What is the National Data Guardian?
The National Data Guardian (NDG) is an independent body in the United Kingdom that advises and challenges the health and care system to improve data security and privacy. The NDG was created in response to concerns about data breaches within the NHS, with a particular focus on patient data protection. Their role is to oversee the use of patient data by health and social care organizations, ensuring that patient’s rights are respected, their information is kept confidential and secure, and that they are informed about how their data is being used.
The NDG has established ten Data Security Standards for healthcare providers to follow when handling sensitive patient information. These standards include requirements such as ensuring strong passwords are used, regularly updating software systems, encrypting all portable devices containing personal data, and conducting risk assessments of third-party suppliers handling personal information amongst others. Healthcare organizations must comply with these standards in order to be deemed trustworthy stewards of patient information.
Importance of Data Security
Data security is a crucial aspect of any organization, no matter its size or industry. With the rise of technology and the increasing amount of data being stored digitally, it has become more important than ever to protect sensitive information. Cyber attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and can cause significant damage to businesses if they are not properly secured.
Protecting sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property is essential for maintaining trust with clients and stakeholders. A breach in data security can result in lost revenue due to a damaged reputation or legal consequences from regulatory bodies. Additionally, proper data security measures can help prevent identity theft and other forms of fraud that can harm individuals or companies alike.
Standard 1: Data Security Policy
What is a Data Security Policy?
A data security policy is a set of guidelines and procedures that an organization follows to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. It defines the measures and controls necessary to safeguard data assets throughout their lifecycle, from creation, storage, processing, and transmission to destruction.
Elements of an Effective Data Security Policy
One of the most important elements of an effective data security policy is to have clear guidelines for handling sensitive information. These guidelines should outline what types of data are considered sensitive and how they should be stored, transmitted, and accessed. It’s also crucial to have a plan in place for responding to security breaches or other incidents that may compromise the integrity of your data.
Another key element is employee education and training. All staff members who handle sensitive information should be trained on best practices for protecting that data, including password management, encryption techniques, and safe browsing habits. Regular refresher courses can help ensure that everyone stays up-to-date on the latest threats and strategies for prevention.
Regular audits and assessments are essential to ensuring the ongoing effectiveness of your data security policy. By regularly reviewing your policies and procedures, you can identify areas where improvements might be needed and make adjustments as necessary. This can help minimize the risk of security breaches or other incidents that could jeopardize your business’s reputation or financial stability.
Standard 2: Access Control
Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a type of access control mechanism that restricts system access based on the roles or responsibilities of individual users within an organization. RBAC is an effective way to manage data security and privacy, particularly when it comes to sensitive information. This is because it ensures that only authorized individuals have access to certain data.
In RBAC, permissions are assigned based on job functions rather than individual users. This means that people with similar job functions will typically have the same level of access to different types of data. In practice, this can mean creating groups or roles such as “doctor” or “nurse,” each with its own specific set of permissions for accessing patient records.
Standard 3: Data Encryption
What is Data Encryption?
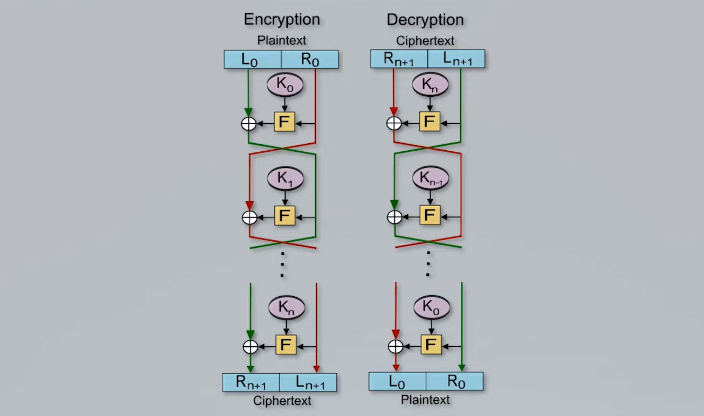
Data encryption is a process of converting plain text data into unreadable code that can only be deciphered by authorized individuals or systems. This technique is used to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensure its confidentiality.
