Introduction

The Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is a standardized test that measures the verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, critical thinking, and analytical writing skills of prospective graduate students. In recent years, the GRE has gained popularity among data security professionals who wish to pursue an advanced degree in this field. However, many individuals are intimidated by the exam and unsure of how to prepare for it.
This guide aims to demystify the GRE for those interested in pursuing a graduate degree in data security. We will provide a comprehensive overview of what the exam entails and strategies for preparing for it effectively. Additionally, we will explore some common misconceptions about the GRE and offer tips on how to overcome test anxiety. By following these guidelines, you can feel confident as you approach this important step in your career journey.
What is GRE?
Definition and Meaning of GRE

The GRE, or Graduate Record Examinations, is a standardized test used in the admission process for most graduate schools in the United States. The exam is designed to measure a student’s readiness for graduate-level coursework and assess their abilities in reading comprehension, analytical writing, and quantitative reasoning.
The GRE is split into three sections: Verbal Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, and Analytical Writing. Each section comprises multiple-choice questions that range from basic to complex problem-solving abilities. The Verbal Reasoning section tests your ability to understand written material and evaluate arguments presented within it. The Quantitative Reasoning section evaluates your mathematical skills through algebraic problem-solving and data analysis. The Analytical Writing section gauges your ability to articulate complex ideas through well-written essays.
How GRE Is Used In Data Security
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a protocol used in data security to create secure tunnels between two networks. It encapsulates and encrypts the data packets, making it difficult for intruders to intercept and read them. GRE also helps in hiding the IP addresses of the communicating devices, providing an additional layer of security.
In addition to providing secure connections, GRE can also be used to implement Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs allow remote users or devices to securely access a private network over the internet. By encapsulating and encrypting traffic from remote devices using GRE tunnels, businesses can provide secure access without compromising on security.
GRE tunnels are commonly used by organizations that have distributed branches or offices spread across different locations. The protocol helps connect these branches with their headquarters securely through encrypted tunneling mechanisms.
Types of GRE Protocols
The first type of GRE protocol is Standard GRE, which provides basic tunneling capabilities for encapsulating multiple protocols within an IP packet. It can be configured with any transport protocol, including TCP and UDP. Another type of GRE protocol is the Enhanced GRE (EGRE), which offers improved performance by reducing overhead and improving scalability.
There’s also the Keyed GRE (KGRE), which adds an extra layer of security by requiring authentication before a tunnel can be established. This prevents unauthorized access to the network and ensures that all communication between endpoints remains confidential. The choice of a specific type of GRE protocol depends on the specific needs and requirements of an organization or project, with factors like speed, security, reliability, and scalability taken into consideration when choosing one over the other.
Understanding GRE Tunneling
How GRE tunneling works?
GRE tunneling works by creating a virtual point-to-point connection between two endpoints using the Internet Protocol (IP) network as a medium. This enables data packets to be sent securely from one location to another, even if they are located on separate networks.
When sending data through a GRE tunnel, the data is encapsulated with additional headers that include routing information necessary for transmitting it across the IP network. The original source and destination addresses are retained in these headers, allowing the receiving endpoint to correctly identify where the packet originated from and where it should be delivered.
GRE tunneling can be used in many scenarios such as connecting remote locations over public networks or implementing secure VPNs between two points without having to rely on complicated and expensive hardware solutions.
Benefits Of GRE Tunneling In Data Security
One of the key advantages of using GRE tunnels is that they provide a secure and encrypted connection between two endpoints. This means that all data transmitted through the tunnel is protected from eavesdropping, tampering, or interception by unauthorized parties.
Another benefit of GRE tunneling in data security is its ability to bypass network restrictions imposed by firewalls or other security measures. Since GRE tunnels encapsulate traffic within another protocol, such as IP, it can easily traverse networks without being detected by traditional firewall rules.
GRE tunnels are also useful in improving network performance by reducing packet fragmentation and increasing throughput. By encapsulating packets within larger payloads, GRE tunnels can reduce the number of packets sent over a network and decrease the likelihood of packet loss or delays caused by congestion.
GRE Tunneling Vs. IPSEC
GRE is a simple protocol that provides encapsulation only, while IPSec offers both encapsulation and encryption. GRE is often used in situations where there is no need for encryption such as connecting remote networks over the Internet.
On the other hand, IPSec provides more advanced security features such as authentication and encryption to ensure secure communication between endpoints. It’s commonly used when privacy and confidentiality of data are critical concerns, for instance, in business organizations or government agencies that deal with sensitive information.
