Introduction
Definition Of Cookies

Cookies are small files created by websites that store user data such as login credentials, website preferences, and shopping cart items. They are essentially a way for websites to recognize returning visitors and offer personalized experiences. While cookies can be useful in improving the browsing experience, they can also pose a risk to data security.
Disabling cookies on web browsers can enhance data security by preventing third-party tracking and reducing the risk of malware attacks. Third-party cookies are used by advertisers to collect user information across multiple websites, which can lead to invasive targeted advertising or even identity theft. Additionally, some cyber criminals use cookies as a mechanism for delivering malware onto users’ devices.
Importance Of Cookies For Websites And Online Businesses

Disabling cookies may sound like a great way to protect your data privacy, but it can also cause some negative impacts on your online experience. Cookies are text files that contain small pieces of data sent from a website to the user’s computer or device. Without them, websites cannot remember login details or user preferences. Disabling cookies can hinder website functionalities and make the user experience less efficient.
The Issue Of Data Privacy And Security
While cookies have some benefits such as personalizing web experiences, they can also pose a threat to data privacy. Hackers or malicious third parties can exploit vulnerabilities in cookies to access sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and credit card details. They could also use tracking cookies to monitor user activity across multiple sites without their consent. By disabling cookies, users reduce the risk of being tracked or having their private information compromised.
How Cookies Can Be Used for Malicious Purposes?
Cookies can be used by cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information stored on your device. When you allow cookies, they are typically designed to store your preferences and login credentials for convenience. However, some websites may use third-party cookies that track your browsing behavior and collect personal data without your consent. This opens the door for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities in the cookie itself or access other parts of your system through the cookie.
Furthermore, cookies are a common tool for phishing attacks and social engineering tactics. Malicious actors can create fake websites that mimic legitimate ones and prompt users to enter their login details or credit card information. The fake website then uses cookies to capture this sensitive data and transmit it back to the attacker’s servers.
How Cookies Can Be Used In Phishing Attacks?
One common type of phishing attack that uses cookies is called “session hijacking.” In this technique, an attacker steals a user’s session cookie and uses it to impersonate them on a legitimate website. With this access, the attacker can perform actions on behalf of the user without their consent or knowledge. For example, they could transfer money from the user’s bank account or send spam emails from their email address.
How Disabling Cookies Can Protect Your Data?
When you disable cookies, websites cannot access the information stored in them. This means that they cannot use it to identify you or track your behavior across other sites. While some websites may not function properly without cookies enabled, most will still work normally with basic functionality.
In addition to protecting your privacy, disabling cookies can also prevent cyberattacks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and session hijacking. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in cookies to gain unauthorized access to user accounts or steal sensitive information.
How Does Disabling Cookies Enhance Data Privacy?
By disabling cookies, users limit the amount of information that websites can collect about them, making it harder for third parties to track their online behavior. Even though cookies are not inherently harmful, they can expose users’ sensitive information if left unchecked. Hackers and other cybercriminals may use cookies to obtain login credentials or other personal details that could be used against them. Disabling cookies does not mean you cannot access a website; it only means that you won’t have personalized content recommendations or targeted advertising.
Limiting Data Collection And Tracking
Disabling cookies can prevent websites from collecting users’ personal information without their consent. It limits the ability of third-party advertisers and trackers from accessing sensitive data such as location, device ID, and IP addresses. This approach is particularly important for individuals who value their privacy or work with sensitive information online.
Reducing The Risk Of Cyber Attacks
Disabling cookies is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of cyber attacks. Another benefit of disabling cookies is that it helps protect against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. XSS attacks occur when a hacker injects malicious code into a website’s cookie file, allowing them to hijack user accounts or steal sensitive data. By disabling cookies, users can prevent XSS attacks by ensuring that their browser does not accept any external scripts from untrusted websites.
Alternatives To Cookies
Alternative Methods For Tracking User Behavior
Device fingerprinting. This involves collecting information about a user’s device, such as its screen size and operating system, to create a unique profile that can be used to track their activity across multiple websites. While not foolproof, it can provide valuable insights into a user’s behavior without relying on cookies.
Contextual targeting. Instead of tracking individual users, this approach focuses on analyzing the content of the page being viewed to deliver relevant ads or content. This method doesn’t require any personal data from users and can offer a more tailored experience without sacrificing privacy.
How to Disable Cookies?