Types of Data Encryption
One of the most common is symmetric encryption, which relies on a single secret key to both encrypt and decrypt data. This type of encryption is fast and efficient but requires that users securely share the key with all parties who need access to the encrypted data.
Another popular option is asymmetric encryption, which uses two different keys – one public and one private – to protect data. The public key can be freely shared while the private key must be carefully guarded by its owner. Asymmetric encryption provides an added layer of security since even if someone intercepts the public key, they cannot use it to decrypt any intercepted messages without first obtaining or cracking the private key.
A third type of data encryption that may be used in conjunction with symmetric or asymmetric methods is hashing. Hashing involves transforming input data into a fixed-size output known as a hash value or message digest. While not technically an encryption method, hashing adds additional security by making it difficult for attackers to tamper with protected data without being detected by comparing hash values before and after any changes are made.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Encryption
The primary advantage of data encryption is enhanced security as it protects sensitive information from being accessed by unauthorized persons. This is especially important when handling confidential data such as medical records, financial transactions, and personal identification details.
Another advantage of data encryption is that it ensures integrity during transmission and storage. Encryption makes it harder for cybercriminals to tamper with data while in transit or at rest. In addition to this, encrypted data can be used as evidence in legal proceedings because its authenticity can be verified.
However, one major disadvantage of data encryption is that it can slow down the process of accessing and processing files. This means that larger files may take longer to encrypt and decrypt compared to small ones, making the process more time-consuming. Additionally, if the key or password used for encrypting the data falls into the wrong hands, it could lead to security breaches.
Standard 4: Data Backup and Recovery
Why is Data Backup and Recovery Important?
Data backup and recovery are critical for any organization or individual that handles sensitive information. In the unfortunate event of a cyber attack, natural disaster, power outage or any other unforeseen circumstance that could potentially damage data, having a reliable backup system in place can prove to be a lifesaver. The purpose of data backup is to create duplicates of important files and store them either on-site or offsite as an extra layer of protection against permanent loss.
Data recovery, on the other hand, involves restoring lost or damaged files from backups. It is important for organizations to have a solid plan in place for data recovery because it reduces downtime during an incident while ensuring business continuity. Without adequate backup and recovery systems, businesses risk losing valuable information which can result in financial losses due to lost sales opportunities, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Types of Data Backup and Recovery
Some common types include full backups, incremental backups, differential backups, and mirror backups. Full backups involve copying all data to a backup location, while incremental backups only copy changes made since the last backup. Differential backups copy changes made since the last full backup.
Best Practices for Data Backup and Recovery
Organizations should regularly back up their data to a secure location. This practice ensures that if there’s an unexpected disaster or cyberattack, they can retrieve their lost data from the backup location. Secondly, it’s essential to test backups regularly to confirm that the saved data is validated and usable in case of an emergency. Lastly, a documented procedure should exist on how employees can access backed-up files in case the original ones are lost.
Standard 5: Incident Management
What is Incident Management?
Incident management refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving security incidents. The objective is to minimize the impact of a security breach on an organization’s operations and reputation.
Steps in Incident Management
Incident management involves a set of steps that are taken in response to a security breach or incident. First and foremost, the goal is to contain the incident by isolating any affected systems or networks. Once contained, the next step is to investigate the cause of the incident and identify any compromised data.
Following this, the organization must evaluate any legal obligations they may have in terms of reporting the incident to authorities or affected individuals. It’s also important to notify key stakeholders within the organization so that everyone can work together on developing an appropriate response plan. After taking all necessary actions related to containment, investigation, reporting and communication – it’s time for remediation efforts – instituting new policies/procedures and training employees to prevent future incidents.
