Introduction

The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized our world, changing the way we interact with technology and how it impacts our daily lives. IoT devices are everywhere, from smart homes to connected cars, wearables to medical equipment. These devices have made life easier and more convenient for us, but they also present unique security challenges that must be addressed. With the increasing number of connected devices in our homes, offices, and public spaces comes an increased risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
The potential consequences of a cyber attack on an IoT device can be severe – from financial loss to personal harm. For example, a hacker could gain access to your home security system or even your medical device, putting you or your loved ones at risk. As such, it’s essential to understand the data security concerns associated with IoT devices so that you can take steps to protect yourself.
Understanding IoT Devices
Definition And Examples Of IoT devices
IoT devices are physical objects that are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other. These devices use sensors, software, and network connectivity to collect and exchange data in real time. IoT devices range from simple gadgets like smart lights and thermostats to complex systems like self-driving cars, drones, and industrial robots.
One of the most common examples of IoT devices includes wearables such as fitness trackers or smartwatches that monitor our health metrics in real-time. Another example is a smart home system that allows homeowners to control their lighting, temperature, security cameras, and even appliances remotely through a mobile app. In the healthcare industry, IoT medical devices such as insulin pumps or pacemakers allow doctors to monitor patients’ health conditions more closely.
How IoT Devices Work And Communicate With Each Other
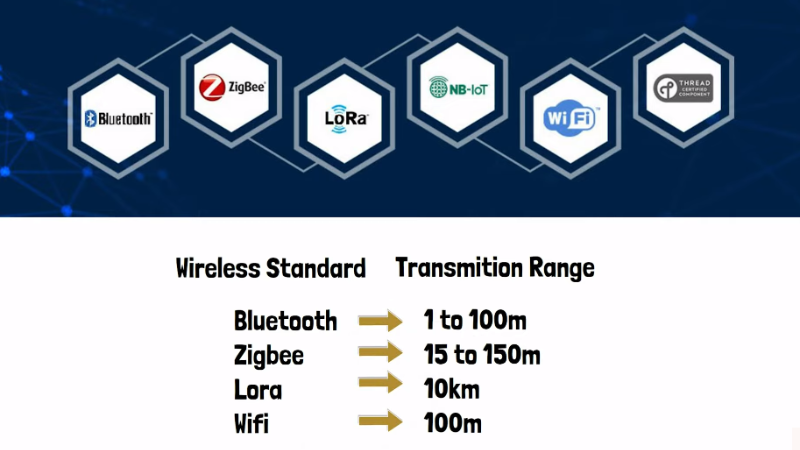
IoT devices often operate on low-power networks, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or ZigBee, which enable them to consume less energy while still being able to transmit data over long distances. Devices can also connect through Wi-Fi or cellular networks, which provide faster speeds but require more power. This network connectivity enables IoT devices to perform various functions such as monitoring physical conditions like temperature, humidity, and air quality.
To ensure secure communication between IoT devices, they need strong encryption methods when exchanging information. Security protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) help protect against unauthorized access by encrypting data during transmission and helping verify the identity of both parties involved in the communication process.
Data Security Threats of IoT Devices
Overview Of Data Security Threats Posed By IoT devices
While IoT devices make our lives easier, they also pose significant data security threats. These threats come in many forms, including hacking, malware attacks, and data breaches.
Cyberattacks And Data Breaches
One of the biggest concerns surrounding IoT devices is cyberattacks. These attacks can take many forms, including malware, ransomware, and phishing scams. Once a device is compromised, hackers can gain access to sensitive information such as personal data and financial information. This not only puts individuals at risk but also businesses that collect customer data through their IoT devices. Another area of concern is data breaches caused by vulnerabilities in IoT devices’ security systems.
Unauthorized Access To Personal Data
Unauthorized access to personal data is a growing concern in the age of the Internet of Things (IoT), where interconnected devices collect and transmit sensitive information. Whether it’s through hacking or simply accessing a device that has not been properly secured, unauthorized individuals can gain access to data such as home addresses, financial information, and even medical records.
