Encryption and decryption are essential tools for protecting data in the digital age. Encryption converts data into unreadable ciphertext, safeguarding it from unauthorized access. It relies on mathematical algorithms and cryptographic keys, making it extremely challenging for hackers to decipher sensitive information. Decryption, on the other hand, reverses this process, allowing authorized individuals to access encrypted data using the decryption key. These security measures are vital for preserving data privacy, protecting against cyberattacks, ensuring secure communication, complying with legal requirements, and mitigating insider threats.
Encryption:
What Is Encryption?
Encryption converts plain text or data into an unreadable format known as ciphertext. This transformation is accomplished using algorithms and cryptographic keys. The primary objective of encryption is to protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring that even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains indecipherable.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption relies on mathematical algorithms to scramble data. A cryptographic key is used to perform this transformation, and without the corresponding decryption key, deciphering the ciphertext is virtually impossible. This process makes it incredibly challenging for hackers and cybercriminals to access sensitive information.
The Importance of Encryption:
Protecting Confidentiality
One of the fundamental reasons for using encryption is to protect the confidentiality of data. Encryption ensures that only authorized individuals can access and understand the information, whether it’s your messages, financial transactions, or business communications.
Data Security in Transit
Encryption plays a pivotal role in securing data during transmission. When you send an email, make an online purchase, or log into your bank account, the data exchanged is encrypted. This prevents eavesdroppers from intercepting and deciphering your sensitive information.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many industries and organizations are bound by regulatory requirements to safeguard data. Encryption helps businesses meet these compliance standards, ensuring customer data remains secure and protected.
Types of Encryption:
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. While it is efficient, it requires a secure method of key exchange. If the key falls into the wrong hands, the data is compromised.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This eliminates the need for a secure key exchange, making it a popular choice for securing communications.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption is a method where data is encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device. This ensures that even service providers cannot access the content of your messages.
Decryption:
What Is Decryption?
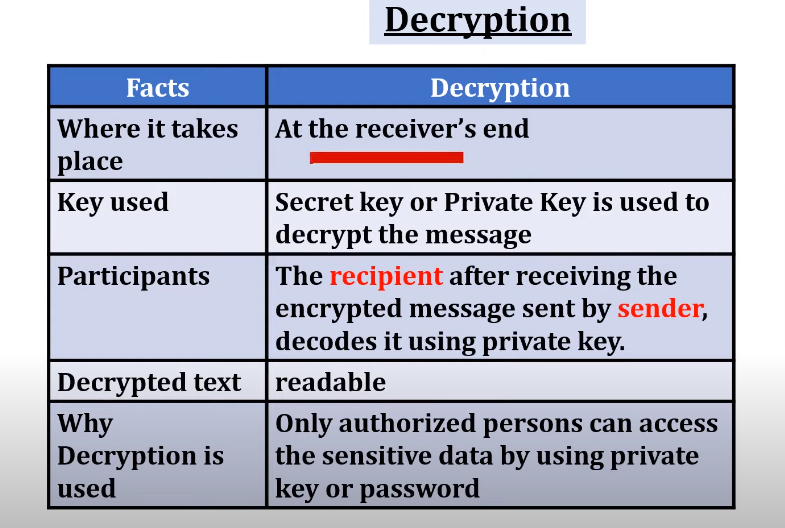
Decryption is the reverse process of encryption, where ciphertext is transformed back into its original plaintext form. This process requires the appropriate decryption key, which only authorized individuals possess.
The Role of Decryption Keys
Decryption keys are the linchpin of the decryption process. It is virtually impossible to reverse the encryption and access the original data without them. This ensures that even if hackers gain access to the ciphertext, they cannot decipher it without the key.
Decrypting Data in Real-Time
Decryption is essential in various scenarios, such as accessing secure websites, opening encrypted files, or reading encrypted messages. In these instances, the decryption process happens seamlessly and in real-time, allowing users to access the necessary information.
Key Differences Between Encryption and Decryption:
1. Transformation Process
- Encryption transforms plaintext into ciphertext.
- Decryption reverses the process by converting ciphertext back into plaintext.
2. Purpose
- Encryption is for securing and protecting data from unauthorized access.