Incident Management Tools
One of the most popular incident management tools is a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. A SIEM tool collects security events from various sources across an organization’s network and analyzes them to identify potential threats. Another useful incident management tool is a vulnerability scanner that continuously scans systems for vulnerabilities and generates alerts when it detects a potential threat.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools are becoming increasingly important in incident management. They provide real-time monitoring capabilities for endpoints such as laptops, desktops, or servers. EDR tools can detect suspicious activities on these devices and trigger rapid responses to mitigate the impact of any security incidents
Standard 6: Employee Training
Why is Employee Training Important?
Employee training is crucial in ensuring that an organization complies with the National Data Guardian (NDG) data security standards. The NDG has set out ten standards that all healthcare organizations should adhere to when handling patient information. Training employees on these ten standards will help them understand the importance of data protection and how to handle sensitive information safely.
Types of Employee Training
Various types of employee training can help organizations meet the National Data Guardian Data Security Standards. One such type is induction training, which helps new employees understand their role in maintaining data security and how to handle sensitive information. This includes introducing them to policies and procedures related to data security.
Another type of employee training is refresher training, which should be provided periodically to ensure that employees are up-to-date with any changes in policies or procedures related to data security. Additionally, regular cybersecurity awareness training can help employees recognize and avoid potential threats such as phishing emails or malware attacks.
Specialized training may be necessary for specific roles within an organization, such as those responsible for handling personal data on a daily basis. This could include GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliance training or HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations for healthcare providers dealing with patient health information.
Best Practices for Employee Training
Conduct regular training sessions for all employees that cover topics such as data protection policies, data handling procedures, and cybersecurity measures. These training sessions can be conducted in various formats like online courses, webinars or workshops.
Provide continuous feedback and reinforcement on good practices related to data security. This can be done through regular reminders via emails or posters with key messages about data security.
Ensure that employees understand the consequences of not adhering to company policies on data protection. This can involve highlighting the legal and financial implications of a breach and putting in place disciplinary measures for any violations of company policy.
Standard 7: Physical Security
Importance of Physical Security
Physical security refers to the measures taken to protect computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from physical threats such as theft, environmental hazards, and unauthorized access. These measures are critical in preventing unauthorized access or tampering with sensitive data.
Physical security is also important in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and guidelines. The National Data Guardian (NDG) has outlined ten data security standards that organizations must adhere to ensure the safety of patient information.
Types of Physical Security
There are different types of physical security that can be implemented to ensure the safety and protection of data. The first type is access control, which restricts entry to authorized personnel only. This can include biometric scanners, key cards, or passwords. Secondly, surveillance monitoring can be used to monitor activities in restricted areas through cameras and sensors. Finally, alarm systems can alert security teams of breaches or unauthorized access.
Another important aspect of physical security is environmental controls. This includes temperature and humidity monitoring for server rooms and data centers to prevent equipment damage due to overheating or moisture buildup. Fire suppression systems also contribute to protecting equipment from fire hazards.
Best Practices for Physical Security
One key practice is to secure entry points with access controls such as proximity cards, biometric scanners or PIN codes. Additionally, surveillance cameras can be used to monitor entry points and sensitive areas within the facility. Organizations should also have policies in place regarding visitor access and procedures for escorting visitors through secured areas.
Another practice is to implement environmental controls such as temperature regulation and fire suppression systems to prevent equipment damage or loss of data due to environmental factors. Regular maintenance checks on these systems should also be conducted.
Standard 8: Network Security
What is Network Security?
Network security refers to the set of practices and technologies put in place to protect an organization’s computer network from unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or disruption. It involves designing and implementing policies and procedures aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within a network. Network security is essential for any organization that handles sensitive information such as personal identifiable information (PII), financial records, healthcare records among others.
Types of Network Security
The first type is access control, which involves limiting who has permission to access certain areas of the network. This can be done through passwords, authentication procedures or biometric scanners. Another important aspect is encryption, which involves converting data into a code that only authorized parties can read. In addition, firewalls act as a barrier between an internal network and external networks such as the internet.
Another type of network security is intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS). An IDPS monitors networks for any unusual activity that could signal an attempted breach or attack. Additionally, anti-virus software serves as another level of protection by identifying and removing any malware or viruses from the system before they can cause harm.