Common IoT Device Vulnerabilities
Lack Of Encryption And Authentication
The lack of proper encryption and authentication methods puts connected devices at risk for cyber attacks. These vulnerabilities can lead to the theft of sensitive user information, unauthorized access to personal networks, and even control over physical systems such as home security systems or medical devices. Hackers are always searching for these weaknesses in order to exploit them for their own gain.
Default Or Weak Passwords
Default or weak passwords continue to be one of the biggest security concerns for IoT devices. In many cases, manufacturers set default passwords that are easy to guess or even leave the device with no password at all. This makes it easier for attackers to gain access to the device and its data.
Weak passwords can also lead to brute force attacks, where an attacker uses a program to try a large number of possible passwords until they find the right one.
Unpatched Software And Firmware
Unpatched software and firmware offer these criminals easy targets. One reason why unpatched software and firmware pose such a significant security risk is that they often contain vulnerabilities that hackers can easily exploit. These vulnerabilities may be known or unknown, but either way, they create opportunities for attackers to gain access to an IoT device’s network or manipulate its behavior.
Another reason why unpatched software and firmware present such a challenge is that many devices rely on outdated versions of these programs. Some manufacturers may not prioritize updating their devices’ software or firmware, leaving them exposed to attack for extended periods.
Insecure Network Connections
An insecure network connection creates an opportunity for unauthorized access. This means that someone could potentially gain access to your device and tamper with its settings or steal sensitive information. In some cases, these attacks can even spread to other devices on the same network.
Potential Consequences of IoT Data Breaches

Financial Losses
Cybercriminals may steal sensitive financial information, such as bank account details and credit card numbers, leading to fraudulent activities like identity theft and unauthorized transactions. This can lead to significant financial losses for both individuals and businesses.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is one of the most prevalent forms of cybercrime, where criminals steal your personal information like your social security number, credit card details, and other sensitive data to commit fraud.
Damage To Reputation
If a company’s IoT device falls victim to a cyber-attack or data breach, it can result in serious damage to its reputation.
When customers trust their personal information and data with a company, they expect that information will be kept secure. A breach in security could not only lead to financial losses and legal repercussions but also cause irreparable damage to the brand’s reputation. Consumers may lose faith in the product and the company as a whole, which can ultimately lead to lost revenue and customer loyalty.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices
Choosing Secure IoT Devices
It’s important to look for devices that have encryption built-in. This means that the data being transmitted between the device and its connected devices is scrambled and unreadable by anyone who intercepts it.
Choose IoT devices from reputable manufacturers who prioritize security in their products. These companies will often release regular updates and patches to address any vulnerabilities discovered in their devices.
Consider whether or not the device has a strong password system. Ideally, users should be able to create unique passwords for each of their IoT devices, rather than using a common password across all of them.
Regularly Updating Software And Firmware
Manufacturers regularly release updates to address these vulnerabilities, so it’s important to install them as soon as they become available.
In addition to security, updating software and firmware can also improve the performance of IoT devices. Updates often include bug fixes and new features that enhance functionality or fix issues that may have been impacting device performance.
Implementing Strong Passwords And Two-Factor Authentication
Strong passwords should be at least 12 characters long and contain a mix of upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols. However, even strong passwords can be compromised if they are reused across multiple accounts or if they are stored in an unsecured location. Two-factor authentication provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of identification before gaining access to their accounts.
Using Secure Network Connections And Firewalls
Secure network connections, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), encrypt all data between devices and servers, making it difficult for hackers to intercept or steal sensitive information. Firewalls act as barriers between your internal network and the external networks that you connect with. They can block unauthorized traffic based on pre-defined rules or criteria set by you.
Protecting Personal Data on IoT Devices
Understanding What Personal Data Is Stored On IoT Devices
Understanding what personal data is stored on these IoT devices is crucial for protecting sensitive information from potential cyber-attacks or theft. This includes understanding how the device handles the personal data being collected and whether it is encrypted or not. Consumers should also consider the privacy policies set by the IoT device’s manufacturer as well as review third-party applications’ access to their personal information.
Limiting The Collection Of Unnecessary Personal Data
By only collecting what is necessary, companies can reduce the risk of a data breach or misuse of personal information. This also helps to build trust with consumers who may be hesitant about using IoT devices due to privacy concerns.