How To Disable Cookies On Popular Browsers
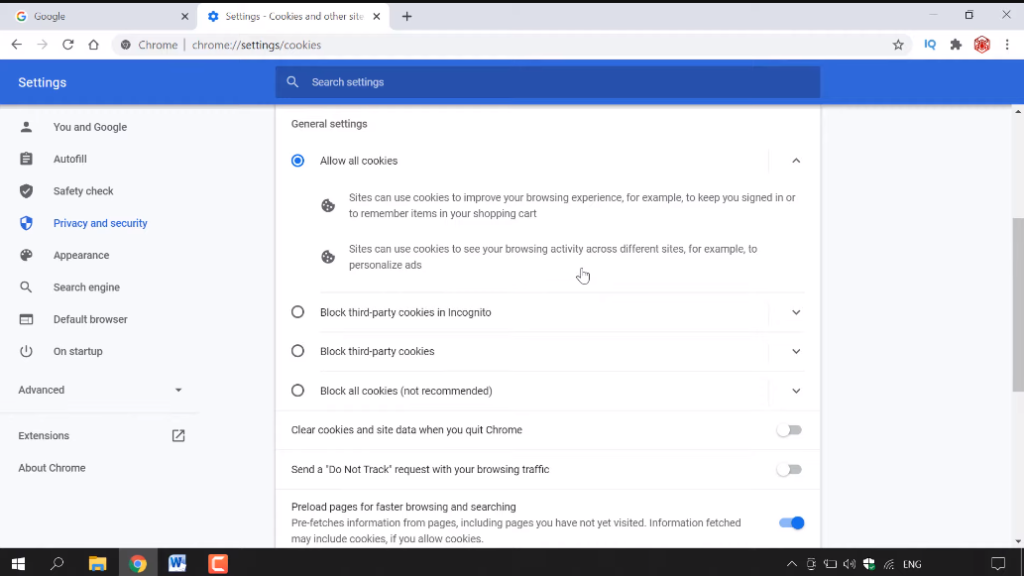
Google Chrome users can disable cookies by going to the Settings menu and clicking on Privacy and Security. From there, they should select Site Settings and then Cookies and site data. Users can either block all third-party cookies or choose which sites they want to block or allow.
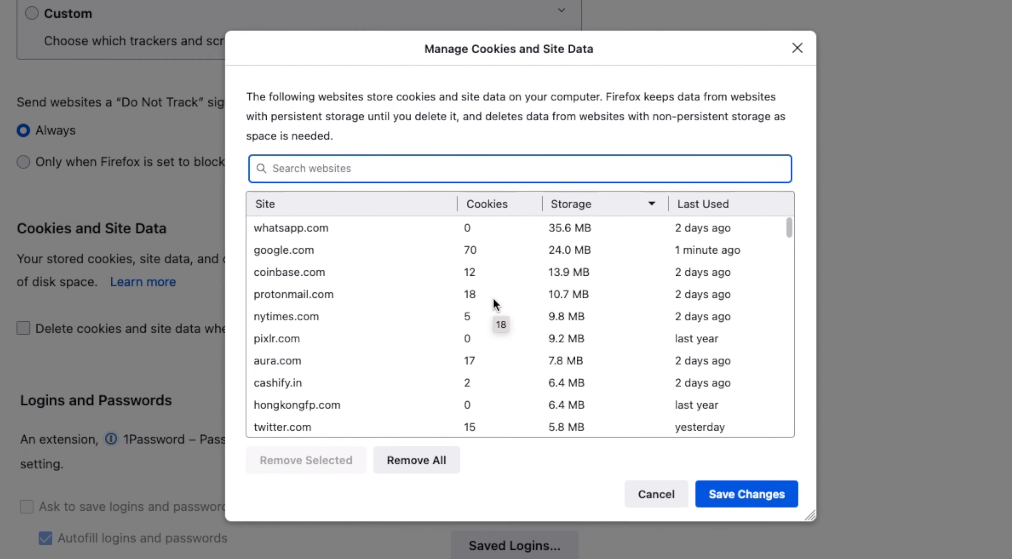
Mozilla Firefox users can disable cookies by going to the Options menu, selecting Privacy & Security, and then navigating to the Cookies and Site Data section. Like Google Chrome users, they have an option of blocking all third-party cookies or only accepting those from trusted sites.
Safari users on Mac devices can disable cookies by opening the Safari browser Preferences window, selecting the Privacy tab followed by the Manage Website Data button where they will be able to see if any website has stored its cookie file in their browser memory – this list could be cleared out from here while also disabling future cookie storage requests from every website visited thereafter through different available options like Block All.
The Impact Of Disabling Cookies On Website Functionality
Disabling cookies can have an impact on website functionality, as users may not be able to access certain features or settings without them. For example, if a user disables cookies, they may not be able to save their login information and preferences, resulting in the need to enter this information every time they visit the site.
Moreover, disabling cookies does not necessarily mean losing all functionalities of a website. Some websites offer alternative ways for users to log in or save preferences without relying on cookies.
How Websites Can Function Without Cookies?
Websites can still function without cookies by using other methods of storing user data. For example, session storage and local storage are two alternatives to cookies that allow websites to store temporary or permanent data on a user’s device. These methods work similarly to cookies but do not track a user’s activity across multiple websites.
Managing Cookie Settings For Individual Websites
Managing cookie settings for individual websites is an effective way of controlling the amount of data that websites collect from you. By managing cookie settings, you have the option to allow or disallow certain types of cookies. For instance, you can block third-party cookies that are known to be used by advertisers to track your online activities.