Best Practices for Network Security
Maintain strong passwords and authentication protocols. This can include requiring users to change their passwords frequently, using two-factor authentication methods, and disabling default account settings. Additionally, organizations should provide regular training on cybersecurity best practices for employees to help prevent common mistakes such as clicking on suspicious links or downloading malware.
Have a plan in place for responding to potential breaches or incidents. This includes having a team in place that can quickly identify and contain any threats, conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities in the system, and ensuring that all employees know what steps they should take if they suspect a breach has occurred.
Standard 9: System Security
What is System Security?
System security refers to the measures taken by organizations to protect their computer systems and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. In today’s digital age, businesses have become increasingly reliant on technology and data storage systems. As a result, cybersecurity threats have also become more sophisticated and frequent.
To safeguard their sensitive information, companies need robust system security protocols in place that are designed to detect and prevent various cyber attacks such as malware infections or phishing attempts. This can be achieved through a combination of hardware and software solutions like firewalls, encryption software, anti-virus programs, intrusion detection systems (IDS), etc.
Best Practices for System Security
Implement strong password policies and ensure that passwords are frequently updated. It is also advisable to use tools such as multi-factor authentication and encryption for sensitive data. Regular backups should be taken and stored in a secure location, and access control measures should be implemented to restrict unauthorized access.
All software must be kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This includes operating systems, web applications, plugins, and other software programs used within the organization. Any obsolete technologies or unsupported software should be immediately removed from the system.
Employees must receive regular training on system security best practices. They should understand how phishing attacks work and know how to identify suspicious emails or links. They must also learn how to report security incidents promptly so that they can be resolved quickly before they cause any damage.
Standard 10: Privacy and Confidentiality
What are Privacy and Confidentiality?
Privacy and confidentiality are integral concepts in data security standards. Privacy refers to an individual’s right to control the sharing of their personal information. Confidentiality, on the other hand, pertains to protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. In healthcare settings, privacy and confidentiality are particularly important because of the nature of the information being shared.
Maintaining privacy and confidentiality is not only a legal requirement but also essential for building trust between patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
The National Data Guardian Data Security Standards have been developed to ensure that confidential information is kept secure and that patients’ privacy is not compromised. Each of the ten standards covers a specific aspect of data security, from encryption to staff training. Compliance with these standards is required by all organizations handling NHS patient data.
It is important for healthcare providers to take these standards seriously as breaches in data security can have serious consequences for patients and healthcare professionals alike. Organizations found to be non-compliant with the standards may face fines or even legal action.
FAQs
What are the consequences of not following the National Data Guardian Data Security Standards?
Failing to comply with the National Data Guardian (NDG) Data Security Standards can result in severe consequences. It can lead to a breach of data privacy and put sensitive information at risk. This could potentially damage an individual’s reputation or even result in identity theft. Additionally, not following these standards may also result in legal action being taken against the company or organization responsible for safeguarding the data.
Another consequence of not adhering to NDG standards is reputational damage. If sensitive information is leaked due to negligence on behalf of a company or organization, it can significantly harm public perception and trust. This could lead to clients and customers choosing to take their business elsewhere, resulting in financial losses.
Non-compliance with NDG standards may lead to regulatory fines and penalties from governing bodies such as the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO). These fines could be significant and have long-lasting financial repercussions for businesses that fail to ensure compliance.
Are the Standards applicable to all types of organizations?
The National Data Guardian Data Security Standards are applicable to all types of organizations that handle sensitive and personal information. This includes healthcare providers, government agencies, financial institutions, and private companies. The standards were created with the aim of ensuring that all organizations handling sensitive data do so in a secure and responsible manner.
How often should the Standards be reviewed and updated?
It is recommended that data security standards are reviewed at least once a year to ensure they remain current with changing cybersecurity risks. Additionally, it is essential to review and update the standards whenever there is a significant change in organizational structure or business operations. This includes mergers and acquisitions or when introducing new technologies into the organization’s infrastructure. These changes can have an impact on how sensitive information will be stored, accessed, or shared within the organization.
