Encryption programs are indispensable for safeguarding internet user privacy. They achieve this by converting data into an unreadable format called ciphertext, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. These programs secure data in transit and at rest, authenticate websites and individuals, and enable private communication. Choosing the right encryption program involves considering factors like encryption strength, ease of use, compatibility, regular updates, and open-source versus closed-source options.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is a complex process involving converting plain, readable data into a coded format using mathematical algorithms. This transformation renders the data unreadable without the corresponding decryption key. It acts as a digital lock, ensuring only authorized parties can access and understand the information.
The Mechanics of Encryption
To comprehend how encryption programs function, envision a secret message. Encrypting this message involves using a mathematical formula (the encryption algorithm) and a unique key, transforming it into an unintelligible jumble of characters. Without the key, deciphering this code is nearly impossible. Only those with the correct key can unlock and reveal the original message.
The Role of Encryption in Privacy Protection:

1. Securing Data in Transit
When we send data over the internet, such as emails, instant messages, or financial transactions, it embarks on a journey through various networks and servers. During this journey, the data is vulnerable to interception by cybercriminals with malicious intent. Without encryption, sensitive information would be akin to sending a postcard through the digital highway, exposed to prying eyes.
2. Protecting Data at Rest
Data isn’t only at risk while in transit; it also faces threats when stored on our devices or remote servers. Physical theft of devices or unauthorized server access can expose our data to potential misuse. This is where encryption programs shine in their ability to protect data at rest.
3. Authentication and Verification
Beyond securing data, encryption also plays a pivotal role in verifying the legitimacy of websites and the identities of individuals we interact with online. This aspect of encryption is crucial in preventing various cyberattacks, including phishing.
4. Privacy in Messaging and Communication
In an era of digital communication, privacy in messaging and communication is paramount. We send personal messages, share confidential information, and engage in sensitive conversations through various communication platforms. Encryption programs also come to the forefront here, ensuring that our conversations remain private and secure.
Types of Encryption Programs
Different situations require different encryption methods. Here are the main types:
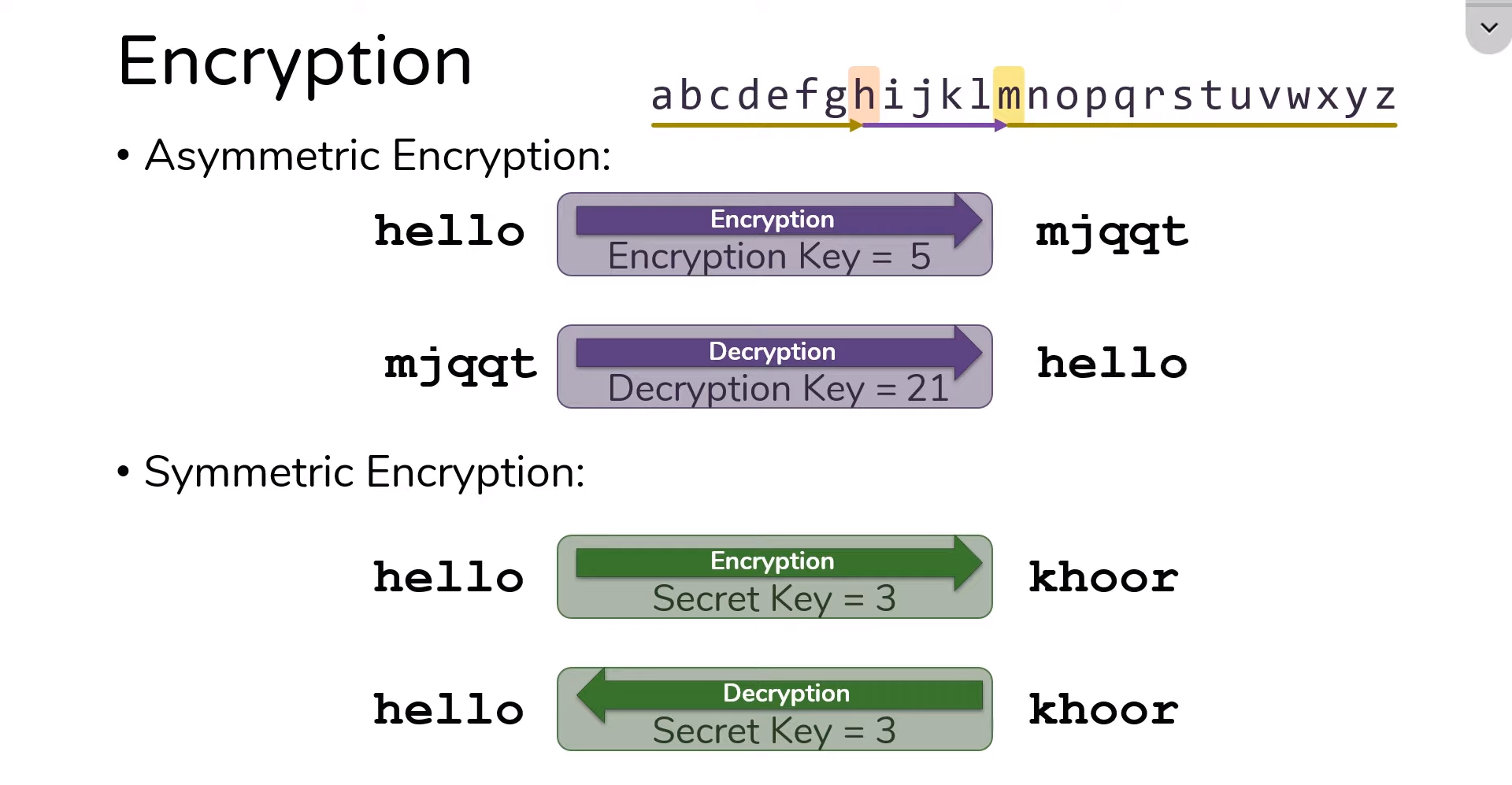
1. Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric or private-key encryption employs a single key for encryption and decryption. This means that the same key is used to lock and unlock the data. The key is typically a string of characters or bits.