GRE vs. Other Protocols
Advantages And Disadvantages Of GRE
Advantages of GRE
One of the biggest advantages of taking the GRE is that it is accepted by a wide range of graduate and business schools all over the world. This means that if you plan on studying abroad, you can take this test and apply to multiple schools without having to take different entrance exams for each one. Additionally, GRE scores are valid for up to five years, so you can take the test early and still submit your application at a later date.
Disadvantages of GRE
On the other hand, there are also a few disadvantages to consider when taking the GRE. One major disadvantage is that it can be quite expensive to register for and take. Additionally, some students may find certain sections (such as the math section) particularly challenging or intimidating. While many schools accept both GRE and GMAT scores for business programs, some top-tier programs may prefer GMAT scores instead.
When To Use GRE And When Not To Use It?
GRE should not be used when communicating with non-GRE-capable devices or networks. In such cases, using GRE could lead to compatibility issues and communication breakdowns. It’s also important to note that the use of GRE can add an additional layer of complexity to the network architecture, which could increase maintenance costs and reduce overall efficiency.
On the other hand, there are several scenarios where the use of GRE could prove invaluable in enhancing data security. For instance, when setting up VPN connections between remote sites or for connecting cloud infrastructure with on-premise networks. By encapsulating packets in a secure tunnel through public networks like the Internet, it becomes much harder for hackers to intercept and compromise sensitive information.
GRE in Network Virtualization
How GRE Is Used In Network Virtualization
GRE allows the creation of a virtual point-to-point link between two networks over an intermediate network by encapsulating the payload of one protocol within another protocol. In network virtualization, GRE can be used to transport packets between different Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), or to connect multiple virtual machines on different hosts.
Benefits Of GRE In Network Virtualization
The first benefit is improved security through the use of encapsulation, which creates an additional layer of encryption for data transmission. This makes it harder for hackers to intercept and decode sensitive information.
Another benefit of using GRE in network virtualization is increased flexibility and scalability. GRE allows organizations to create virtual networks within their physical networks, which means they can add or remove resources as needed without affecting other parts of the system. This helps organizations reduce costs associated with maintaining separate physical networks for different purposes.
GRE also provides better performance and reliability than traditional networking protocols because it reduces the overhead associated with routing and switching packets between different devices. As a result, organizations can achieve higher speeds and lower latency when transmitting data across their networks.
GRE vs. VXLAN
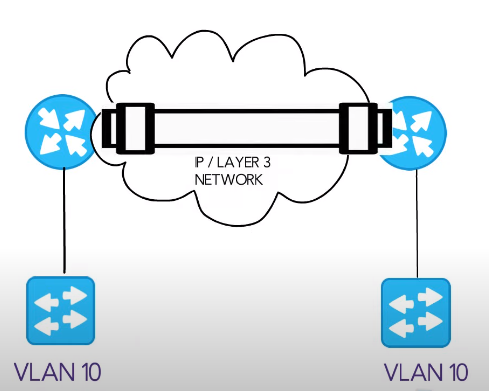
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) and VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) protocols encapsulate the original packet into a new packet, which is then transported over an IP network. However, there are significant differences between the two protocols.
GRE is an older protocol that has been widely used for many years. It offers basic encryption and authentication features, making it relatively simple to use and implement. On the other hand, VXLAN is a newer protocol that provides more advanced features such as multi-tenancy and scalability. It also supports larger networks than GRE.
When choosing between GRE and VXLAN for data security purposes, it’s important to consider factors such as your organization’s specific needs and budget. While GRE may be a good choice for smaller organizations with limited resources, larger enterprises may benefit from the added functionality of VXLAN.
GRE in Cloud Computing
How GRE Is Used In Cloud Computing
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) in cloud computing provides a secure tunnel for communication between virtual machines (VMs). By encapsulating the traffic within a GRE tunnel, it becomes virtually impossible for an attacker to intercept or tamper with the data being transmitted over the network. This makes GRE an essential tool for securing sensitive data and ensuring that it remains confidential.
Another use case of GRE in cloud computing is to enable communication between different networks that may be using different protocols. For instance, if you have two VMs running on separate networks with incompatible protocols, you can create a GRE tunnel between them to seamlessly transfer data across both networks. This not only simplifies network management but also enhances flexibility and scalability.
GRE can be employed in cloud-based disaster recovery solutions to create backup tunnels that facilitate seamless failover in case of a primary system outage. In such scenarios, all traffic will automatically be redirected through the backup tunnel without any disruption or delay.