It’s important to note that disabling all cookies may affect website functionality and prevent you from accessing certain features or services. Therefore, it’s advisable to only disable those that pose a potential threat and leave those necessary for a smooth browsing experience.
The Debate on Cookies and Data Privacy
The Perspectives Of Businesses And Advertisers
From the perspective of businesses, disabling cookies can seem like a daunting task as it may limit their access to customer data. However, with increasing concerns about data privacy and security, many businesses are opting to disable cookies as a proactive measure. By doing so, they can safeguard sensitive information from being misused or exploited by unauthorized third parties. Moreover, disabling cookies can also help businesses build trust with their customers by demonstrating their commitment to protecting personal information.
From the perspective of advertisers, disabling cookies presents both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, advertising platforms heavily rely on cookies to track user behavior and preferences in order to deliver targeted ads. With these tracking tools disabled, advertisers may find it more difficult to reach their intended audience or personalize ad content effectively. However, this shift towards greater data privacy can also encourage advertisers to adopt more ethical and transparent practices that prioritize user consent and choice over intrusive targeting methods. Additionally, advertisers who are able to adapt quickly could benefit from this trend by developing new ways of collecting relevant data without infringing on individual privacy rights.
The Perspectives Of Privacy Advocates And Users
Privacy advocates have long been critical of cookies and their potential to track user behavior online. They argue that cookies enable advertisers, marketers, and even hackers to collect sensitive information about users without their consent. By disabling cookies, users can take a significant step towards safeguarding their privacy online. Without tracking data from cookies, third-party advertisers and other entities will be unable to target users based on their browsing habits.
On the other hand, some users may not be familiar with the risks associated with cookies or may not fully understand how they work. As such, they may not see any issue with allowing websites to employ them. These individuals might argue that disabling cookies could limit their browsing experience by making it more difficult for them to access certain sites or features that rely on cookie data.
The Regulatory Landscape For Cookies
The regulatory landscape for cookies has drastically changed in recent years. With the increasing importance of data privacy and security, governments around the world have taken measures to regulate the use of cookies on websites. In 2018, the European Union implemented its General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires websites to obtain explicit consent from users before storing or accessing any personal information through cookies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Risks Of Disabling Cookies?
One of the primary risks is that it can make the browsing experience less personalized. Websites use cookies to remember user preferences and settings, such as login details or language preferences, which makes future visits more seamless. Disabling cookies can mean that users have to manually enter these details every time they visit a website.
Another risk of disabling cookies is that they can affect the performance of some websites. Some websites use cookies to track user behavior and optimize their page load times accordingly. Without this information, a website might take longer to load or not function as smoothly as intended. Additionally, some websites might even block access altogether if they detect that cookies are disabled.
Disabling cookies can also limit the ability of businesses to collect valuable insights into user behavior and improve their services accordingly. Cookies provide information on how users interact with a website and what content they engage with the most. This data helps businesses tailor their offerings to better meet customer needs and preferences, which in turn leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What Are The Best Alternatives To Cookies?
Local storage. Unlike cookies, local storage does not send data back and forth between the server and client every time a page loads. This means less data is being exchanged, reducing risks associated with data interception. Furthermore, local storage can store larger amounts of data than cookies, making it ideal for applications that require a lot of user input or interaction.
Session tokens. These are unique identifiers generated by servers that are sent to clients when they first connect to a website or application. The token is then used to establish communication between the two without transmitting sensitive information such as login credentials or credit card details. Session tokens are more secure than cookies because they cannot be manipulated by attackers who might try to hijack the session by stealing the cookie.
Fingerprinting. Fingerprinting involves collecting information about a user’s device such as its hardware configuration and installed software instead of relying on third-party tracking technologies like cookies or scripts. Although this method has its drawbacks since it relies on certain technical specifications being met in order for it work properly – meaning some devices may not have enough information available for fingerprinting – it still provides an anonymous way of tracking users without putting their personal information at risk.
What Are The Legal Requirements For Cookies?
In the European Union (EU), website owners must adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) guidelines, which mandate that users must give explicit consent before any tracking cookies can be used. Additionally, website owners must clearly state what data they collect through cookies and how it will be used.
In the United States, there is no national law mandating cookie usage compliance; however, several states have passed laws requiring website owners to inform users about their use of cookies actively. For instance, California has implemented The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) which requires businesses to disclose information about their data collection practices.
Conclusion
Disabling cookies can significantly enhance data security. Cookies are used to track user behavior, which can be exploited by cybercriminals for malicious purposes. By disabling cookies, users limit the amount of information that websites and advertisers can collect about them.
Furthermore, disabling cookies protects users from session-hijacking attacks. Session hijacking is a technique used by attackers to gain unauthorized access to a user’s session on a website. This could allow an attacker to steal sensitive data such as passwords and credit card information.