How it works:
- Data Encryption: The plaintext (original, readable data) is combined with the encryption key using a specific algorithm to encrypt data. This process generates ciphertext, which is the encrypted data.
- Data Decryption: The recipient uses the same key and the decryption algorithm to decrypt the data. This process reverses the encryption, turning the ciphertext back into plaintext.
2. Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, is a more complex system that uses two distinct keys: public and private. These keys are mathematically related but serve different purposes.
How it works:
- Public Key Encryption: The public key is used for encryption. Anyone can use your public key to encrypt a message meant for you, but only you, as the holder of the private key, can decrypt and read it.
- Private Key Decryption: The private key is kept secret and used to decrypt encrypted messages with your public key. It ensures that only the recipient can access the original content.
3. End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2E) is a subset of asymmetric encryption and is a vital component of secure messaging apps and platforms. Only the sender and recipient can access a message’s content.
How it works:
- Key Pairing: The sender and recipient exchange their public keys.
- Encryption: When the sender sends a message, it’s encrypted using the recipient’s public key. Only the recipient, with their private key, can decrypt and read the message.
- Decryption: When the recipient receives the message, their private key decrypts it, revealing the original content.
The Benefits of Encryption Programs
Privacy Assurance
Encryption programs provide a strong sense of privacy, making it exceedingly difficult for unauthorized individuals or entities to access sensitive data. This assurance protects personal information, financial details, and confidential communications.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries and regions have stringent data protection regulations, such as the GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the healthcare sector. Encryption is often a mandatory compliance component, helping organizations avoid legal consequences and reputational damage.
Trust in Online Transactions
The widespread use of encryption in online banking and e-commerce instills trust among consumers. When they see the padlock icon in their web browser, they know their transactions are secure, encouraging online activity.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Key Management
While encryption is a potent tool, managing encryption keys can be challenging, especially for large organizations. A lost or compromised key can lead to data loss or breaches.
User Responsibility
Users must play an active role in ensuring their data remains secure. This includes setting strong passwords, updating software, and being cautious about sharing personal information.
Choosing the Right Encryption Program
Consider Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate encryption program depends on your specific requirements. Evaluate whether you need encryption for data at rest, during transmission, or both, and whether you require a personal or business solution.
Verify Security Protocols
Ensure that the encryption program you choose employs strong, industry-standard encryption algorithms and has a reputation for security.
User-Friendliness
The ease of use is crucial, especially if you’re not a tech expert. Opt for encryption programs with intuitive interfaces and clear instructions.
Conclusion
Encryption programs are a robust defense mechanism in a digital world with privacy threats. They provide a secure means to protect internet users’ privacy by safeguarding data in transit and at rest, securing communications, and ensuring compliance with regulations. While challenges and misconceptions exist, the benefits of encryption programs far outweigh the drawbacks. Individuals and organizations can confidently navigate the digital landscape by choosing the encryption solution and taking personal responsibility for online security.
FAQs:
Can encryption be cracked by determined hackers?
While encryption is highly secure, no system is entirely immune to attacks. Determined hackers may employ advanced techniques, but the strength of encryption lies in the complexity of the algorithms and the length of encryption keys. The longer and more complex the key, the more susceptible the encryption to cracking.
Are all encryption programs equally secure?
No, the security of encryption programs can vary. Choosing reputable programs that use strong encryption algorithms and have a history of regular updates and security audits is essential.
Can encryption slow down data transfer?
Yes, encryption can introduce some latency, especially with large data volumes. However, modern encryption algorithms are designed to minimize this impact, and the trade-off between security and speed is generally acceptable for most users.
What should I do if I forget my encryption key?
Forgetting your encryption key can lead to data loss, as it’s nearly impossible to recover encrypted data without it. It’s crucial to keep your encryption key in a secure place or use a secure key management system to avoid this situation.
Is end-to-end encryption the most secure option for messaging apps?
End-to-end encryption is among the most secure options for protecting the privacy of your messages. It ensures that only you and the intended recipient can read the messages. However, using trusted messaging apps that implement end-to-end encryption correctly is essential.