Benefits Of GRE In Cloud Computing
One of the main benefits of using GRE in cloud computing is its ability to provide a secure and encrypted tunnel for data transfer. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access or interception during transmission. Additionally, this feature also allows organizations to save money on expensive leased lines as they can use less-expensive internet connections instead.
Another significant benefit of GRE in cloud computing is its ability to support multicast traffic efficiently. Multicast traffic can be complicated to manage over a wide area network (WAN), but with GRE tunnels, it becomes easier for organizations to transfer large files and other resources without impacting network performance negatively. This feature makes it ideal for businesses that require high-speed data transfers between remote locations such as branch offices or data centers located in different regions.
GRE Vs. Other Cloud Networking Protocols
While GRE has its advantages, it is not the only networking protocol available for use in these scenarios.
Other networking protocols commonly used in cloud computing include Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) and Network Virtualization using Generic Routing Encapsulation (NVGRE). These protocols offer similar benefits as GRE but have some differences in how they operate. VXLAN, for example, uses a 24-bit segment ID to allow more extensive segmentation of the network than GRE.
When choosing between different cloud networking protocols, it’s essential to consider factors such as scalability, performance, security, and compatibility with existing systems. Ultimately, the choice of which protocol to use will depend on specific business needs and priorities.
Security Issues with GRE
Common Security Threats Associated With GRE
Susceptibility to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. This is because GRE tunnels do not provide any form of encryption, thereby exposing the transmitted data to interception by attackers. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by intercepting packets transmitted between endpoints and injecting malicious code or altering the contents of such packets.
Spoofing attacks. Since the GRE protocol does not have any built-in mechanisms for authentication, attackers can easily impersonate legitimate endpoints to gain access to the network and carry out malicious activities such as stealing sensitive information or launching cyberattacks.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. An attacker can flood a network with excessive traffic targeted at a particular endpoint, causing it to be overwhelmed and unable to process legitimate requests. This can lead to disruption of critical services, loss of productivity, and potential financial losses due to downtime.
Best Practices for Securing GRE
Use encryption. Encryption ensures that no one can read the data transmitted through GRE tunnels, even if they intercept it. There are two types of encryption that can be used with GRE: Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). IPsec encrypts all traffic between two networks while TLS encrypts only the traffic between two endpoints.
Limit access to GRE tunnels by using access control lists (ACLs). ACLs enable network administrators to specify which devices or users can access the tunnel. This helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Monitor GRE traffic for anomalies. Network administrators should regularly review logs and look out for suspicious activity such as unusually large amounts of data being transmitted through a tunnel or unexpected connections. Early detection of anomalies can help prevent security threats before they cause serious harm to your network.
Role of Firewalls in Securing GRE
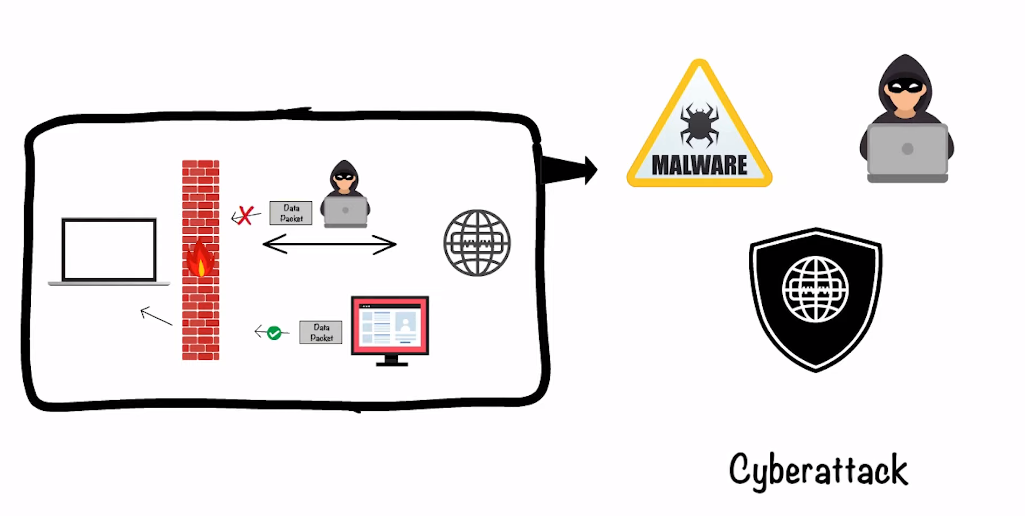
Firewalls are essential for securing GRE because they protect against unauthorized access and prevent malicious attacks such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). By monitoring traffic, firewalls can detect suspicious activity and block it before it reaches its destination. Firewall rules can also be configured to allow or deny specific types of traffic, ensuring that only authorized parties have access.
