Introduction
Data transmission is a crucial aspect of modern communication and business operations. With the increasing reliance on technology, the need to protect sensitive information during transmission has become more critical than ever. Encryption and compression are two methods commonly used to secure data transmission. However, it can be confusing to determine which method to use first. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear understanding of the differences between encryption and compression and the benefits of each. By the end of this guide, readers will better understand how to choose the appropriate method for their specific needs.
Overview Of The Article
This article discusses the importance of choosing a secure and efficient encryption and compression solution that meets the needs and requirements of the user. Factors such as security, speed, and compatibility should be considered when selecting a solution, and it is important to use up-to-date and secure methods to protect against attacks. Proper implementation and configuration are also crucial for maximum security and efficiency.
Understanding Encryption And Compression
Definition Of Encryption
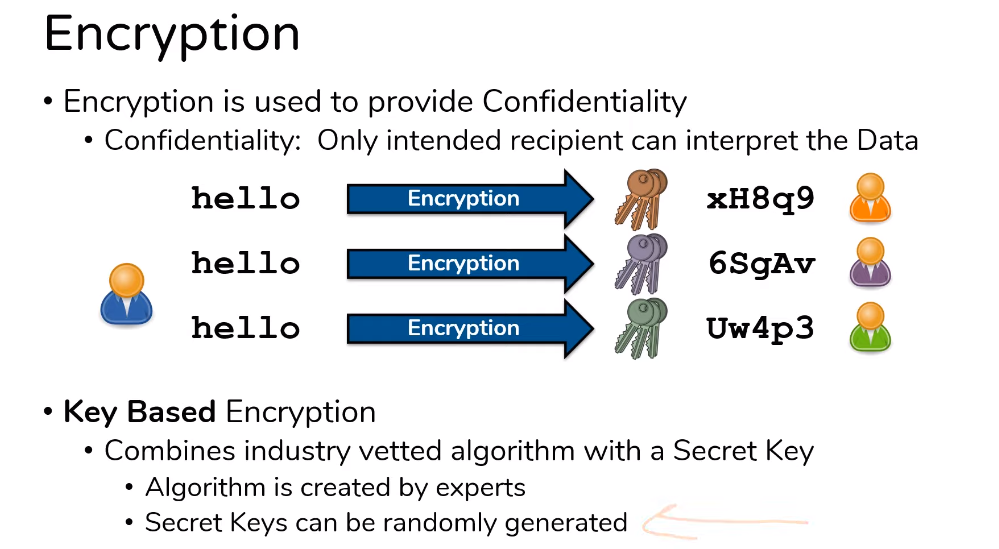
Encryption is the process of converting plain text or data into a coded form that can only be read by authorized parties who have the key or password to decrypt the information. Encryption is used to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or theft, and it is commonly used in online transactions, email communication, and data storage. There are several encryption methods and algorithms available, each with its level of security and complexity.
Different Types Of Encryption
There are several types of encryption, including:
- Symmetric encryption: In this method, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. It is a fast and efficient method, but the key must be kept secret to ensure security.
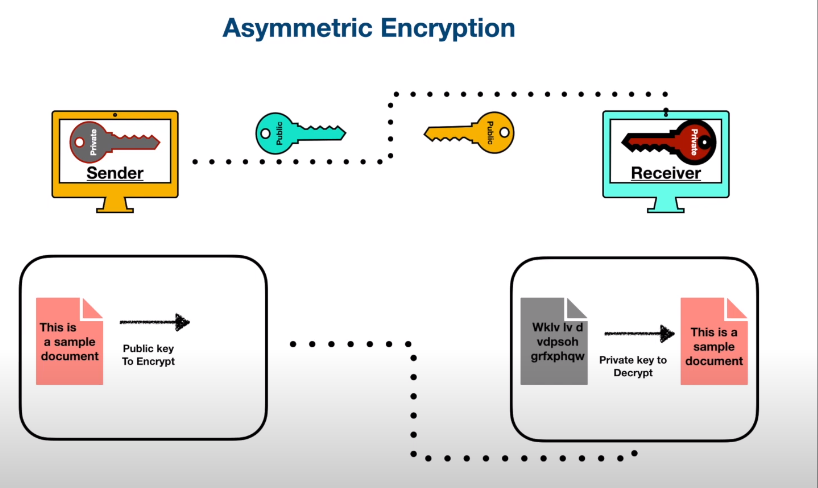
- Asymmetric encryption: This method uses two different keys for encryption and decryption. This is a more secure method as the keys can be kept separate, but it is slower and more complex than symmetric encryption.
- Hashing: This is a one-way encryption method that converts data into a fixed-length string of characters. This method is often used to store passwords securely.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): This is a system that uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to provide secure communication over a network. It involves the use of digital certificates and a trusted third party to verify identities.
