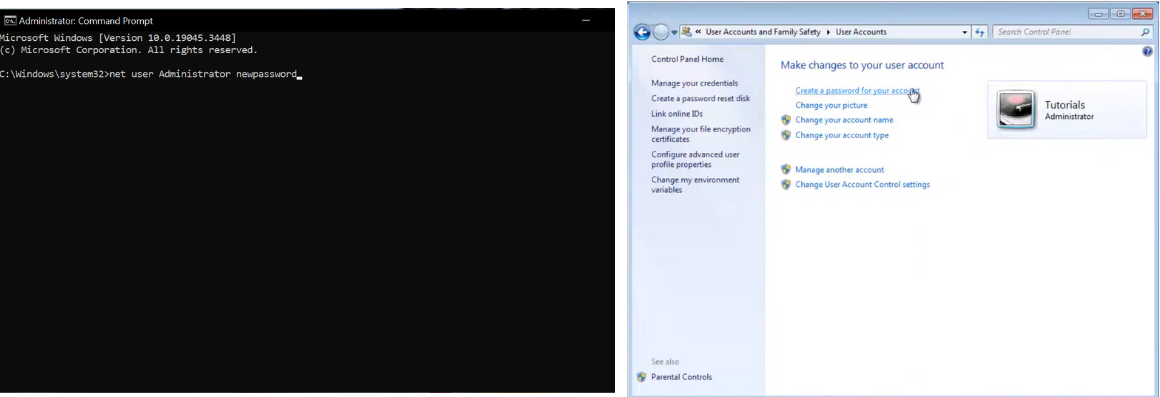
Method 2: Change Password via Command Prompt
If you have administrative access, you can also change the administrator password using Command Prompt:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Press Win + X and choose “Windows Terminal (Admin)” on Windows 10.
- On Windows 8 or 7, search for “cmd” in the Start menu, right-click on “Command Prompt,” and select “Run as administrator.”
- Type the command: Replace “new password” with your desired password.
SQL
net user Administrator newpassword
If you want to change the password for a different user, replace “Administrator” with the username.
- Press Enter: The system will confirm that the command has been completed successfully.
- Log in with the new password: Log in using the new credentials after changing the password.
FAQs:
What if I forget my Windows admin password?
If you forget your admin password, you can use recovery options or tools to reset or change it. Ensure you have these recovery methods set up in advance.
What are the risks of changing the Windows admin password?
Risks include locking yourself out of your computer if you forget the new password, potential loss of access to encrypted files if recovery keys are unavailable, service disruptions, and impacts on shared resources and applications. Proper planning and precautions can mitigate these risks.
Can I use the same password for multiple accounts, including the admin account?
It’s not recommended to use the same password for multiple accounts, especially if one of them is the admin account. Using unique, strong passwords for each account improves security.
Do I need administrative privileges to change the admin password?
Yes, you need administrative privileges to change the admin password. Administrative access is required to modify system settings.
What should I do if changing the admin password disrupts services or applications?
If changing the admin password disrupts services or applications, update the credentials within those services or applications to use the new password. Properly plan and communicate any changes to minimize disruptions.
What if I have multiple administrator accounts on my Windows system?
If you have multiple administrator accounts on your Windows system, you can change the password for each account individually, following the same steps outlined in the guide.
Conclusion
Changing the Windows administrator password is fundamental to maintaining the security and integrity of your system or network. By understanding the reasons for changing the password and potential risks and following the provided step-by-step instructions, you can effectively manage your admin password and reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Remember to keep your new password secure and unique, and only perform this security-sensitive action if you have the necessary permissions and need to do so.