Implementing GRE in Data Security
Steps Involved In Implementing GRE
The implementation of GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) in data security involves several steps that need to be followed carefully. The first step is to configure the routers at both ends of the network for GRE tunneling. This entails setting up a virtual tunnel interface and assigning IP addresses to both ends, as well as specifying the source and destination IP addresses.
Once the routers have been configured, the next step is to enable GRE on them by setting up a tunnel interface on each router. This will allow data packets to be encapsulated within a GRE header before being transmitted over the internet or other networks.
After configuring and enabling GRE, it’s essential to verify that it’s working correctly by testing connectivity between devices at either end of the tunnel. This can be done by sending ping requests from one device to another and checking for successful replies,
Tips For Successful Implementation Of GRE
Start with a plan: Before you start studying for the GRE, it is important to have a clear plan in place. This should include setting a study schedule, identifying your strengths and weaknesses, and determining what resources you will need to succeed.
Make use of practice tests: One of the best ways to prepare for the GRE is by taking practice tests. These will help you get familiar with the format of the exam as well as identify areas where you need improvement.
Focus on vocabulary: The GRE places a lot of emphasis on vocabulary, so it’s essential that you spend time studying key terms and concepts. Consider using flashcards or other tools to help memorize words.
Don’t neglect math skills: While many people focus primarily on verbal skills when preparing for the GRE, it’s important not to neglect your math abilities. Make sure to review basic mathematical principles and formulas.
Use available resources: There are many resources available online and in print that can help you prepare for the GRE. Take advantage of these materials as much as possible to ensure success on test day.
Stay consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to preparing for any exam, including the GRE. Make sure that you stick with your study schedule even when things get tough or life gets busy.
Conclusion
The GRE exam plays a crucial role in determining the potential of candidates looking to pursue a career in data security. The exam evaluates the candidate’s analytical and critical thinking skills, which are essential in this field. It also tests their verbal reasoning abilities, which is necessary for effective communication with colleagues and clients.
This comprehensive guide has provided an overview of all aspects of the GRE exam, including its structure, content, and scoring system. It has also highlighted various strategies that candidates can use to prepare for the exam effectively. These tips include taking practice tests, setting realistic goals, and seeking guidance from experienced mentors or tutors.
FAQs
How Does GRE Differ From Other Tunneling Protocols?
GRE does not provide any encryption mechanisms on its own and relies on other security protocols such as IPSec to provide data confidentiality. In contrast, IPSec includes both encryption and authentication mechanisms which make it more secure than GRE. Secondly, unlike PPTP and L2TP which are designed specifically for point-to-point communication between two devices, GRE can be used to create multi-protocol tunnels between multiple devices across different networks.
Another major difference is that GRE does not have built-in support for NAT (Network Address Translation) traversal while other VPN protocols like IPSec do. This can cause issues when trying to connect to a remote site behind a NAT gateway. However, there are workarounds available such as using UDP encapsulation instead of the default TCP encapsulation method with GRE.
What Are The Benefits Of Using GRE In Network Virtualization And Cloud Computing?
With GRE, virtual machines can communicate with each other even if they are located on different physical servers or have different IP addresses. This is essential for applications that require distributed architectures, such as those found in cloud computing environments.
Another benefit of using the GRE is that it allows for the secure transmission of data over public networks. By encapsulating packets within a GRE tunnel, data can be transmitted securely without the risk of interception or eavesdropping. This is especially important for enterprises that rely on cloud services to store sensitive data.
GRE offers increased flexibility in terms of network design and management. Virtual networks created using GRE tunnels can be easily scaled up or down depending on demand, making them highly adaptable to changing business needs. Additionally, since GRE operates at the OSI layer 3 levels, it does not require any changes to existing applications or hardware configurations.
How Can I Implement GRE In My Data Security Strategy?
Use it as a tunneling protocol. By setting up a GRE tunnel, you can encapsulate and encrypt sensitive data traffic between two endpoints in your network, thereby protecting it from prying eyes. In addition, GRE tunnels can also help you bypass firewalls and other network restrictions that may prevent certain types of data traffic from flowing through.
Use GRE for network virtualization purposes. This involves creating multiple logical networks on top of a physical network infrastructure, with each network assigned its own unique set of IP addresses and routing rules. By doing so, you can isolate different types of traffic based on their source or destination addresses, making it easier to manage security policies and prevent unauthorized access.