- Decryption is for granting authorized access to encrypted data.
3. Key Usage
- Encryption uses an encryption key to perform the transformation.
- Decryption uses a decryption key that corresponds to the encryption key.
4. Security Focus
- Encryption focuses on data security and confidentiality.
- Decryption focuses on controlled data access while maintaining security.
Why Use Encryption and Decryption?
1. Data Privacy
When you encrypt your data, you lock it behind a complex code that only you or authorized parties can unlock. This ensures that even if a malicious actor gains access to your data, they won’t be able to decipher it without the decryption key. Whether it’s your financial records, personal messages, or healthcare information, encryption helps maintain the confidentiality of your data.
2. Protection Against Cyberattacks
Hackers employ various tactics to breach systems and steal sensitive information. Encryption acts as a formidable barrier against such threats. Even if hackers manage to infiltrate a system, the encrypted data they access remains incomprehensible without the decryption key. This acts as a deterrent, discouraging cybercriminals from pursuing your data.
3. Secure Communication
Encryption ensures that your communication remains confidential and secure. Whether you’re sending an email, making an online purchase, or using a messaging app, encryption creates a secure tunnel through which your information travels. This makes it extremely challenging for eavesdroppers to intercept and decipher your messages or transactions. It ensures that what you share with others remains between you and the intended recipient.
Insider threats, where employees or individuals with internal access misuse or steal data, pose a significant risk. Encryption helps mitigate these threats by limiting access to authorized personnel. Even if an insider gains access to encrypted data, they cannot misuse it without the decryption key, typically held by a select few.
6. Protecting Mobile Devices
The increasing use of mobile devices for personal and professional purposes has made data security critical. Encryption safeguards the data stored on smartphones, tablets, and laptops. In the event of theft or loss, the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized users, reducing the risk of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
7. Preserving Confidentiality in the Cloud
Cloud storage and services have become ubiquitous but present security challenges. Encryption ensures that data stored in the cloud remains confidential. Service providers may encrypt data both in transit and at rest, adding a layer of protection to your files and documents.
8. Secure Financial Transactions
Online banking and e-commerce rely heavily on encryption to secure financial transactions. When you pay or access your bank account online, encryption ensures that your financial details are kept safe from interception or tampering.
Balancing Security and Convenience:
Passwords and Encryption
Strong, unique passwords are often used to protect decryption keys. However, managing a multitude of passwords can be challenging. This is where password management tools come into play, ensuring security and ease of use.
Key Management
In enterprise settings, effective key management is vital. It involves securely storing and managing encryption keys to prevent data breaches. Key rotation and encryption key lifecycle management are key components of a robust security strategy.
The Future of Encryption:
Quantum Computing and Encryption
As technology continues to evolve, so do the challenges and threats to encryption. The emergence of quantum computing poses a potential threat to current encryption methods. However, researchers are working on quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to address this concern.
Advancements in Secure Communication
We can expect to see further advancements in secure communication tools. End-to-end encryption will become more prevalent, protecting messages and voice and video calls.
Conclusion:
Encryption and decryption are the cornerstones of data security in our increasingly digital world. Encryption transforms sensitive information into an unreadable format, safeguarding it from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Decryption allows authorized individuals to access and utilize encrypted data, ensuring controlled and secure data access. The significance of encryption and decryption extends to protecting data privacy, defending against cyberattacks, securing communication, and meeting regulatory requirements.
FAQs:
What are the different types of encryption?
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Utilizes a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- End-to-End Encryption: Ensures that data is encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device.
What is decryption, and how does it work?
Decryption is the reverse process of encryption, where ciphertext is transformed back into its original plaintext form. This process requires the appropriate decryption key, which only authorized individuals possess. Decryption is essential for accessing encrypted data in real time.
What is the role of decryption keys?
Decryption keys are crucial in the decryption process. They are required to reverse the encryption and access the original data. It is nearly impossible to decipher encrypted information without the correct decryption key.
How does encryption preserve confidentiality in the cloud?
Cloud storage and services often use encryption to ensure that data stored in the cloud remains confidential. This can include encrypting data in transit and at rest and protecting files and documents.