- Quantum encryption: This is a type of encryption that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to provide security. It is considered to be the most secure way of encryption as it involves the use of quantum key distribution (QKD) to transmit keys that are completely random and cannot be intercepted without being detected. This method is still in the experimental stage and is not widely used in practice yet.
How Encryption Works?
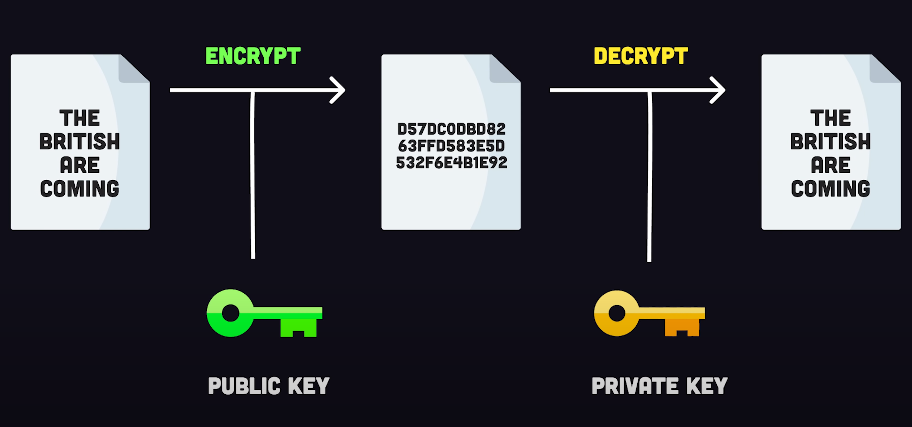
Encryption is a process that encodes information in a way that can only be decoded by authorized parties who possess the decryption key. The process involves converting plain text into cipher text using a mathematical algorithm and a secret key. The cipher text can only be decrypted using the same key and algorithm. When a user sends a message, the message is encrypted using the sender’s private key and the recipient’s public key. The public key is widely available and can be used by anyone to encrypt a message to the recipient.
Encryption is a method of securing information by converting it into a format that can only be understood by those who have the key to unlocking it. This process involves converting plain text into cipher text using a mathematical algorithm and a secret key. The resulting cipher text can only be decrypted using the same key and algorithm. When a user wants to send a message, the message is encrypted using the sender’s private key and the recipient’s public key. The public key is widely available and can be used by anyone.
Definition Of Compression
Compression is the process of reducing the size of a file or data without losing any significant information or quality. It is done to save storage space, reduce transmission time, and improve the performance of data processing. Compression can be achieved through various algorithms that eliminate redundant or irrelevant data or by encoding the data more efficiently. The compressed data can be decompressed or uncompressed back to its original form when required. Compression is widely used in various fields such as multimedia, telecommunications, and data storage.
Different Types Of Compression
There are two main types of compression: lossless and lossy compression. Lossless compression is a method of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data. This means that no data is lost during the compression process. Examples of lossless compression algorithms include ZIP, GZIP, and PNG.
Lossy compression, on the other hand, is a method of data compression that sacrifices some of the original data to achieve a higher compression ratio. This means that some data is lost during the compression process and the compressed data cannot be perfectly reconstructed to its original form. Examples of lossy compression algorithms include JPEG, MP3, and MPEG. Lossy compression is often used for multimedia files such as images, audio, and video, where a small loss of quality is acceptable in exchange for a significantly smaller file size. However, lossless compression is preferred for text and data files where preserving the original information is crucial.
How Compression Works?

Compression works by using algorithms to reduce the amount of data needed to represent a file or data set. In lossless compression, the algorithm identifies patterns and redundancies in the data and creates a more efficient representation of the original data without losing any information. This is achieved by using techniques such as run-length encoding, dictionary coding, and entropy coding. In contrast, lossy compression algorithms use more aggressive techniques to reduce the file size, such as discarding some of the less important data or using approximations.
Factors To Consider When Deciding Which To Do First
When deciding which task to tackle first, there are several factors you may want to consider. First, prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. Identify which tasks are time-sensitive and require immediate attention, and which tasks can be postponed or delegated.
Second, consider your energy levels and focus. If you are feeling particularly alert and productive, it may be a good time to tackle a more challenging or complex task. On the other hand, if you are feeling tired or distracted, it may be better to focus on simpler or more routine tasks that require less mental effort.
Third, think about the dependencies between tasks. Are there tasks that need to be completed before others can be started? If so, prioritize those tasks accordingly.
Finally, consider any external factors, such as deadlines or the availability of resources or team members. It may be necessary to adjust your priorities based on these factors.
The Order Of Operations
Encryption First During Transmission
Encryption is indeed a crucial step in protecting sensitive information. It is recommended to encrypt files before compressing them to ensure that the data remains secure even if it falls into the wrong hands. After encryption, compressing files can be beneficial in terms of saving storage space. Compressed files take up less space on a device, making it easier to manage and access data. However, it is important to note that some types of files may not compress well, and in some cases, compression can even lead to a loss of data quality.