However, determining what constitutes “necessary” personal data can be tricky. Companies should carefully evaluate their data collection practices and consider if each piece of information collected serves a legitimate purpose in providing the intended service or function of the device. If not, it should not be collected.
Encrypting Personal Data
Encryption can help mitigate these risks by encoding sensitive information such as passwords, financial transactions, and other personal details.
Encryption can be achieved using various methods such as symmetric encryption or asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption involves using the same key to encrypt and decrypt messages, while asymmetric encryption uses two different keys for the same purpose. Both methods have their benefits and drawbacks depending on the use case.
Regularly Reviewing And Deleting Personal Data
To protect yourself from potential security breaches or hacking attempts, it is crucial to regularly review and delete any unnecessary personal data stored on your IoT devices. This process involves taking inventory of what information is being collected and stored by each device and deciding which pieces of data are necessary to keep.
IoT Security Regulations and Standards
Overview Of Current IoT Security Regulations And Standards
There are several IoT security regulations and standards that companies must follow to ensure the protection of their connected devices. One such standard is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which was established by the European Union in 2018. This regulation requires companies to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting and using their personal data, as well as implement measures for data protection and breach notification.
Another significant IoT security standard is ISO/IEC 27001, which outlines a framework for information security management systems. This standard requires organizations to identify potential security risks and implement appropriate controls to mitigate them. Additionally, it provides guidelines on how to manage vulnerabilities and respond to incidents effectively.
In recent years, governments have also introduced legislation focused specifically on IoT device security. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) requires companies operating in California to disclose what personal information they collect about consumers who use their products or services, how that data is used, and with whom it is shared. These regulations highlight the need for greater transparency around data collection practices in order to protect both individuals’ privacy rights and prevent malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities in connected devices.
Governmental And Industry Efforts To Improve IoT Security
The U.S. government has introduced several initiatives and policies to enhance the security of IoT devices, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework and the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP).
Similarly, industries have also started taking proactive measures to ensure the security of their products by implementing various standards, best practices, and guidelines for IoT device manufacturers. For instance, the Internet Society’s Online Trust Alliance (OTA) has developed a framework that outlines best practices for securing IoT devices throughout their lifecycle.
Moreover, industry groups like the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) are working towards developing a common set of guidelines for the secure deployment and management of industrial IoT systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential consequences of an IoT data breach?
An IoT data breach can have severe consequences for individuals, companies, and even entire industries. The theft of sensitive information, such as personal identification numbers or financial information, could lead to identity theft or fraud. In addition, a cybercriminal who gains access to an IoT device might use it to launch DDoS attacks on other systems. This could result in significant downtime and lost revenue for businesses that rely heavily on their online presence.
IoT devices are also increasingly being used in critical infrastructure such as power grids and water supply systems. A breach that impacts these systems could have disastrous results, including widespread outages and service disruptions. With the potential for catastrophic effects on public safety and national security, it is evident why protecting IoT devices from data breaches is crucial.
The potential consequences of an IoT data breach extend far beyond just monetary losses; they can also damage reputations irreparably. Companies that fail to properly secure their IoT devices may face legal action from customers whose data has been compromised or governments seeking accountability for breaches affecting critical infrastructure.
How can I protect my IoT devices from data breaches?
Make sure that all your IoT devices are updated with the latest firmware and software updates. This ensures that any vulnerabilities that could have been exploited by hackers are patched up.
Use strong passwords for your IoT device accounts and Wi-Fi networks. Avoid using common or easily guessable passwords like “password” or “123456”. Instead use complex passwords consisting of a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols.
Secure your home network by activating encryption features like WPA2 on your wireless router to prevent unauthorized access over the network. These steps will go a long way towards securing your connected world from malicious attacks and keeping your personal information safe from prying eyes.
Conclusion
As our world becomes increasingly connected, the importance of data security cannot be overstated. IoT devices have revolutionized the way we live and work, but they also come with inherent risks that need to be addressed. The potential consequences of a security breach can be catastrophic, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage.
To protect yourself and your business from these risks, it is essential to prioritize data security when implementing IoT devices. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments and choosing reputable vendors who prioritize security in their products. Additionally, staying up to date on the latest cybersecurity threats and implementing best practices for data protection can help minimize your exposure to risk.