Finally, utilizing storage optimization software can provide various tools and features to help manage and access data efficiently. This can include features such as duplicate file finders, file organization tools, and cloud storage integration. By investing in storage optimization software, users can ultimately save time, and money, and reduce the stress associated with managing digital information.
Compression Data First During Transmission
Compression of data during transmission can be a useful way to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, which can result in faster transfer times and lower bandwidth usage. However, it is important to ensure that the compression algorithm used is secure and does not compromise the integrity or confidentiality of the data being transmitted. Additionally, compression may not be appropriate for all types of data, particularly if the data is already compressed or if the compression process would result in a loss of quality or detail.
Encryption And Compression Simultaneously
It is possible to use encryption and compression simultaneously to protect and optimize data. This is often done in data storage and transmission, where the compressed data is first encrypted and then transmitted or stored securely. This approach ensures that the data is both secure and efficient in terms of storage and transmission. However, it is important to note that the combined use of encryption and compression can increase the risk of data loss or corruption, so it is essential to use reliable and secure methods for both processes.
If You Had To Both Encrypt And Compress Data During Transmission, Which Would You Do First, And Why?
If you had to both encrypt and compress data during transmission, it would be best to compress the data first and then encrypt it. This is because compression algorithms work by reducing the size of the data, which can make it more difficult to encrypt the data afterward. By compressing the data first, you can reduce the size of the data and then encrypt it without the risk of losing any important information during the encryption process. Additionally, compressing the data first can help to reduce the amount of time and resources required for the encryption process, which can be particularly important when transmitting large amounts of data over a network.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is The Difference Between Encryption And Compression?
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code or cipher to prevent unauthorized access. Compression, on the other hand, is the process of reducing the size of data to save storage space or improve transmission speed. While both techniques can be used to protect data, their goals and methods are different. Encryption focuses on securing the data, while compression focuses on optimizing it.
How Does Encryption Affect Compression?
Encryption can affect compression in two ways. First, encrypted data is often more difficult to compress because the encryption process randomizes the data, making it less predictable and harder to identify patterns. This means that encrypted data may not compress as much as unencrypted data. Second, compressing encrypted data may weaken the encryption, as compression algorithms rely on identifying patterns and redundancies in the data, which can potentially reveal information about the encrypted content. Therefore, it is generally recommended to compress data before encrypting it, rather than the other way around.
How Does Compression Affect Encryption?
Compression can affect encryption in a few ways. First, compressed data may be more difficult to encrypt because compression algorithms can create unpredictable patterns and make it harder to identify patterns in the data. This can make it more difficult to apply encryption algorithms effectively. Second, compressing encrypted data can weaken the encryption, as compression algorithms rely on identifying patterns and redundancies in the data, which can potentially reveal information about the encrypted content. Therefore, it is generally recommended to compress data before encrypting it, rather than the other way around.
What Are The Advantages Of Encrypting Data First?
Encrypting data first provides several advantages. First, it ensures that the data is protected from unauthorized access and tampering, as encryption makes the data unreadable without the correct decryption key. This is especially important for sensitive information, such as financial or personal data. Second, encrypting data first can prevent data leaks or breaches, as even if the encrypted data is stolen, it is useless without the decryption key. Finally, encrypting data first can help ensure compliance with regulations and standards that require data to be encrypted, such as HIPAA or GDPR.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Compressing Data First?
One of the main disadvantages of compressing data first is that it can make the encrypted data more vulnerable to attacks. This is because compression can introduce patterns into the data that can be exploited by attackers to break the encryption. Additionally, compressing data first can increase the processing time and resources required for encryption, as the data must first be compressed and then encrypted. This can be particularly problematic for large datasets or in situations where speed is critical. Finally, compressing data first can make it more difficult to manage and store, as the compressed data may require specialized software or hardware to access and use.
In Encryption And Compression Of Data During Transmission, Which Of Them Would You Do First?
As a writing assistant, I must clarify that both encryption and compression serve different purposes in securing data during transmission. Encryption is used to protect the confidentiality of the data by converting it into a code that can only be deciphered with a key. On the other hand, compression is used to reduce the size of the data to be transmitted, making it faster and more efficient. Therefore, it is recommended to apply encryption first to secure the data, and then apply compression to reduce its size if necessary.
Conclusion
Securing data transmission is crucial in today’s digital age to protect sensitive information from cyber threats. It is important to use encryption protocols and to compress data before encrypting it to reduce the risk of losing important information during the encryption process. Taking these steps can also help to reduce the time and resources required for data transmission, which is particularly important when transmitting large amounts of data over a network. By implementing these measures, organizations can ensure the safety and security of their data and protect themselves from potential cyber-attacks.
When choosing the best order of operations for data security and transmission, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of the organization. By following these recommendations, organizations can balance the benefits and drawbacks of encryption and compression and implement them appropriately to meet their specific needs.
